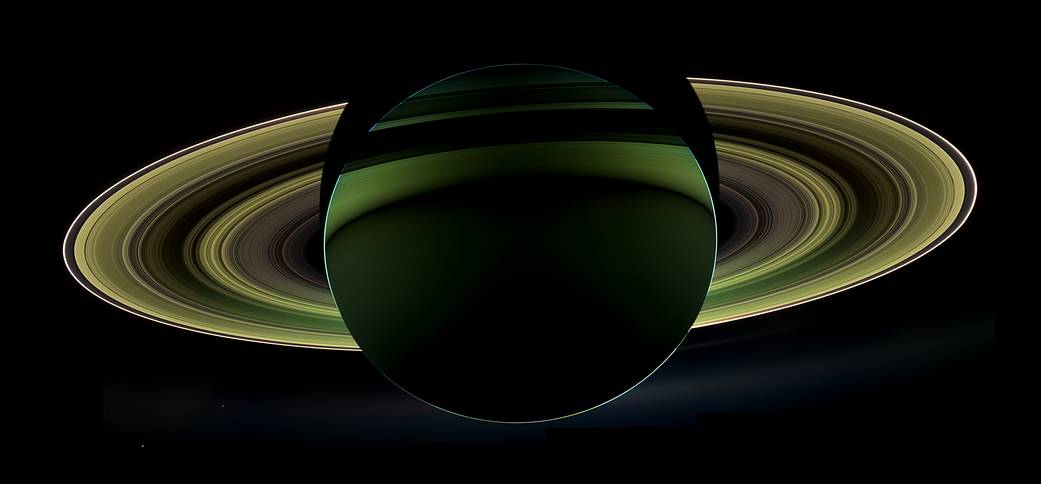
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft has delivered a glorious view of Saturn, taken while the spacecraft was in Saturn’s shadow. The cameras were turned toward Saturn and the sun so that the planet and rings are backlit. (The sun is behind the planet, which is shielding the cameras from direct sunlight.) In addition to the visual splendor, this special, very-high-phase viewing geometry lets scientists study ring and atmosphere phenomena not easily seen at a lower phase.
Since images like this can only be taken while the sun is behind the planet, this beautiful view is all the more precious for its rarity. The last time Cassini captured a view like this was in Sept. 2006, when it captured a mosaic processed to look like natural color, entitled “In Saturn’s Shadow.” In that mosaic, planet Earth put in a special appearance, making “In Saturn’s Shadow” one of the most popular Cassini images to date. Earth does not appear in this mosaic as it is hidden behind the planet.
Also captured in this image are two of Saturn’s moons: Enceladus and Tethys. Both appear on the left side of the planet, below the rings. Enceladus is closer to the rings; Tethys is below and to the left.
This view looks toward the non-illuminated side of the rings from about 19 degrees below the ring plane.
Images taken using infrared, red and violet spectral filters were combined to create this enhanced-color view. The images were obtained with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on Oct. 17, 2012 at a distance of approximately 500,000 miles (800,000 kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale at Saturn is about 30 miles per pixel (50 kilometers per pixel).
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute
2 min read