Test Facility Capabilities
Large, Ambient Engine Test Facility
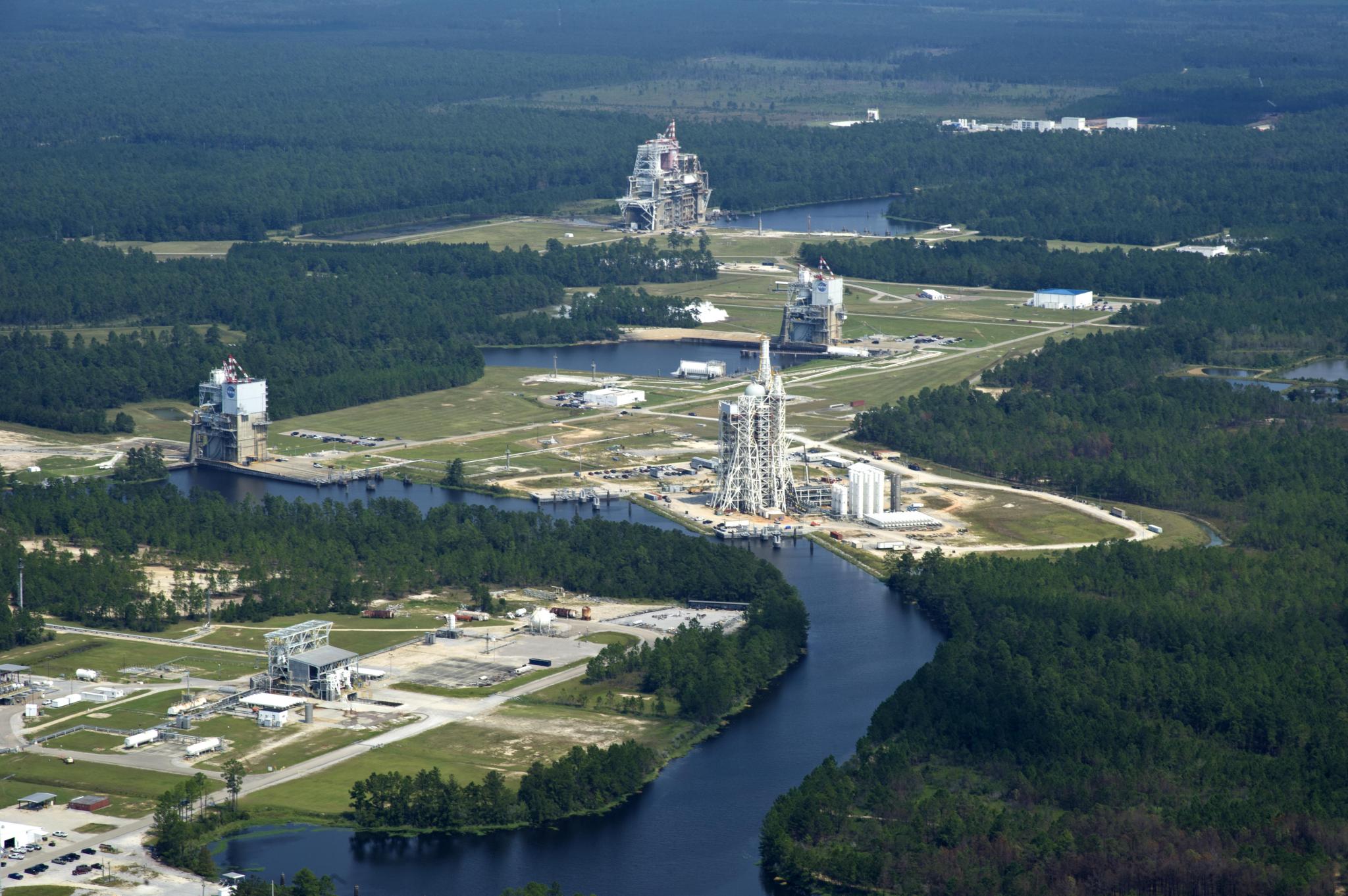
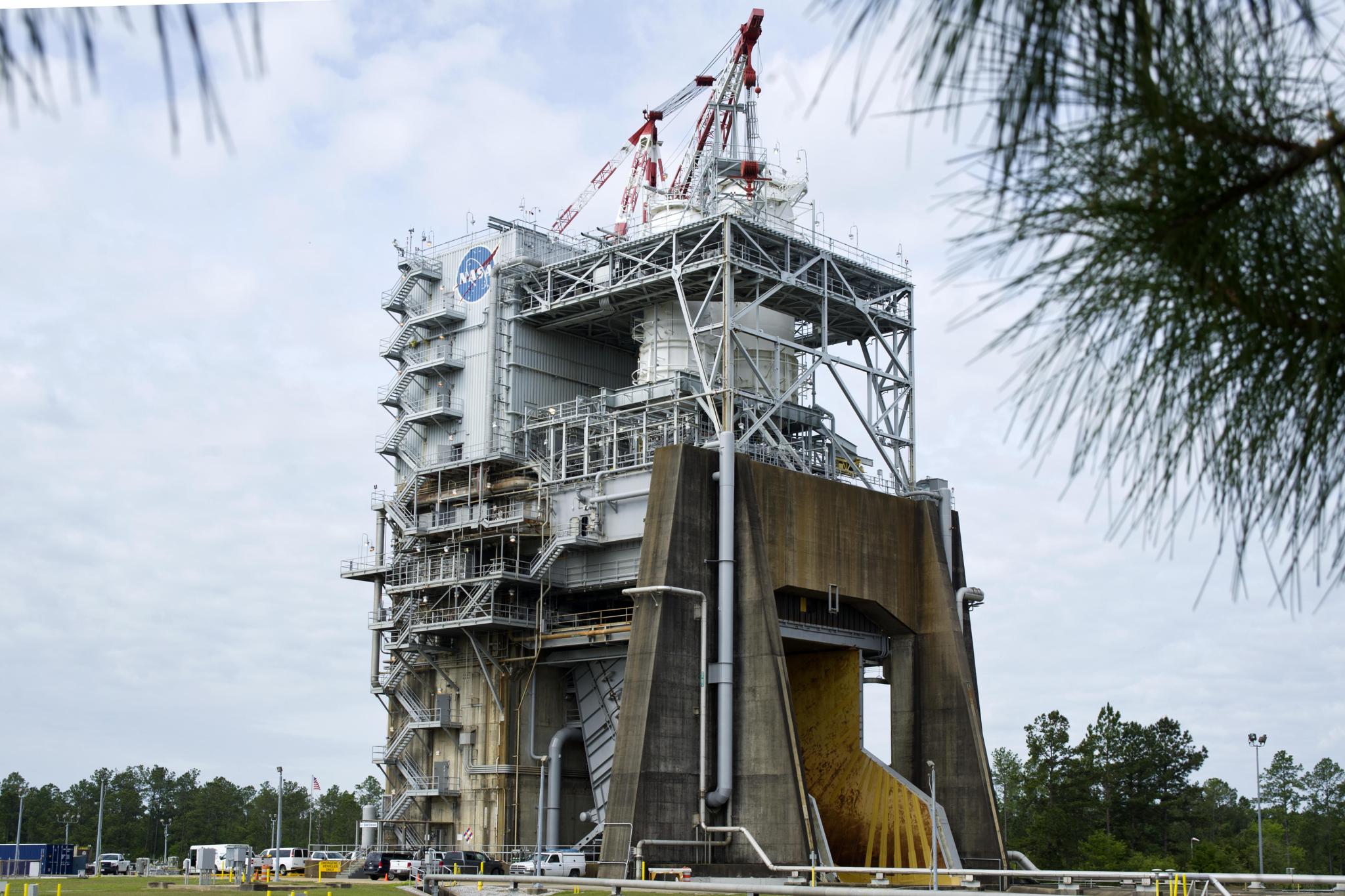
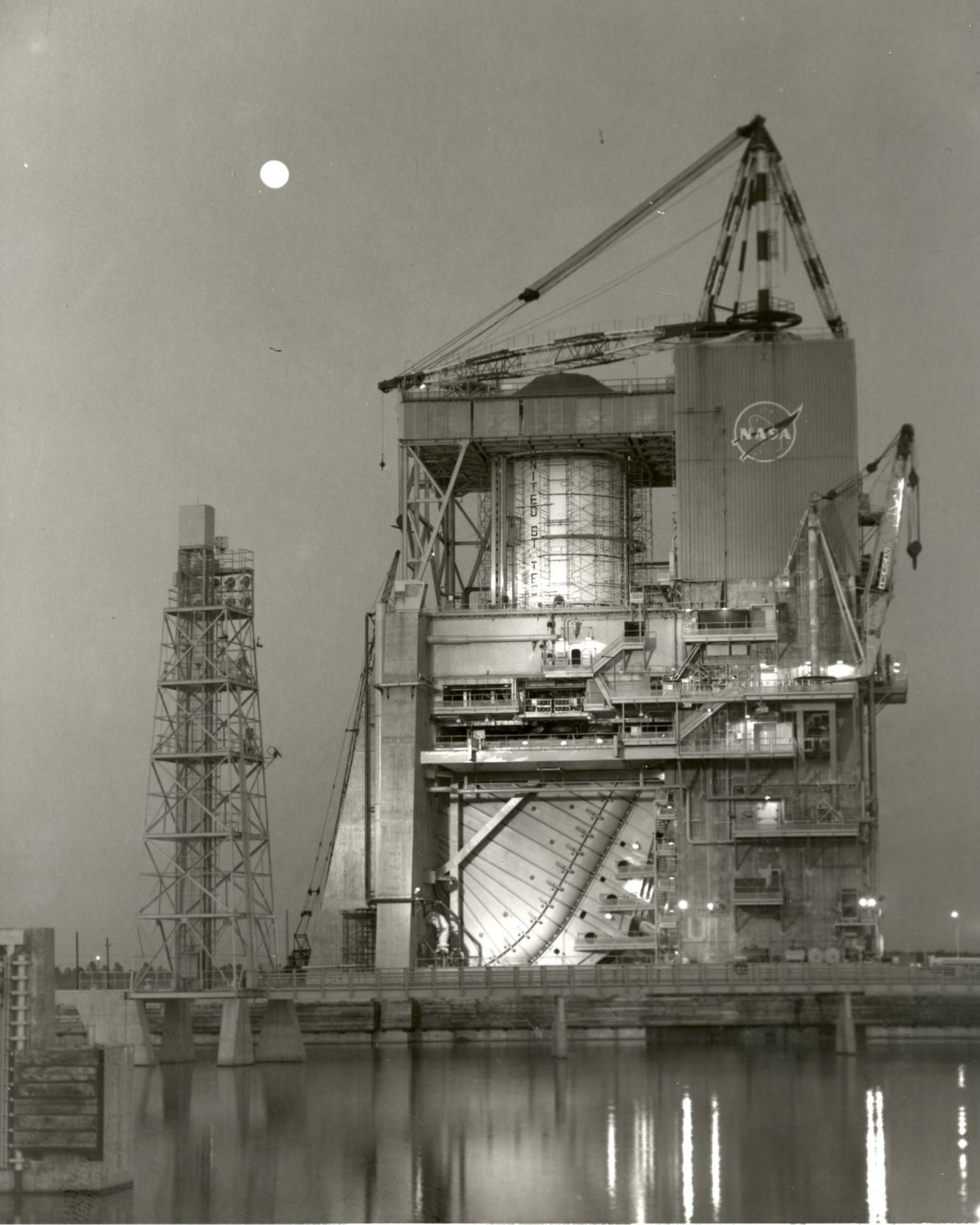
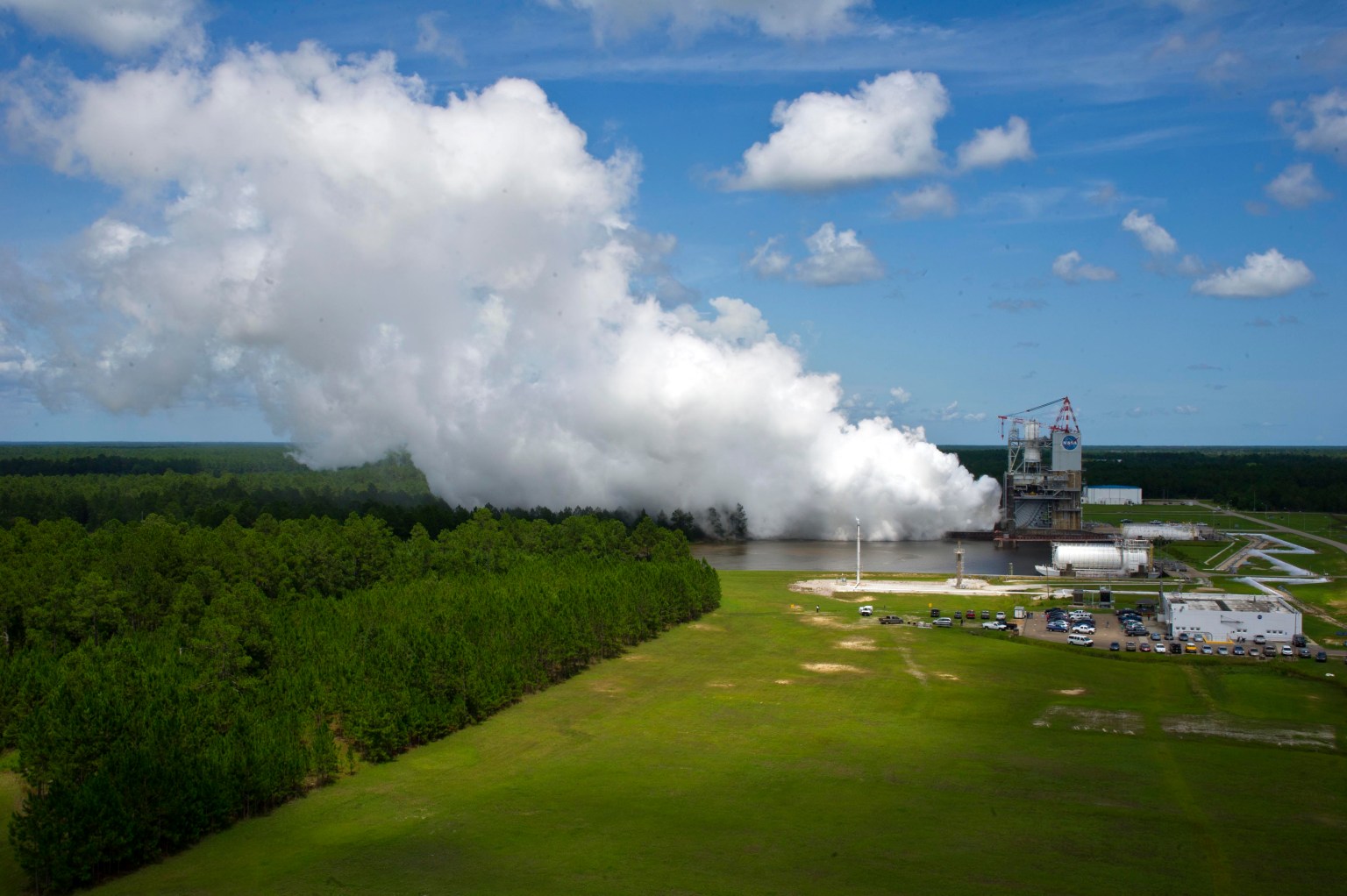
Originally known as the A-1 Test Stand, the renamed Fred Haise Test Stand was designed to test fire the Apollo Saturn V second stage (S-II) – a cluster of five J-2 rocket engines capable of developing a 1.15-million-pound thrust at altitude. The Fred Haise Test Stand was converted to a single-position, vertical-firing test stand used to test liquid rocket engines at sea level conditions. It is currently configured for engine testing, with a 33-foot diameter opening within the thrust drum.
Maximum Thrust: 1,500,000 pounds (original design); 650,000 pounds (current configuration)
Altitude: Ambient
Propellants: Liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen
Current/Scheduled Work:
- NASA SLS (Space Launch System) RS‐25 Engine
Past Propulsion Test Activities:
- AR-22 (Aerojet Rocketdyne engine for the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Experimental Spaceplane Program/Boeing Phantom Express)
- NASA J‐2X power pack assembly and engine (2011‐2013)
- NASA J‐2 power pack assembly (2006‐2008)
- NASA Linear Aerospike power pack assembly, single engine, and dual engine (1998‐2001)
- NASA Space Shuttle Main Engine testing (1975‐2006)
- NASA Saturn S-II (5-engine cluster) stage testing (1967‐1970)
- XRS-2200 (NASA/Boeing Linear Aerospike Engine for X-33 reusable launch vehicle)
- Space Shuttle Main Engine (NASA/Boeing)
Other NASA Stennis Test Facilities and Support Infrastructures
NASA Stennis has many unique test facilities and supporting infrastructure which provides world-class testing services.