Spaceships and Rockets
Commercial Resupply Rockets
These commercial rockets resupply the International Space Station, delivering cargo and scientific investigations.
A little more than two years after the end of the Space Shuttle Program, SpaceX and Orbital ATK (now Northrop Grumman) began successfully resupplying the space station with cargo launched from the United States. This partnership is changing the way NASA does business, helping build a strong American commercial space industry, and freeing the agency to focus on developing the next-generation rocket and spacecraft that will allow us to travel farther in space than ever before.
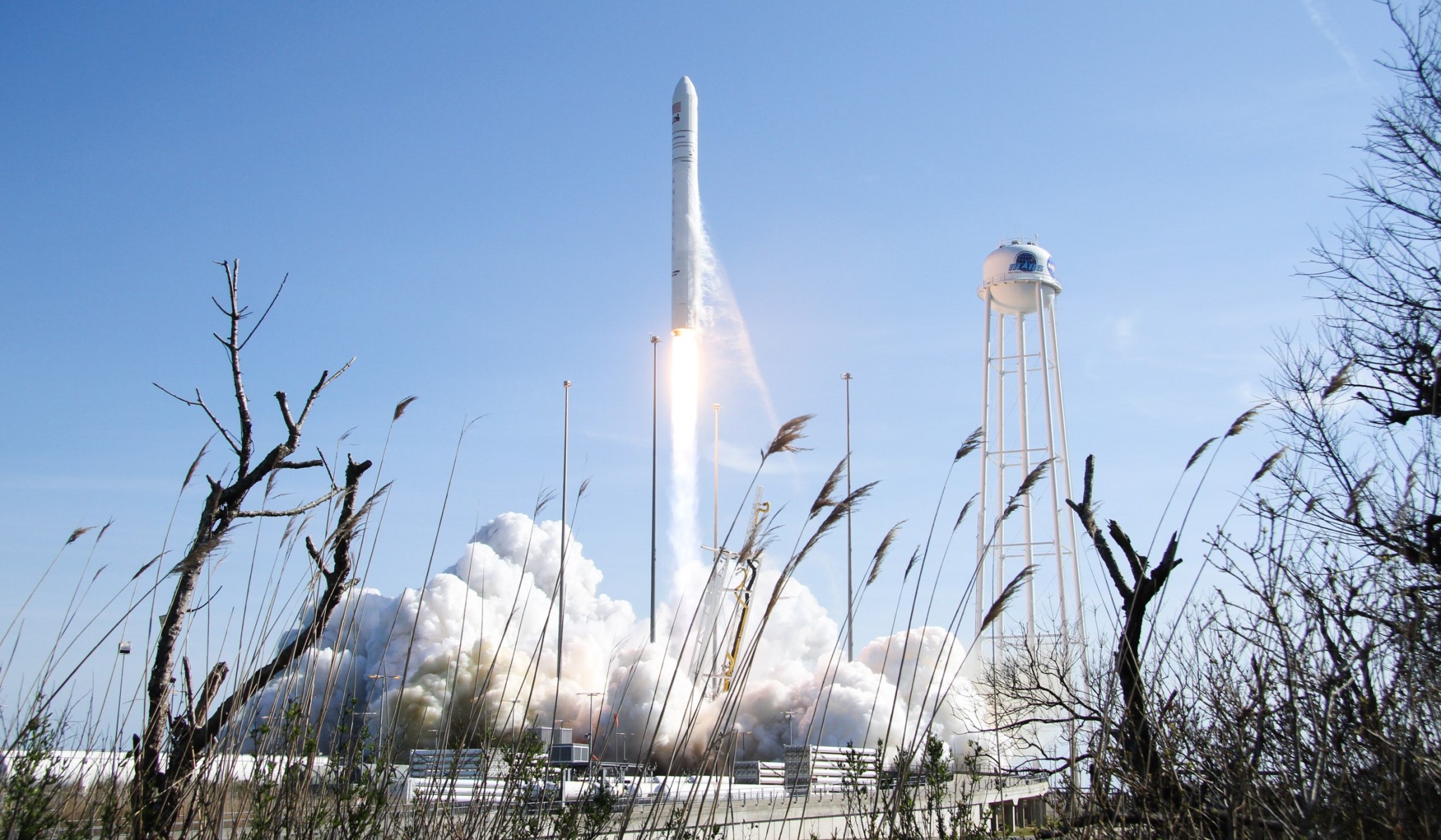
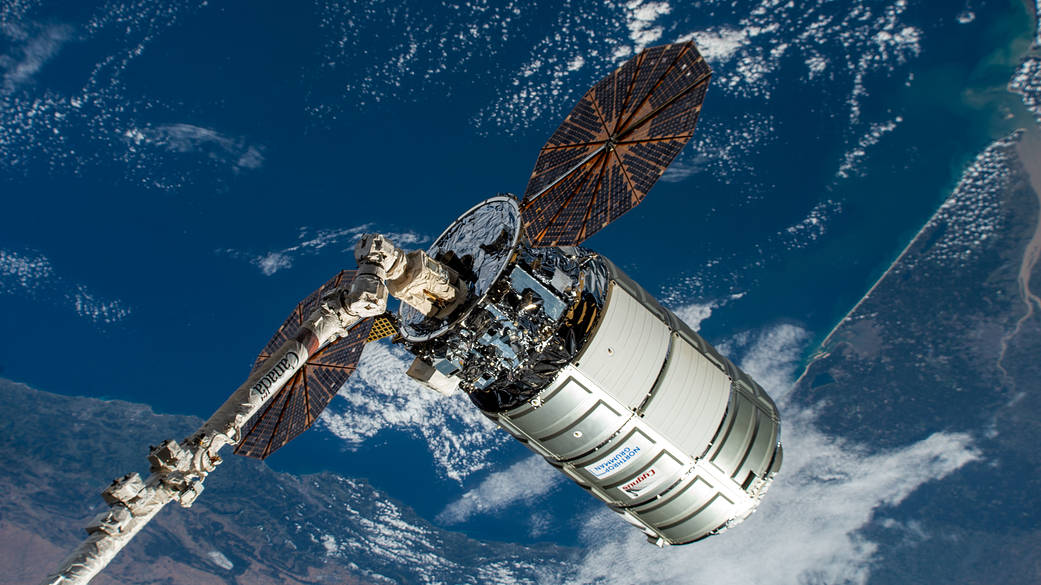
Antares
Northrop Grumman’s Antares rocket, carrying the Cygnus spacecraft, is a two-stage rocket that delivers science and research, crew supplies, and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. The rocket provides low Earth orbit launch capability for payloads weighing up to 17,636 pounds (8,000 kilograms).
The Antares program successfully conducted its inaugural test launch on April 21, 2013, and the Orb-D1 demonstration mission on Sept. 18, 2013, both of which were conducted under the Commercial Orbital Transportation System agreement with NASA. In 2014, Northrop Grumman began delivering cargo to the International Space Station under the agency’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS1) contract. The company was later selected to continue flying resupply missions under NASA’s CRS2 contract.
Technical Overview
- Diameter: 3.9 meters (12.8 feet)
- Height: 42.5 meters (139.4 feet)
- Mass: 290,000-310,000 kilograms (639,341-683,433 pounds)
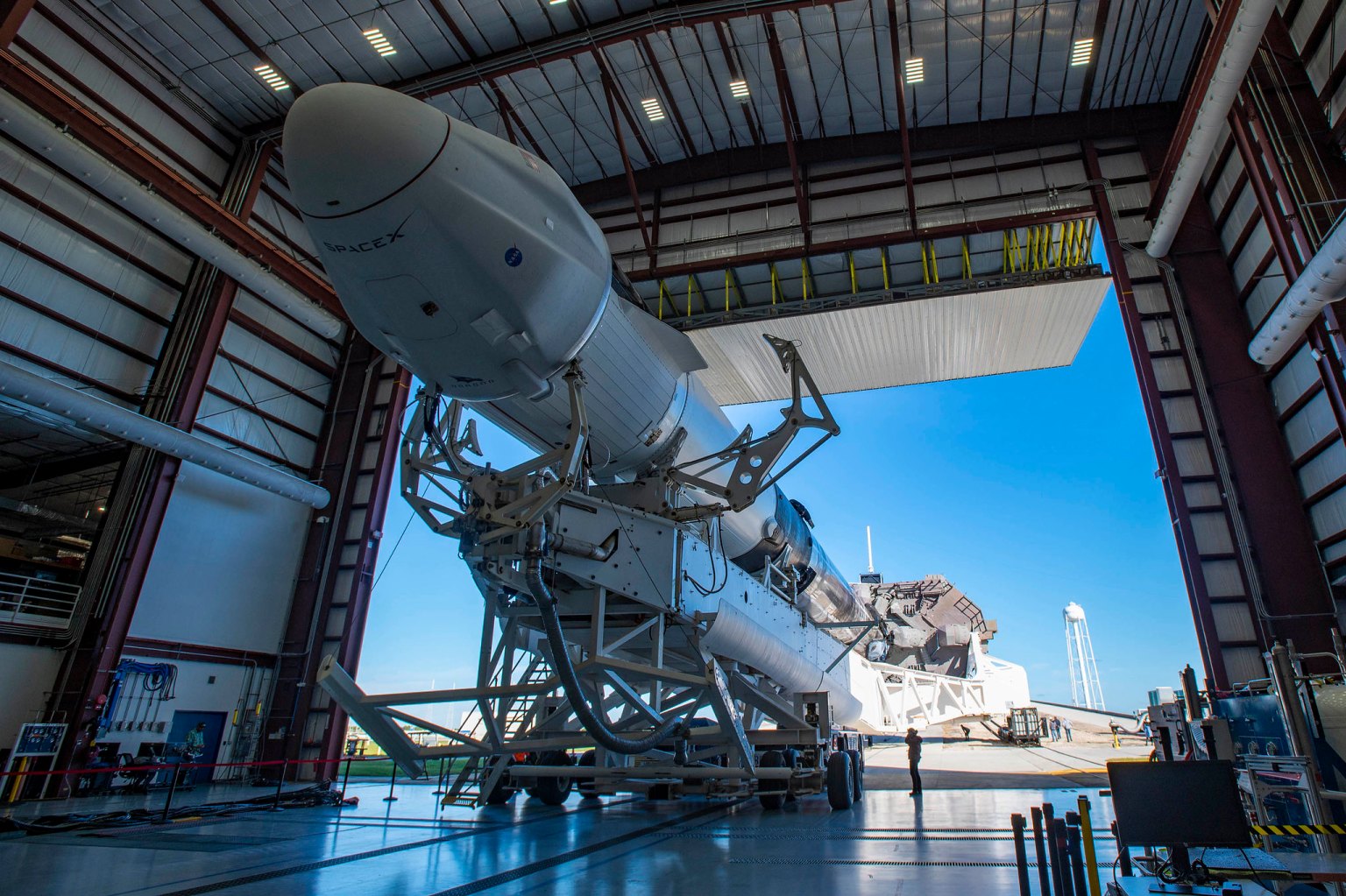
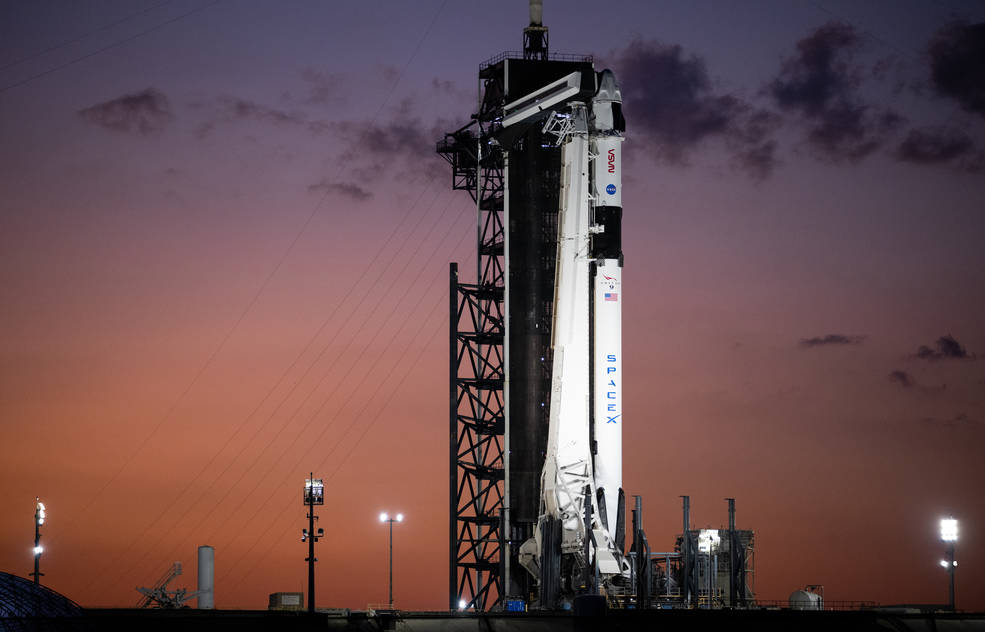
Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX for the reliable and safe transport of satellites and the Dragon spacecraft into orbit. Falcon 9 is the first orbital class rocket capable of re-flight.
Falcon 9 began delivering cargo to the International Space Station for NASA in 2012, making SpaceX the first commercial company to visit the station. Falcon 9 went on to make numerous trips to space, delivering satellites to orbit as well as delivering and returning cargo from the space station for NASA, before becoming certified to launch astronauts.
Technical Overview
- Diameter: 3.7 meters (12 feet)
- Height: 70 meters (229.6 feet)
- Mass: 549,054 kilograms (1,207,920 pounds)
Commercial Resupply
Learn More