Apollo 4
The first all-up test of the three stage Saturn V rocket.
Mission Type
Alternate Name
Launch
Landing
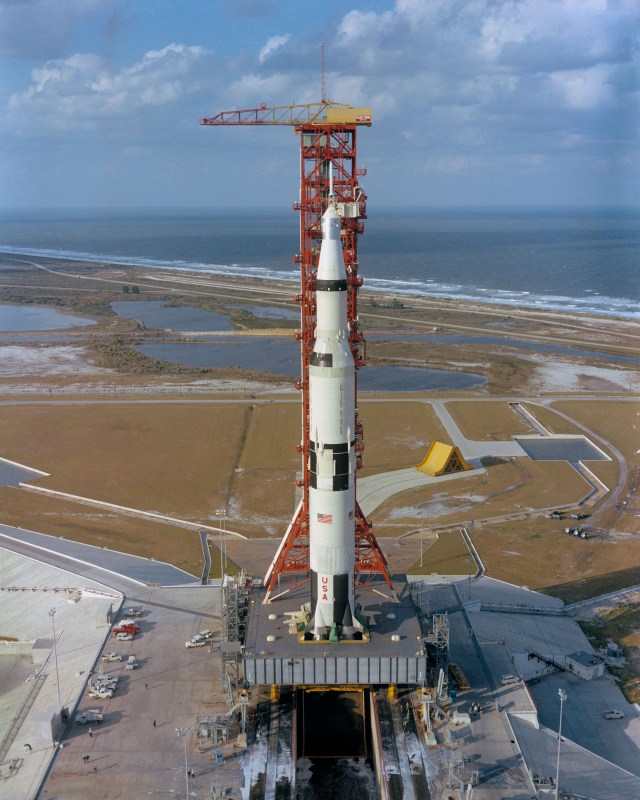
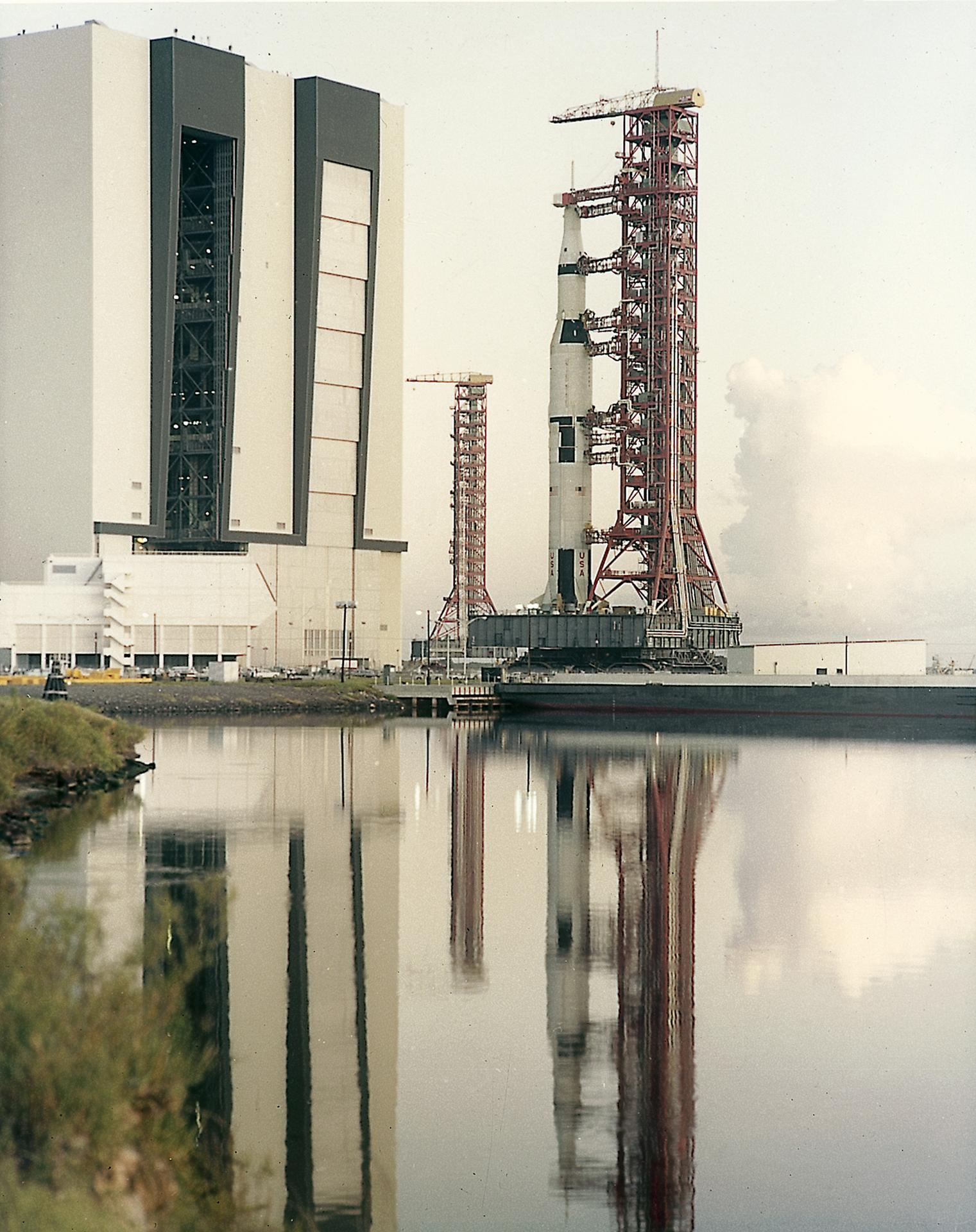
Apollo 4 was First-Ever Launch from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center
Fifty years ago this month, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida experienced the roar of a rocket from Launch Complex…
Read the Story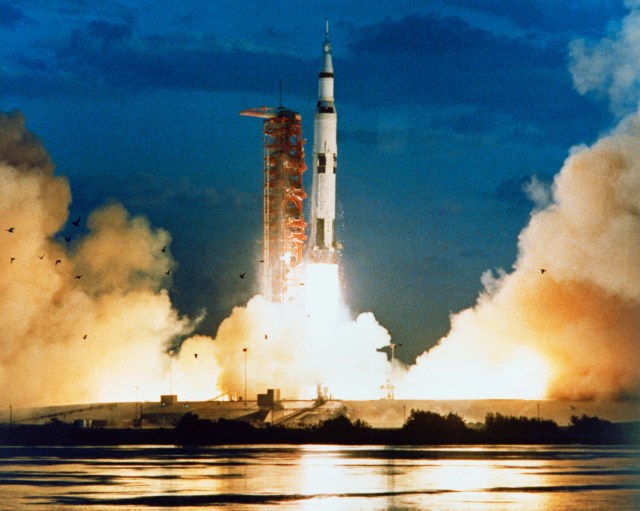
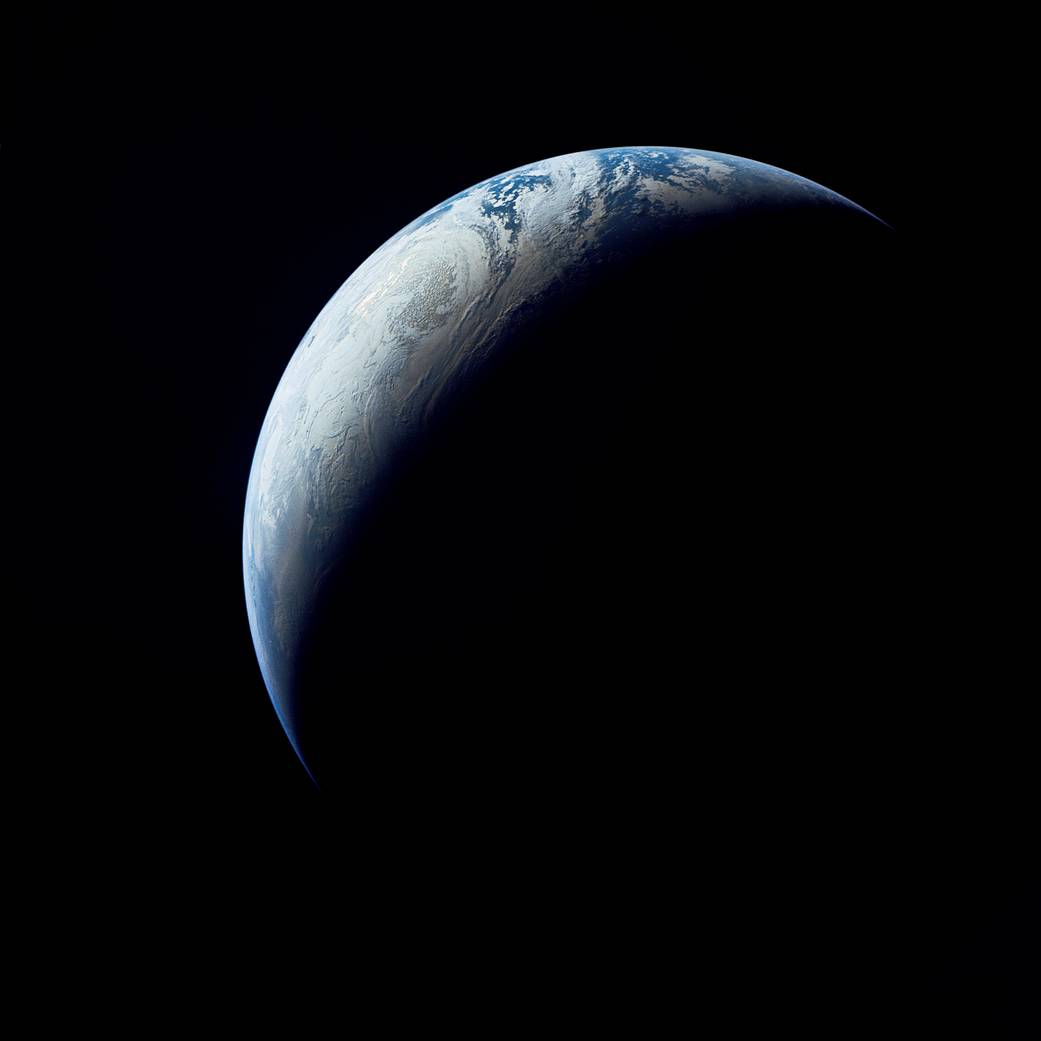
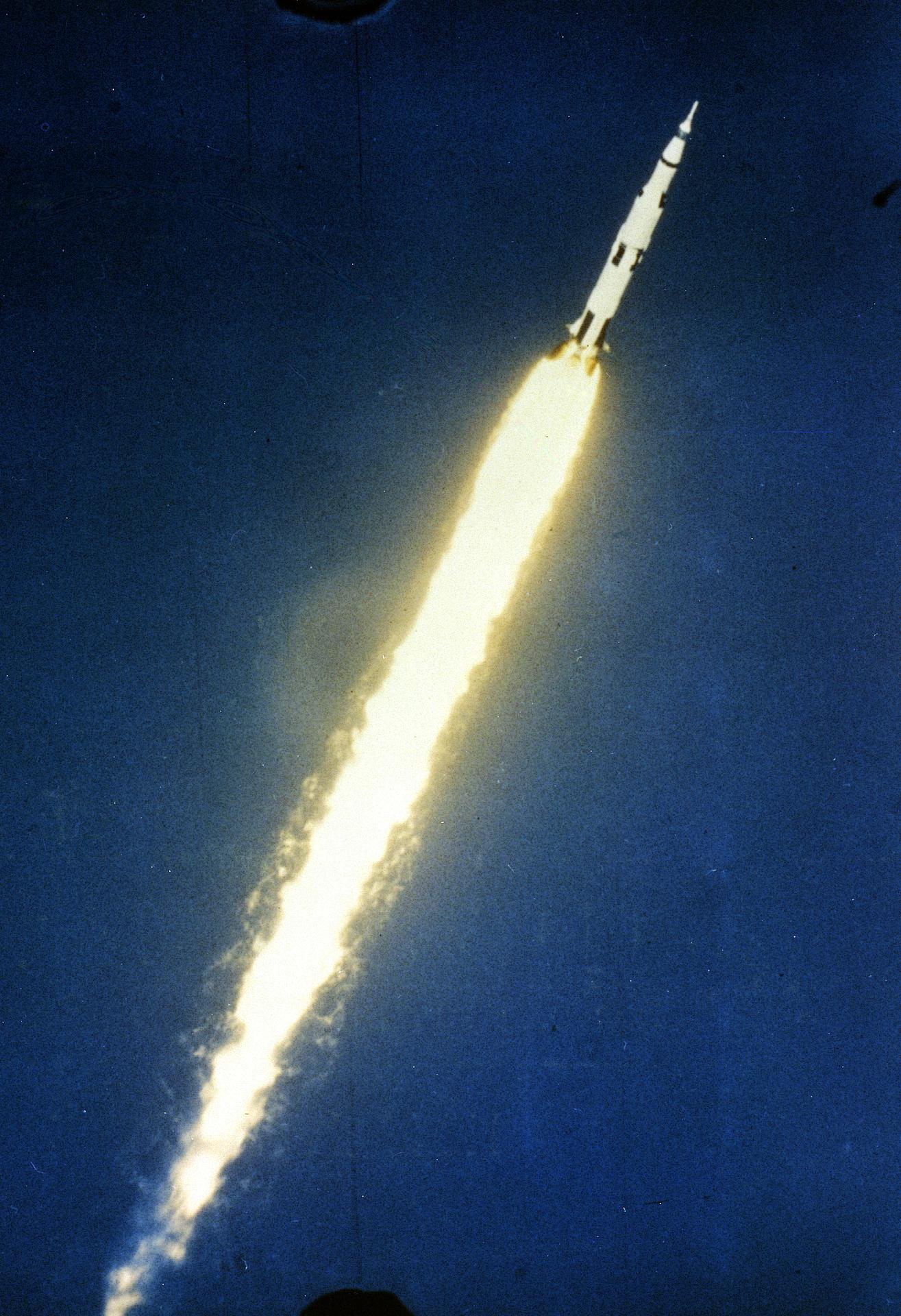
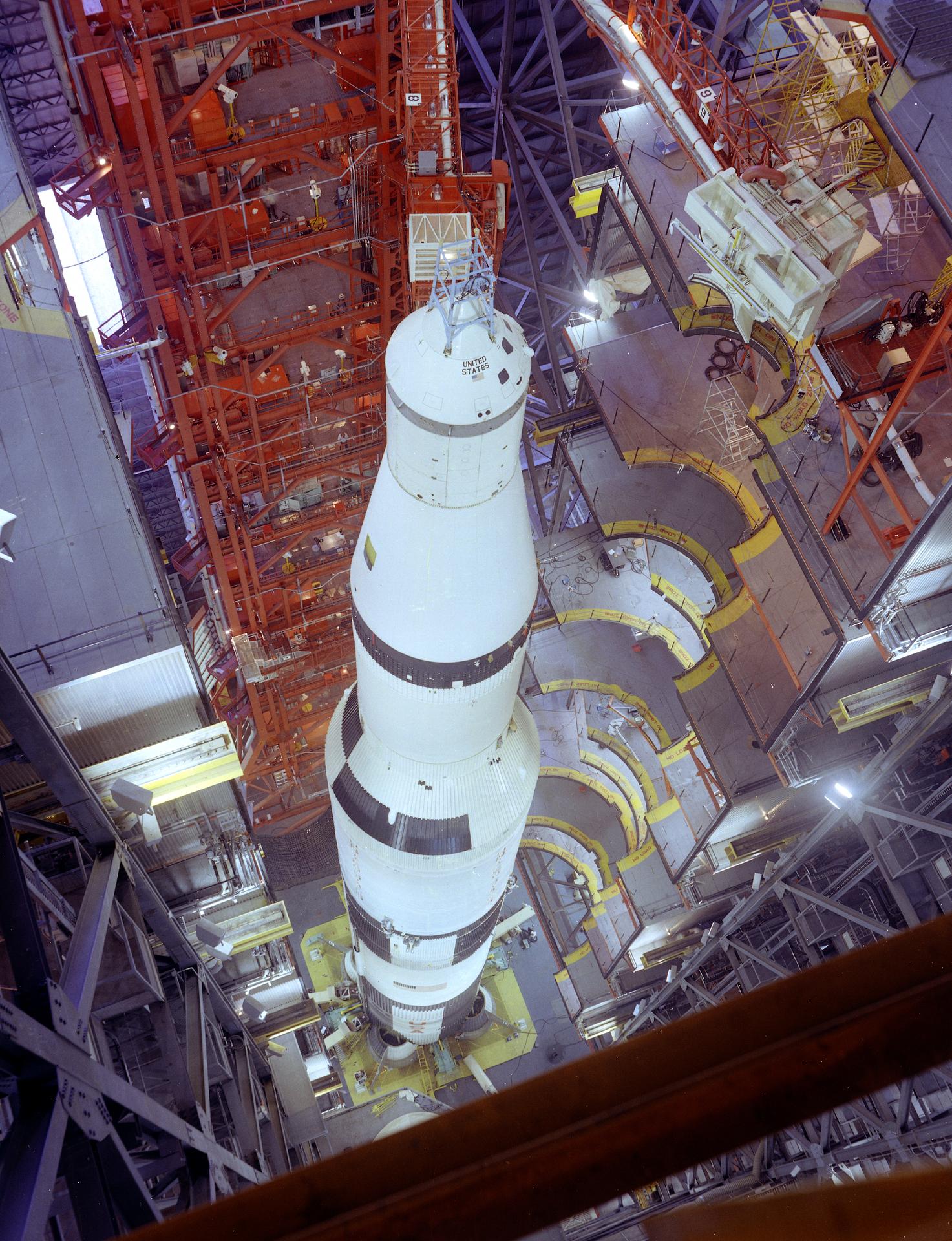
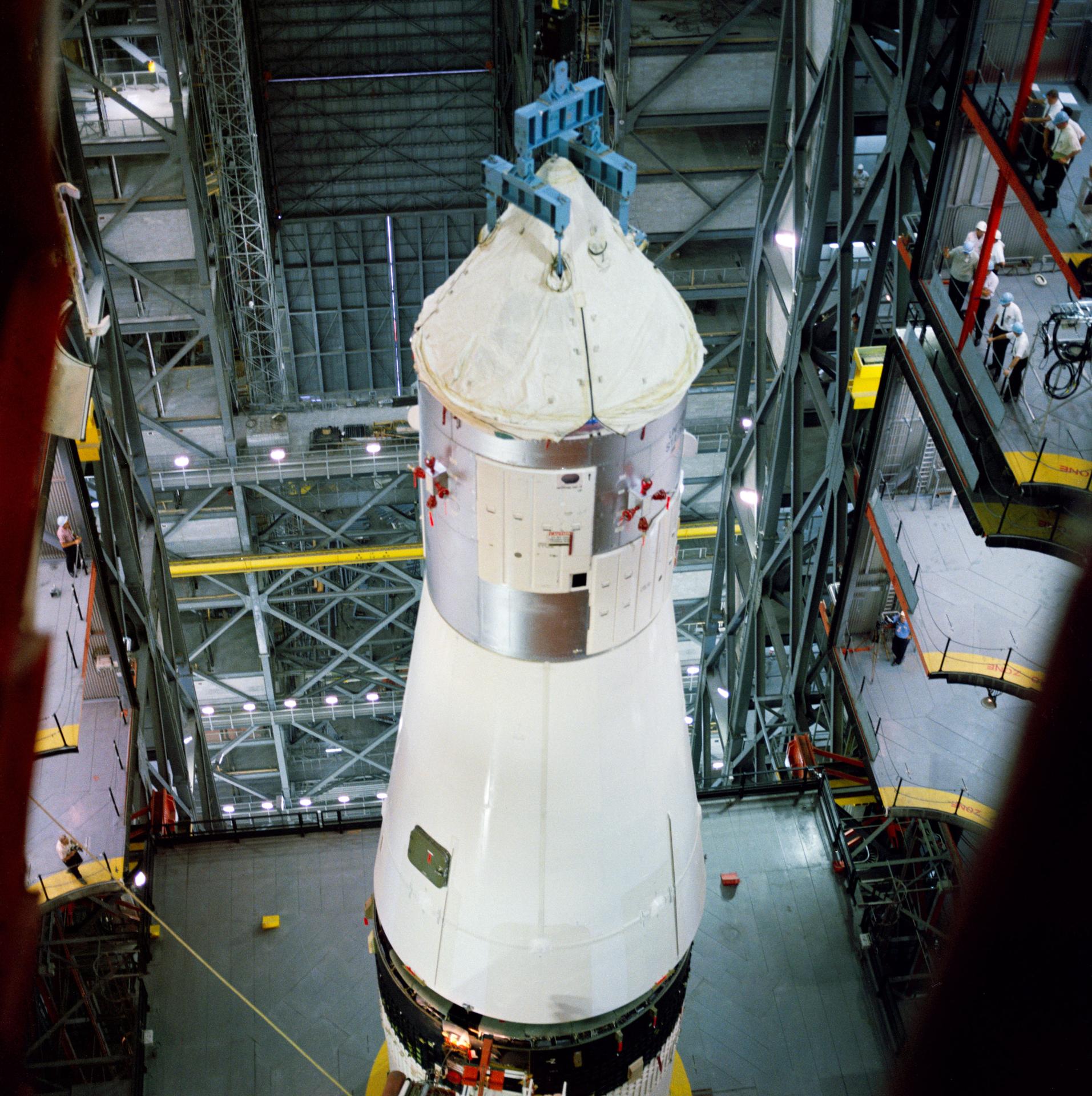
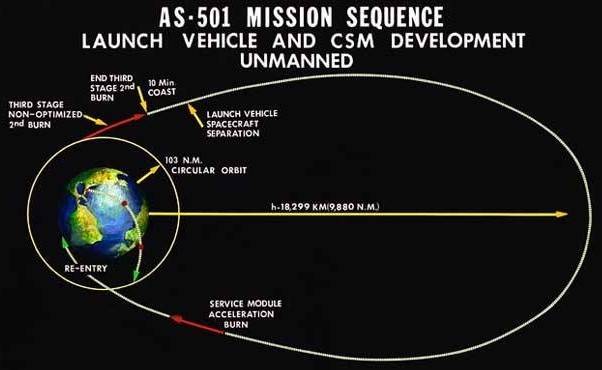
The unmanned Saturn/Apollo 4 (AS-501) mission was the first all-up test of the three stage Saturn V rocket. It carried a payload of an Apollo Command and Service Module (CSM) into Earth orbit. The mission was designed to test all aspects of the Saturn V launch vehicle and also returned pictures of Earth taken by the automatic Command Module apogee camera from about one hour before to one hour after apogee. Mission objectives included testing of structural integrity, compatibility of launch vehicle and spacecraft, heat shield and thermal seal integrity, overall reentry operations, launch loads and dynamic characteristics, stage separation, launch vehicle subsystems, the emergency detection system, and mission support facilities and operations. The mission was deemed a successful test.
Orbital insertion was achieved by ignition of the third (S-IVB) stage, putting the spacecraft (S-IVB and CSM) into a 184 x 192 km parking orbit with a period of 88.2 minutes and an inclination of 32.6 degrees. After two orbits the S-IVB was re-ignited for a simulated translunar injection burn, putting the spacecraft into an Earth-intersecting trajectory with an apogee of 17,346 km. The S-IVB stage then separated from the CSM, and the service propulsion system (SPS) ignited for 16 seconds, raising the apogee to 18,216 km. Later the SPS was re-ignited for 271 seconds to accelerate the CSM to beyond lunar trajectory return velocities. SPS cutoff was followed by separation of the Command Module (CM) from the Service Module and orientation of the CM for reentry. Atmospheric entry at 122 km occurred at a flight path angle of 7.077 degrees with a velocity of 11,140 meters/second. The CM landed near Hawaii at 20:37 UT 9 November 1967 about 16 km from the target landing point.
55 Years Ago: Apollo 4, the First Flight of the Saturn V
On Nov. 9, 1967, with the Space Age barely 10 years old, NASA took one giant leap forward: the first…
Read the Story