Note: Please note that this is an “archived project” and is no longer updated. This article is meant for historical purposes only.
The Mars 2020 rover, with these new advanced scientific instruments, including those from our international partners, holds the promise to unlock more mysteries of Mars’ past as revealed in the geological record,” said John Grunsfeld, astronaut and associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. “This mission will further our search for life in the universe and also offer opportunities to advance new capabilities in exploration technology.
The Mars 2020 rover also will help advance our knowledge of how future human explorers could use natural resources available on the surface of the Red Planet. An ability to live off the Martian land would transform future exploration of the planet. Designers of future human expeditions can use this mission to understand the hazards posed by Martian dust and demonstrate technology to process carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to produce oxygen. These experiments will help engineers learn how to use Martian resources to produce oxygen for human respiration and potentially as an oxidizer for rocket fuel.
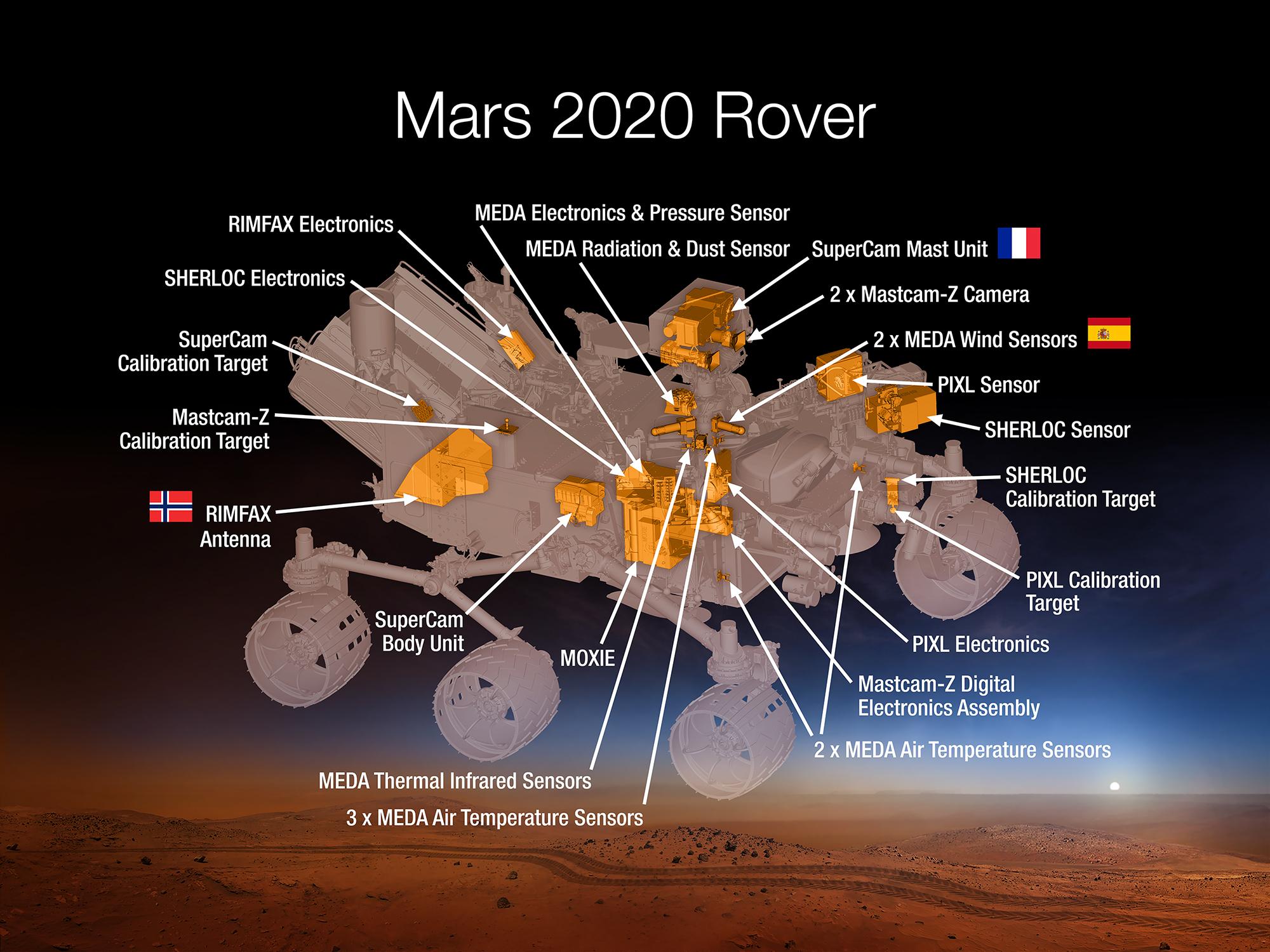
Of the selected payloads, the Game Changing Development Program is funding:
- The Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE), an exploration technology investigation that will produce oxygen from Martian atmospheric carbon dioxide. The Principal Technologist is Michael Hecht, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA), a set of sensors that will provide measurements of temperature, wind speed and direction, pressure, relative humidity and dust size and shape. The Principal Technologist is Jose’ Antonio Rodriguez-Manfredi, Centro de Astrobiologia, Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aeroespacial, Spain.