NASA has selected hundreds of small businesses and dozens of research institutions to develop technology to help drive the future of space exploration, ranging from novel sensors and electronics to new types of software and cutting-edge materials. The newly awarded projects under the agency’s Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) program also
include a high-power electric rocket and a coating to make solar panels more efficient that could be used both in space and here on Earth.
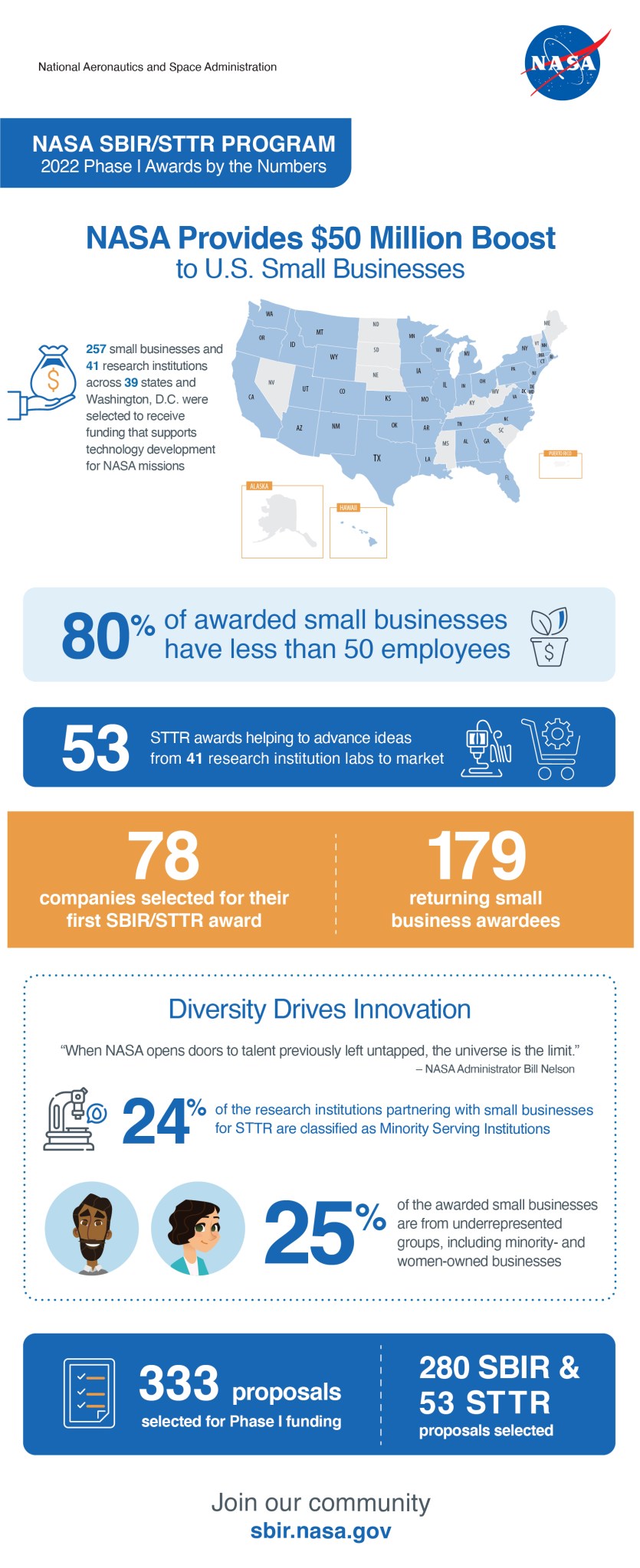
The awards total nearly $50 million, with investments spread out over 39 states and Washington. Under the selection, 333 proposals from 257 small businesses and 41 research institutions – including 10 Minority Serving Institutions – will be awarded first-round funding for technology development. View the full lists of SBIR awardees and STTR awardees online.
“NASA is working on ambitious, groundbreaking missions that require innovative solutions from a variety of sources – especially our small businesses,” said NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy. “Small businesses have the creative edge and expertise needed to help our agency solve our common and complex challenges, and they are crucial to maintaining NASA’s leadership in space. The SBIR program is one of the key ways we do that as well as creating jobs in a growing, sustainable space economy.”
NASA investments in American small businesses and research institutions help provide the innovations needed for the exciting and ambitious missions on the agency’s horizon and foster robust commercial space and technology sectors.
Each proposal team will receive $150,000 – a 20% increase over previous years’ funding – to establish the merit and feasibility of their innovations. Phase I SBIR contracts are awarded to small businesses and last for six months, while Phase I STTR contracts are awarded to small businesses in partnership with a research institution and last for 13 months.
“The selections span a breadth of areas to empower the agency’s work in human exploration, space technology, science, and aeronautics,” said Jenn Gustetic, director of early-stage innovation and partnerships for NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate. “We’re excited about the uses for these technologies for Artemis and other missions, as well as their potential use in the commercial space industry and people’s everyday lives.”
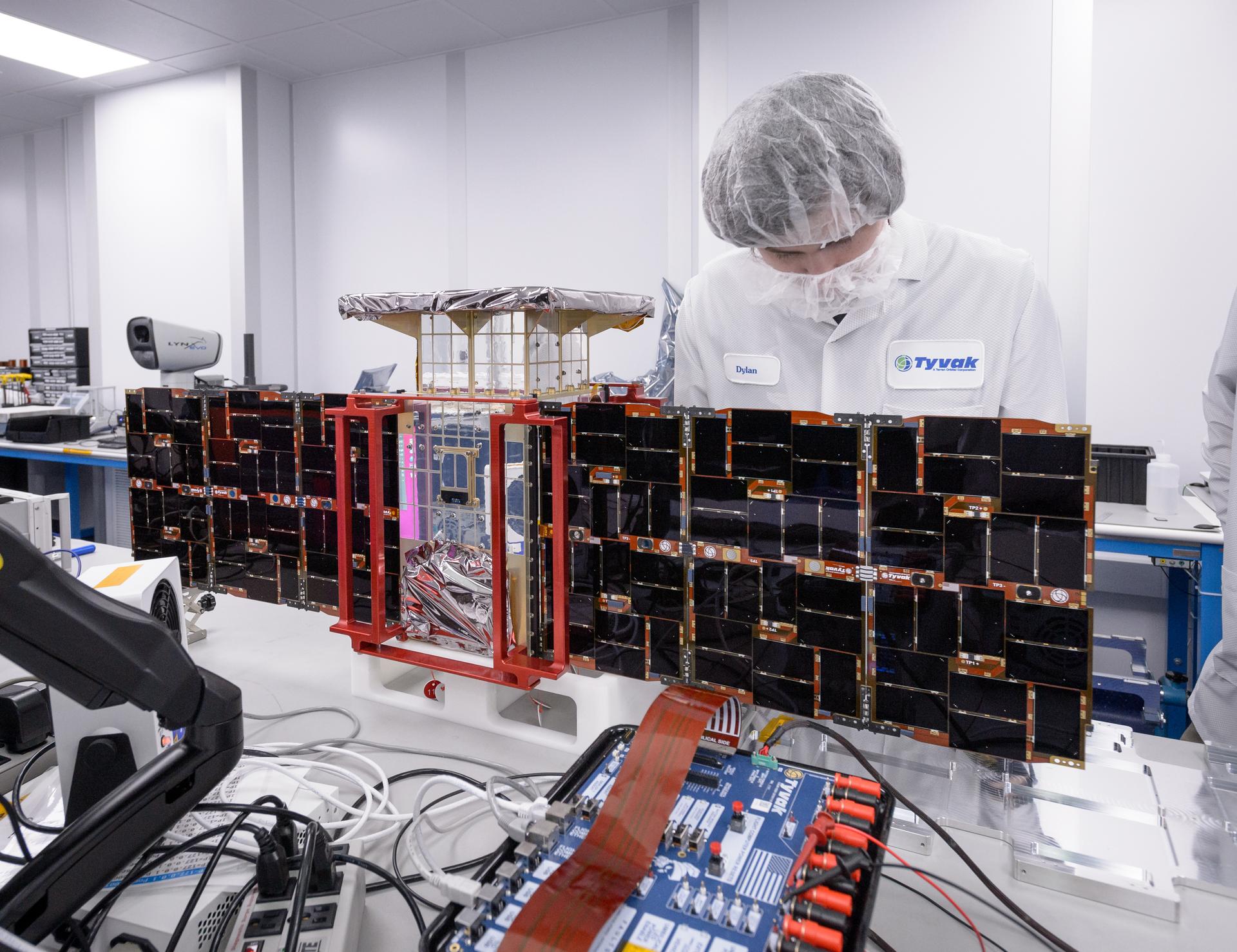
About 30% of the awards will go to first-time NASA SBIR/STTR recipients. This includes Ad Astra Rocket Company based in Webster, Texas. With its Phase I award, the company will develop a new way of manufacturing part of its Variable Specific Impulse Magnetoplasma Rocket, or VASIMR, engine – a high-power electric rocket engine the company has been working on with NASA for 25 years. In the engine, powerful radiofrequency waves are launched by special antennas, called couplers. The waves ionize gas into plasma, which is then accelerated to provide rocket thrust. The Phase I funding will be used to manufacture couplers in a way that increases the engine’s power limit. This innovation will help move the entire engine closer to commercialization, where it could be used for high-maneuverability satellites, lunar settlement cargo delivery, and more.
Nearly 25% of the selected companies are women-owned, veteran-owned, disadvantaged, and/or HUBzone small businesses. For example, D2K Technologies, a women- and minority-owned small business based in Oceanside, California, will create a monitoring and advisory system for health management of solenoid operated valves (SOV) used in industrial applications with its Phase I award. This technology could find use in many of NASA’s research centers, testing centers, and launch sites, since SOVs are basic components of most fluid systems. And, with the widespread use of SOVs in industrial applications, the system could be useful to oil and gas, nuclear, manufacturing, power generation, chemical, food, and pharmaceutical companies. This company is also a first-time NASA SBIR awardee.
“Finding and building a diverse community of entrepreneurs is a central part of our program’s outreach, and the efforts to reach them can start even before Phase I,” said Gynelle Steele, deputy program executive for NASA’s SBIR/STTR program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “For example, working in partnership with NASA’s Minority University Research and Education Project, we started offering M-STTR planning grants last year, which incentivized partnerships between MSIs and small businesses and prepared them to submit a STTR Phase I proposal in 2022.”
M-STTR awardee Oakwood University, a historically Black university based in Huntsville, Alabama, will continue working alongside SSS Optical Technologies, a small business also based in Huntsville, using their Phase I award to develop a new type of coating for photovoltaic (PV) cells embedded in solar sails. The coating could generate extra electricity and improve the overall PV conversion efficiency, which could advance solar sailing and other power and energy conversion needs for space exploration. This technology could improve the efficiency of commercial solar panels.
NASA selected Phase I proposals to receive funding by judging their technical merit and commercial potential. Based on their progress during Phase I, companies may submit proposals for $850,000 in Phase II funding to develop a prototype, as well as subsequent SBIR/STTR Post Phase II opportunities. The NASA SBIR/STTR program is part of the Space Technology Mission Directorate and is managed by NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley.
To learn more about NASA’s SBIR/STTR program and apply to future opportunities, visit:
-end-
Sarah Frazier
Headquarters, Washington
202-853-7191
sarah.frazier@nasa.gov
Tiffany Blake
Ames Research Center, Silicon Valley, Calif.
650-316-0153
tiffany.n.blake@nasa.gov