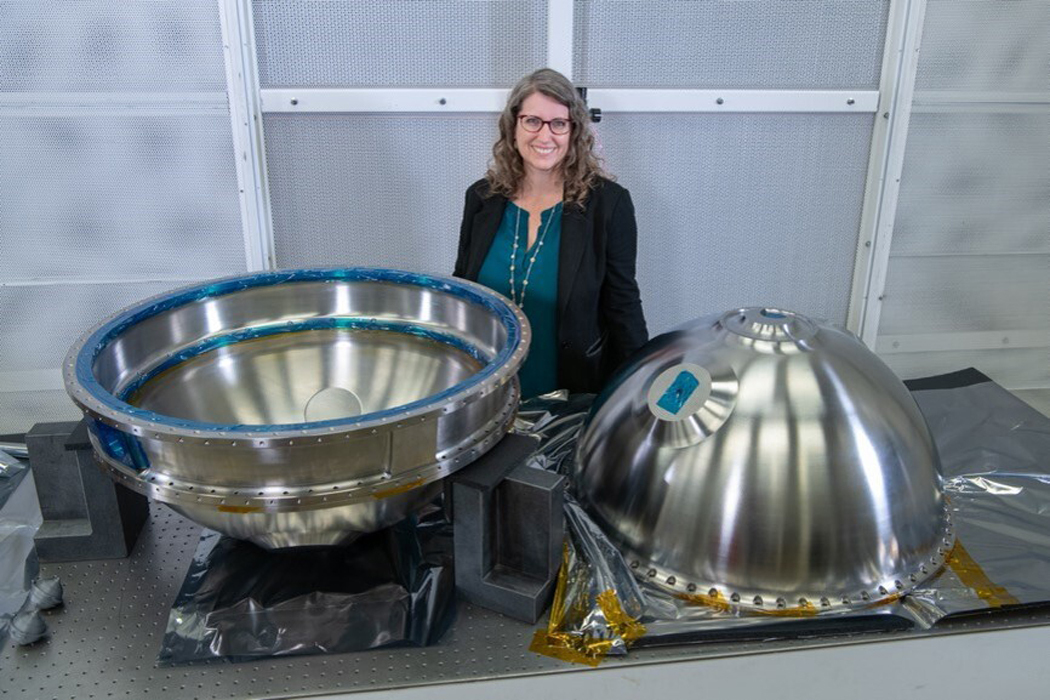
Name: Dr. Stephanie Getty
Title: Director of the Solar System Exploration Division, Sciences and Exploration Directorate and Deputy Principal Investigator of the DAVINCI Mission
Formal Job Classification: Planetary scientist
Organization: Solar System Exploration Division, Sciences and Exploration Directorate (Code 690)
What do you do and what is most interesting about your role here at Goddard? How do you help support Goddard’s mission?
As the Director of the Solar System Exploration Division, I work from a place of management to support our division’s scientists. As the deputy principal investigator of the DAVINCI (Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging) mission, I work with the principal investigator to lead the team in implementing this mission to study the atmosphere of Venus.
I love that I get to work from a place of advocacy in support of my truly excellent, talented colleagues. I get to think strategically to make the most of opportunities and do my best to overcome difficulties for the best possible future for our teams. It’s also a fun challenge that no two days are ever the same!
Why did you become a planetary scientist?
In school, I had a lot of interests and space was always one of them. I also loved reading, writing, math, biology, and chemistry. Being a planetary scientist touches on all of these.
My dad inspired me become a scientist because he loved his telescope and photography including of celestial bodies. We watched Carl Sagan’s “Cosmos” often.
I grew up in southeastern Florida, near Fort Lauderdale. I have a B.S. and Ph.D. in physics from the University of Florida.
How did you come to Goddard?

I had a post-doctoral fellowship in the physics department at the University of Maryland, and a local connection and a suggestion from my advisor led me to Goddard in 2004.
What is most important to you as director of the Solar System Exploration Division, Sciences and Exploration Directorate?
My goal is to provide a supportive environment for our incredibly talented science community in the Division to thrive, to push discovery forward and improve the understanding of our solar system. It’s a priority to encourage effective and open communication. I really try to value the whole person, recognizing that each of us is three-dimensional, with full personal lives. The people create the culture that allows our scientists to thrive and explore.
What are your goals as deputy principal investigator of the DAVINCI mission?
DAVINCI’s goal is to fill long-standing gaps about Venus, including whether it looked more like Earth in the past. Our energetic team brings together science, engineering, technology, project management, and business acumen to build a multi-element spacecraft that will explore Venus above the clouds, and during an hour-long descent through the atmosphere into the searingly hot and high pressure deep layers of the atmosphere near the surface. We hope to launch in June 2029.
What is your proudest accomplishment at Goddard?
I am pleased and proud to be deputy principal investigator on a major mission proposal that now gets to fly. It is an enormous privilege to be entrusted as part of the leadership team to bring the first probe mission back to Venus in over four decades.
What makes Goddard’s culture effective?
Goddard’s culture is at its best when we collectively appreciate how each member of the organization works towards solving our problems. The scientists appreciate the hard, detailed work that the engineers do to make designs. The engineers and project managers are energized by the fundamental science questions that underlie everything we do. And we have brilliant support staff that keeps our team organized and focused.

What goes through your mind when you think about which fundamental science question to address and how?
A lot of the research I have done, including my mission work, has been inspired by the question of how life originates, how life originated on Earth, and whether there are or have been other environments in the solar system that could have ever supported life. These questions are profound to any human being. My job allows me to work with incredibly talented teams to make scientific progress on these questions.
It is really humbling.
Who inspired you?
My 10th grade English teacher encouraged us to connect with the natural world and to write down our experiences. Exploring the manifestations of nature connects with the way I approach my small piece of exploring the solar system. I really love the writing parts of my job, crafting the narrative around the science we do and why it is important.
As a mentor, what is the most important lesson you give?
A successful career should reflect both your passion and natural abilities. Know yourself. What feels rewarding to you is important. Learn how to be honest with yourself and let yourself be driven by curiosity.
Our modern lives can be very noisy at work and at home. It can be hard to filter through what is and is not important. Leaving space to connect with the things that satisfy your curiosity can be one way to make the most of the interconnectivity and complexity of life.
Curiosity not only connects us to the natural world, but also to each other. Curiosity is a defining characteristic of a good scientist, never losing a sense of wonder.
I’m looking out my window as we talk. When I can, I try to make time to pause to reflect on how beautiful and special our own planet is.
What are your hobbies?
I love hiking with my kids. Walking through the woods puts me in the moment and clears my mind better than anything else. It gives my brain a chance to relax. Nature gives perspective, it reminds me that I am part of something bigger. Walking in the woods gives me a chance to pause, for example, to notice an interesting rock formation, or watch a spider spinning an impressive web, or spot a frog trying to camouflage itself in a pond, and doing this with my children is my favorite pastime.
Where is your favorite place in the world?
Any campsite at dusk with a fire going and eating s’mores with my family.
Conversations With Goddard is a collection of Q&A profiles highlighting the breadth and depth of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center’s talented and diverse workforce. The Conversations have been published twice a month on average since May 2011. Read past editions on Goddard’s “Our People” webpage.
By Elizabeth M. Jarrell
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.