Another jam-packed year is in store for NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as the momentum of a busy 2023 is carried forward into the new year. On the horizon are missions to the Moon, more crew and cargo flights to the International Space Station, and several upgrade projects across the spaceport.
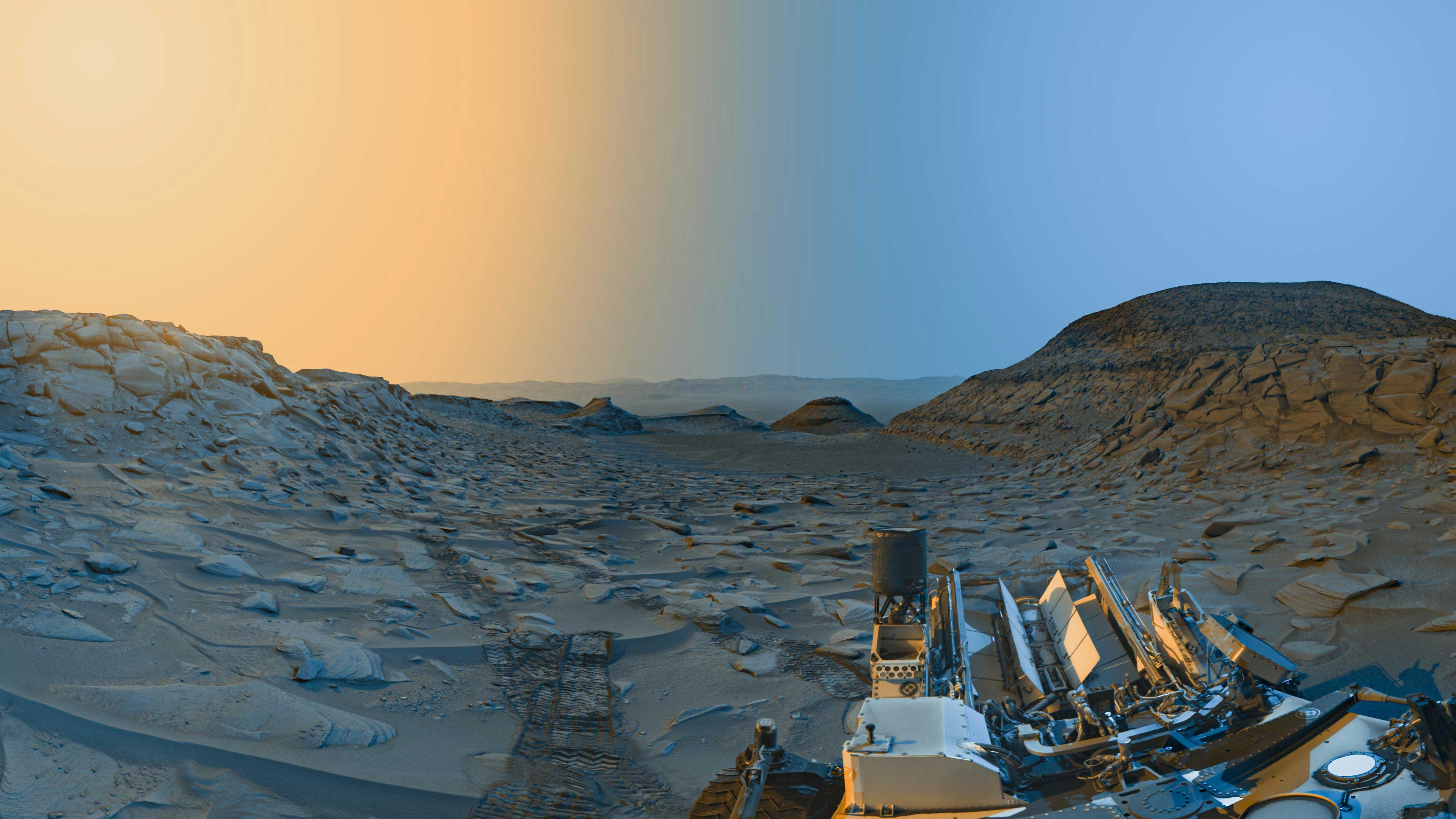
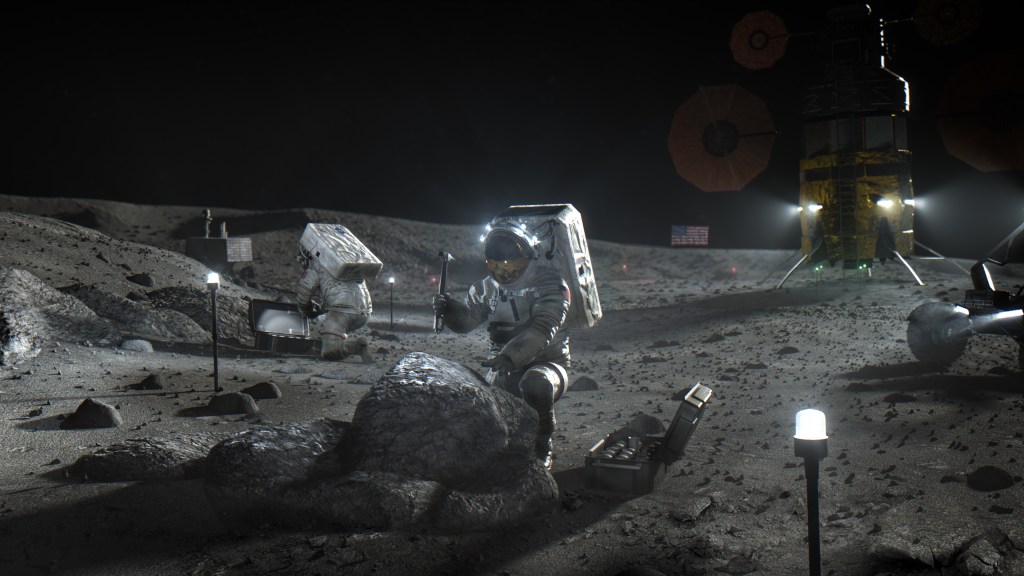
NASA’s first CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative mission with Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is set to begin work in 2024 after lifting off on the inaugural launch of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan Centaur rocket. These missions will help the agency develop capabilities needed to explore the Moon under Artemis ahead of sending astronauts to the lunar surface.
Another CLPS mission, set for launch early in the year aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will send the Intuitive Machines Nova-C lander to a landing site at the Moon’s South Pole region. The mission will carry NASA payloads focusing on plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
Development toward Artemis II, NASA’s first crewed test flight of its lunar-focused Artemis program continues across Kennedy. SLS (Space Launch System) hardware, including twin solid rocket boosters and a 212-foot-tall core stage for the Artemis II mission, will begin stacking and integration inside the Vehicle Assembly Building in the coming months, after which teams will begin a series of testing prior to launch. Processing also is underway on the core stage for Artemis III.
The Artemis II Orion crew and service modules will continue prelaunch processing inside Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building alongside the crew modules for Artemis III and Artemis IV– NASA’s initial missions to land the next humans on the lunar surface.
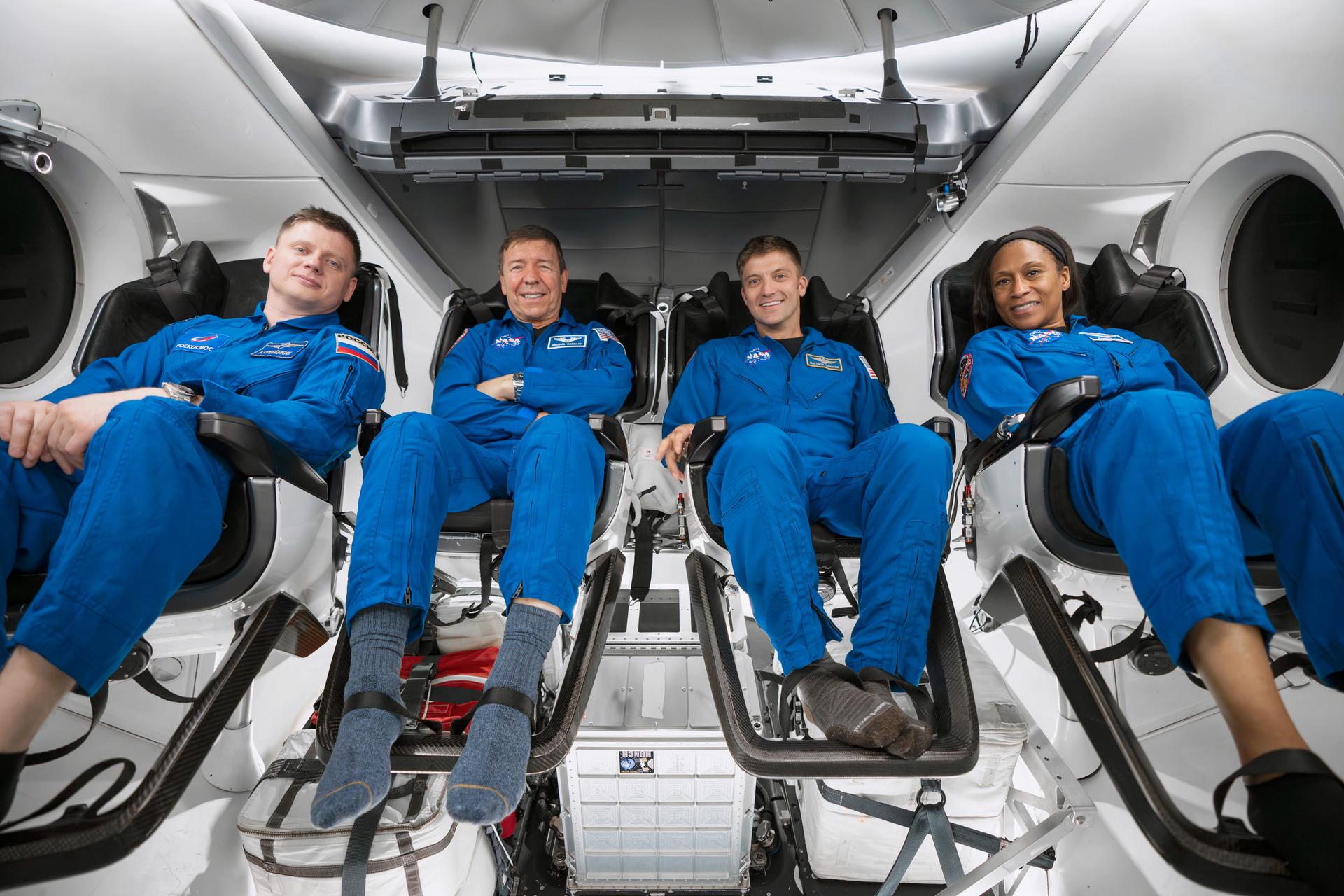
NASA and its commercial partners, Boeing and SpaceX, have three Commercial Crew Program missions set to fly from Florida’s Space Coast, setting up another busy year of traffic for the International Space Station in 2024. Teams are readying for the short-duration Crew Flight Test of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner no earlier than April. Meanwhile, NASA and SpaceX will continue crew rotation missions to the orbiting laboratory with Crew-8 expected no earlier than mid-February and Crew-9 to follow in mid-August.
Other crewed missions to the space station include SpaceX and Axiom Space’s short-duration Axiom Mission 3 and Axiom Mission 4 private astronaut missions.
SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn, the second private short-duration orbital flight will also lift off from Kennedy with four individuals that plan to attempt the first-ever commercial spacewalk.
Along with crewed flights, three of the agency’s Commercial Resupply Services missions hosted on SpaceX’s Dragon cargo spacecraft, Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus, and the debut flight of Sierra Space’s cargo spaceplane, Dream Chaser, are slated to fly from Kennedy next year to deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment, and science investigations to the orbiting laboratory.
NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy has several science and CubeSat missions manifested to fly on commercial rockets next year. They represent a mix of some of the agency’s most complex robotic and scientific missions, as well as smaller cost-efficient missions, and missions sponsored by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative.
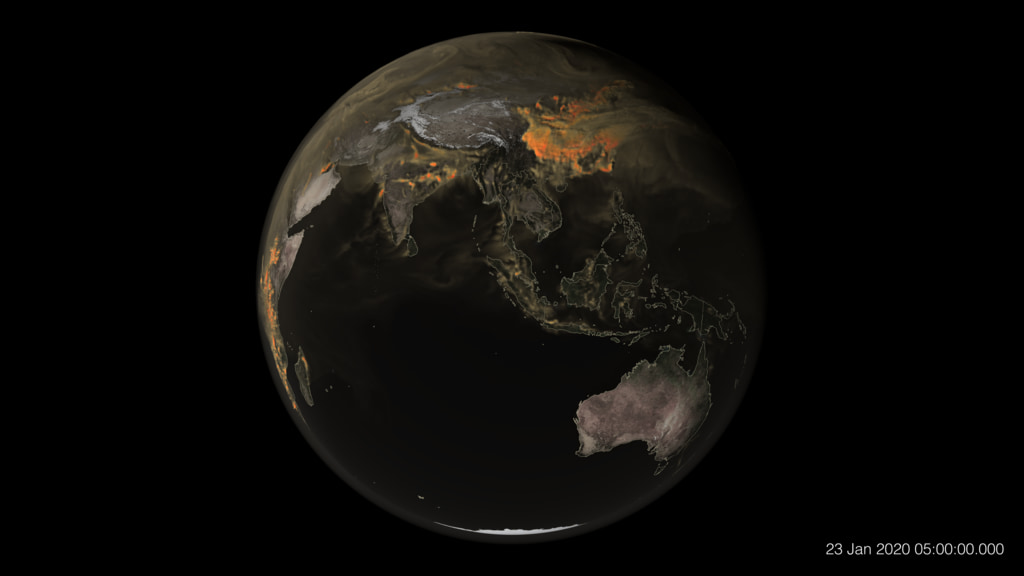
The first of three primary missions is NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft that will launch early next year on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. PACE’s science goals include extending ocean color, atmospheric aerosol, and cloud data records for Earth system and climate studies.
GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U) is slated to launch in April on a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket, the fourth and final satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series of advanced geostationary weather-observing satellites. Scheduled for an October launch on a Falcon Heavy, the agency’s Europa Clipper mission will investigate Jupiter’s moon Europa to determine if it has conditions suitable to support life.
Among the small spacecraft and CubeSat missions slated to launch in 2024 are two dedicated launches on Rocket Lab’s Electron for PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Infrared Experiment), which aims to give researchers a more accurate picture of the energy entering and leaving Earth. Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket will host NASA’s EscaPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) mission that will send two spacecraft to study solar wind energy and momentum through Mars’ unique hybrid magnetosphere.
While next year’s expected cadence of nearly 100 launches from Florida’s Space Coast is likely to mirror 2023’s record-setting pace, something else to look out for will be upgrade and sustainability efforts around the spaceport.
The Indian River Bridge construction project, which opened the first of two spans in June of 2023, and the solar site 6 project of the Utility Energy Services Contract, are expected to wrap up and become fully operational next year.
Restoration and beautification efforts across Kennedy also include the consideration of several sites for development into natural wildflower prairies. In the spring, Spaceport Integration’s sustainability team will work on “Project Arbor at the Spaceport.” It will focus on planting Florida native trees and one seedling from the Artemis Moon Tree project along the Fitness Trail near Operations Support Building II to provide shade, benefit wildlife, and help improve air quality.
A historical marker sponsored by NASA and the Florida Department of State will be installed in early 2024 at the site of Kennedy’s original Headquarters Building making it the first to be located within Kennedy’s secure area.
As 2023 draws to a close, Kennedy Space Center is gearing up to support more groundbreaking missions that will expand human knowledge of Earth and our solar system while protecting the local ecosystem and natural resources.