Using observations from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, researchers have obtained the first X-ray evidence of a supernova shock wave breaking through a cocoon of gas surrounding the star that exploded. This discovery may help astronomers understand why some supernovas are much more powerful than others.
On Nov. 3, 2010, a supernova was discovered in the galaxy UGC 5189A, located about 160 million light years away. Using data from the All Sky Automated Survey telescope in Hawaii taken earlier, astronomers determined this supernova exploded in early October 2010.
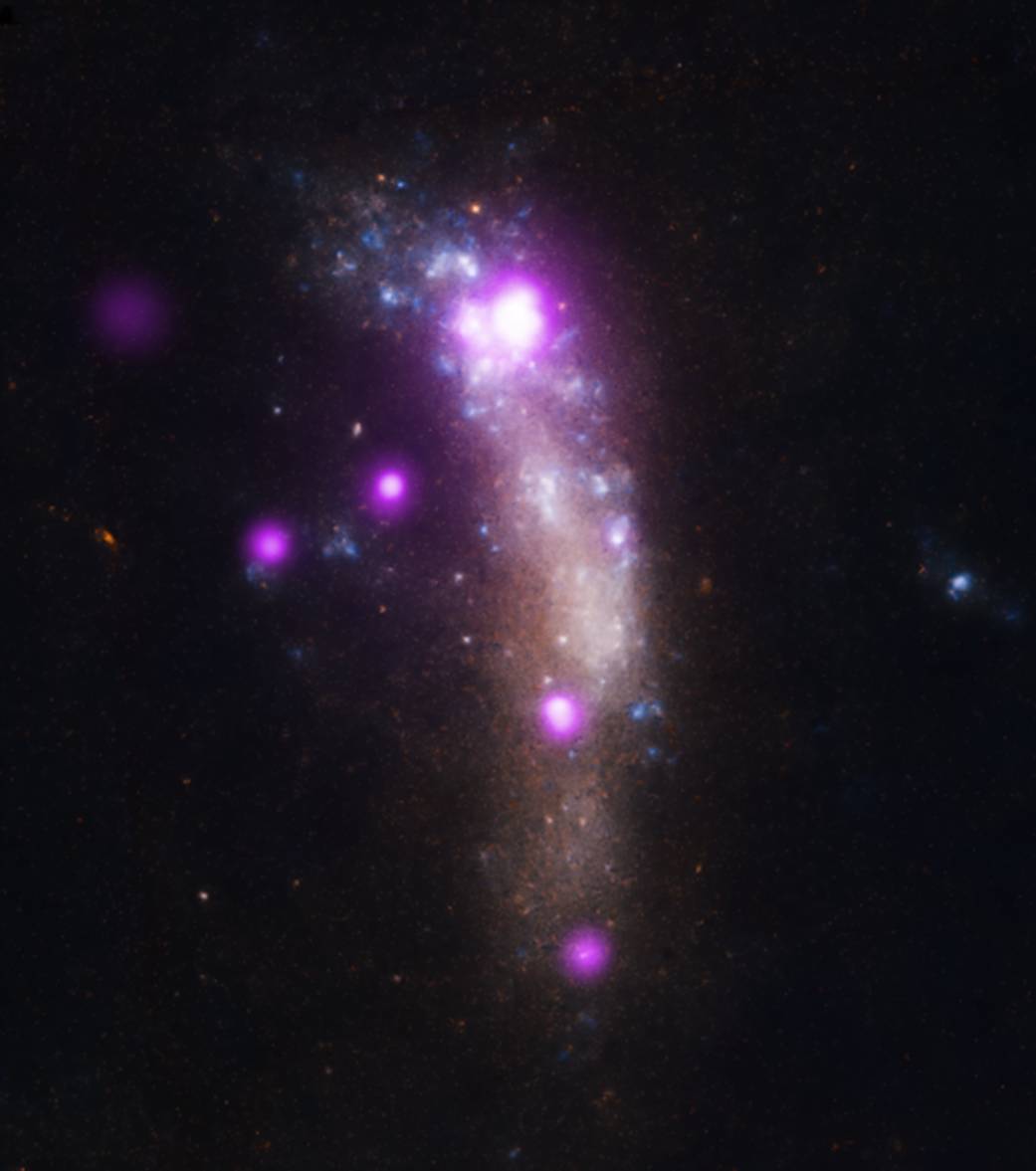
This composite image of UGC 5189A shows X-ray data from Chandra in purple and optical data from Hubble Space Telescope in red, green and blue. SN 2010jl is the very bright X-ray source near the top of the galaxy.
A team of researchers used Chandra to observe this supernova in December 2010 and again in October 2011. The supernova was one of the most luminous that has ever been detected in X-rays.
In the first Chandra observation of SN 2010jl, the X-rays from the explosion’s blast wave were strongly absorbed by a cocoon of dense gas around the supernova. This cocoon was formed by gas blown away from the massive star before it exploded.
In the second observation taken almost a year later, there is much less absorption of X-ray emission, indicating that the blast wave from the explosion has broken out of the surrounding cocoon. The Chandra data show that the gas emitting the X-rays has a very high temperature – greater than 100 million degrees Kelvin – strong evidence that it has been heated by the supernova blast wave.
In a rare example of a cosmic coincidence, analysis of the X-rays from the supernova shows that there is a second unrelated source at almost the same location as the supernova. These two sources strongly overlap one another as seen on the sky. This second source is likely to be an ultraluminous X-ray source, possibly containing an unusually heavy stellar-mass black hole, or an intermediate mass black hole.Image Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Royal Military College of Canada/P.Chandra et al); Optical: NASA/STScI
2 min read