Space Radiation Tissue Sharing Forum
Instructions for accessing NASA Space Radiation tissue sharing information
The NASA Human Research Program (HRP) is now making tissue samples collected from studies funded by the HRP Space Radiation Program Element (SRPE) available to investigators in the space radiation research community. Most of the animals are exposed to charged particles at the NASA Space Radiation Laboratory (NSRL), and some are exposed to neutrons or low-LET radiation at other facilities. There are two categories of shared samples. The first category is available samples that have already been collected by the primary SRPE funded PIs. These samples are stored in the individual PI’s laboratories. The second category, upcoming sacrifices, refers to fresh tissue samples that investigators have an opportunity to collect from an existing SRPE funded study, if such a collection does not interfere with the primary PI’s experiment. Information on both the available and existing study samples is posted on the NASA Life Sciences Data Archive (LSDA) website.
Available Tissue Samples
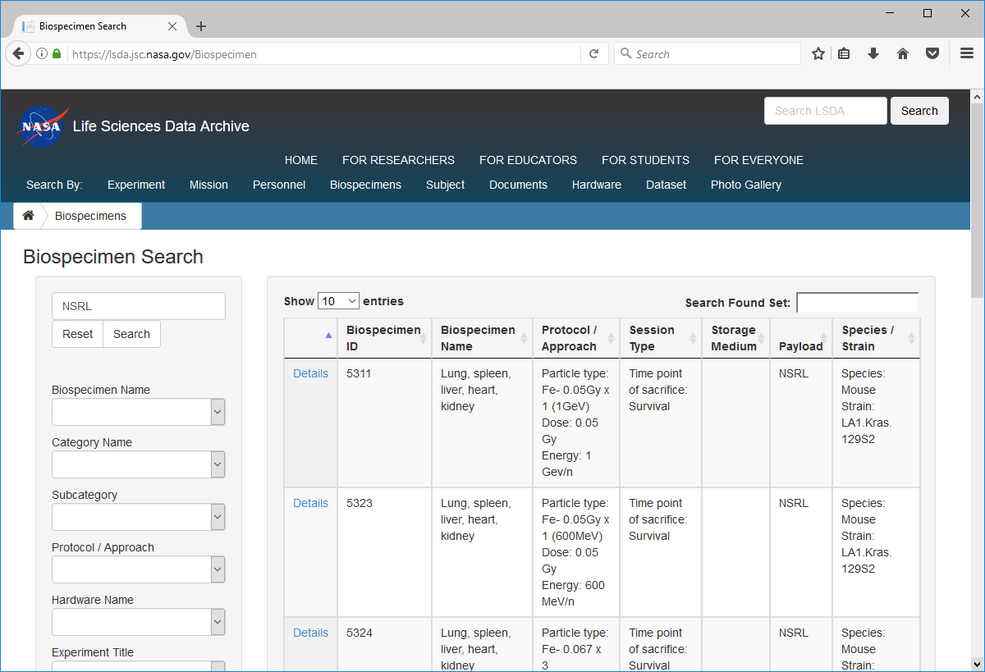
Investigators interested in available samples should visit the LSDA searchable database.
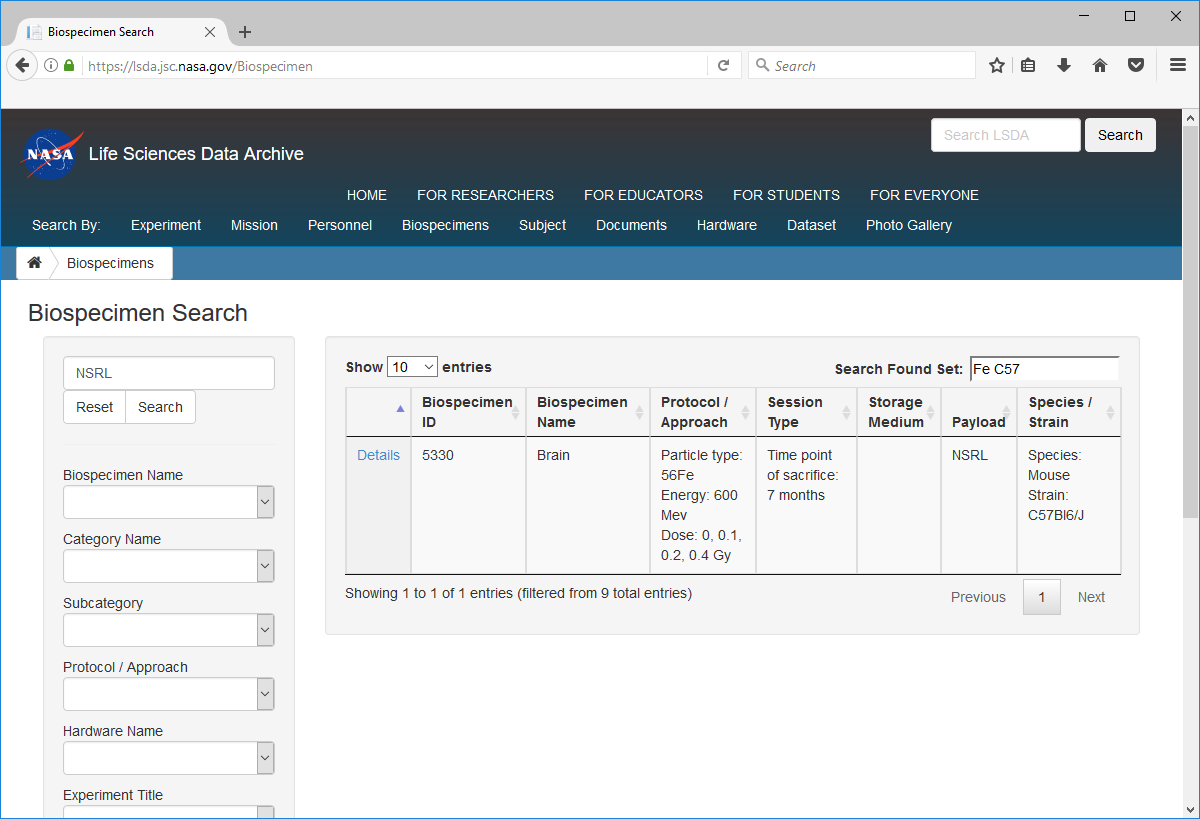
Enter “NSRL” in the top left search box and select “Search”. The found set will be a listing of all NSRL available samples.
To search within the found set, enter criteria in the upper right search box such as “Fe”, “C57”, and/or “lung”. This will further refine the found set.
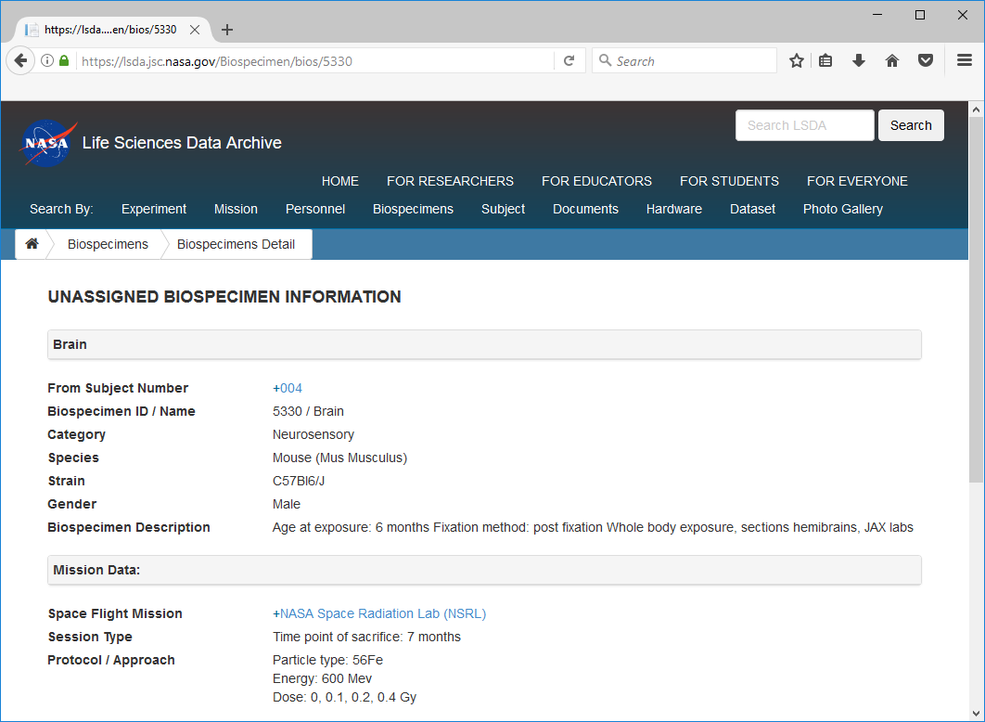
Click “Details” to view the complete set of information about the sample of interest.
Contact Dr. Honglu Wu at honglu.wu-1@nasa.gov for
- PI contact information
- Additional information on existing studies
- Study schedules
______
NASA’s Human Research Program, or HRP, pursues the best methods and technologies to support safe, productive human space travel. Through science conducted in laboratories, ground-based analogs, and the International Space Station, HRP scrutinizes how spaceflight affects human bodies and behaviors. Such research drives HRP’s quest to innovate ways that keep astronauts healthy and mission-ready as space travel expands to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.