Dust
Dust testing is crucial for designing spaceflight hardware destined for the moon to ensure its resilience against lunar surface conditions, preventing potential damage or performance issues caused by abrasive lunar dust particles. NASA JSC boasts a comprehensive suite of capabilities for dust testing, including unique assets to accommodate a wide range of hardware, as well as providing expertise in testing with regolith simulant and other unique requirements. Dust testing capabilities include both ambient dust testing as well as “dirty” thermal vacuum capabilities. The Regolith Simulant Component Test Lab features multiple small vacuum environments and a dispersal test box, offering ambient dispersal capabilities for simulant testing. The 15-foot Dirty Thermal Vacuum Chamber is uniquely designed for dust and planetary surface environments testing. Complementing these facilities is a dedicated Dust Containment and Preparation room, ensuring optimal hardware exposure to dust/regolith. These capabilities invite researchers and developers to leverage NASA JSC’s advanced resources for their own testing and experimentation needs.
Lunar Development and Test Facility
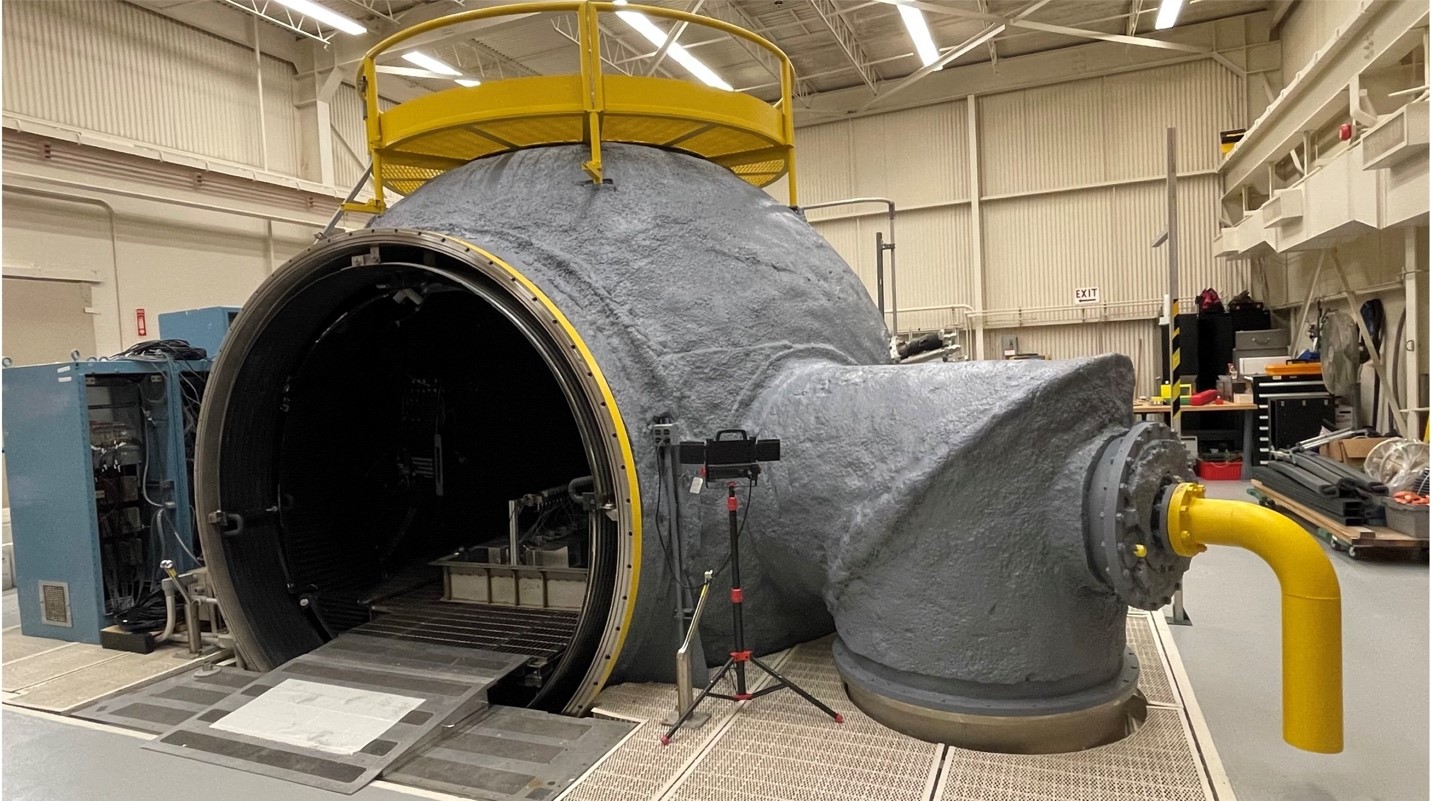
15-foot Dirty Thermal Vacuum Chamber
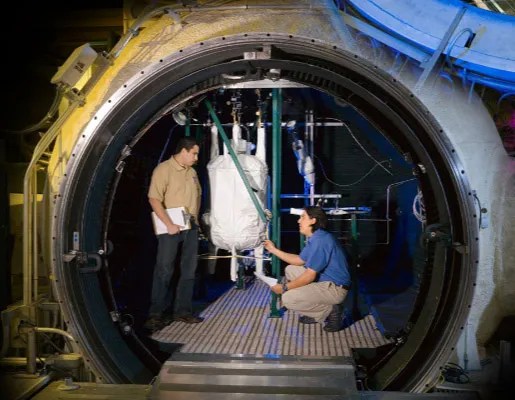
NASA JSC 15-foot dirty thermal vacuum chamber (TVAC) provides unique testing capabilities for dust and planetary surface environments. The 15-foot chamber is a spherical chamber designed to test advanced concepts, especially for ISRU, battery power systems, space vehicle actuators and auxiliary power units.
- 12.5-foot internal diameter spherical chamber with ~78-inch diameter clear entry for easy access
- Vacuum conditions: 1×10^-6 torr to 760 torr
- Thermal conditions: -185°C to +125°C
- Features: Air or GN2 repress options, Residual Gas Analyzer, particulate filtration for testing with regolith simulants, LN2 contamination scavenger plate, interior LED lighting and cameras
- Air, GN2 pressurization
- Feed-throughs for high-power electrical connections and high-channel count data
- Chamber platform and I-beam trolley rated for payloads up to 3,500 lbs
- Regolith bin and drill tube for design and test of excavation, processing, or construction technology
3-foot Dirty Thermal Vacuum Chamber
NASA JSC’s 3-foot dirty thermal vacuum chamber (TVAC) provides unique testing capabilities for dust and planetary surface environments. The 3-foot chamber is a 3ft x 3ft x 3ft cube designed to test component level concepts in a lunar simulated environment.
- 32” x 32” x 32” internal volume of the thermal shroud
- Vacuum conditions: 10^-7 torr to 760 Torr
- Thermal conditions: -185°C to +150°C
- Features: GN2 repress, oil-free vacuum system, particulate filtration for testing with regolith simulants, LN2 contamination coil
- Built-in thermal platen and shroud walls independently controlled for temperature conditioning if needed
Regolith Simulant Component Test Lab
The Component Test Lab offers multiple small vacuum environments for testing in simulant and a simulant dispersal test box with ambient dispersal capabilities.
- Multiple 1’-3’ thermal vacuum bell jars for testing with simulant
- Ambient 2’ x 2’ x 3’ dust box for quick and easy functional testing with fan-blown simulant
- Vacuum box with glove ports and airlock chamber
- Capable of reaching 0.05 torr (ultimate)
- Air or GN2 repress
- Dimensions:
- Chamber: 1.1m x 0.74m x 0.9m (44” x 29” x 35”)
- Airlock: ⌀0.36m x 0.41m (⌀14” x 16”)
- Settling Dust Chamber
- Meets the following industry standards for dust exposure
- SAE J575 Section 4.5
- DIN 40050, Part 9, IP Codes 5K and 6K
- ISO 20653, Section 8.3.1
- IEC 529, IP Codes 5 & 6
- 72”x36”x30” (1.8m x 0.9m x 0.76m) interior
- Max test article weight: 50 lbs (22.7 kg)
- Timed dusting allows for repeated application of dust to moving test articles
- Validated for use with lunar simulants
- Meets the following industry standards for dust exposure
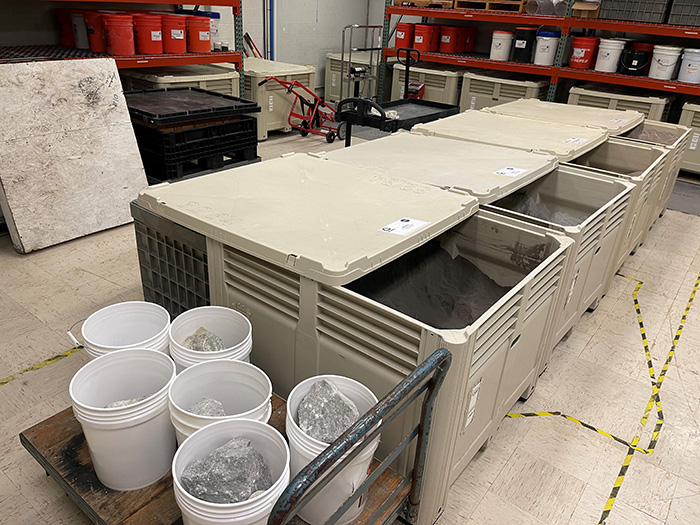
Dust Containment and Preparation
A dedicated preparation room for hardware exposure to dust/regolith and regolith bed preparation is available.
NASA JSC has a specialized facility for the development, handling, and integration of dust and soil simulant materials which require specialized environments.
Regolith Simulant Drill Tube
The regolith simulant drill tube offers a 3 meter deep cylindrical enclosure that can be actively chilled with LN2 to create a frozen simulant for drilling or water capture testing.
- Tube jacket to be flooded with LN2 for cooling and heated GN2 for return to ambient temperature
- 13.5” (.342 m) ID and 42” (1.06 m) drill depth with 4” clearance above soil height
- Designed to be filled with compacted lunar regolith simulant with a target water content of 5% water by weight
- Holds ~370 lbs (168 kg) of simulant for a combined weight of ~984 lbs (446 kg)
Regolith Simulant Test Bin
The Regolith Simulant Test Bin offers an enclosed measurable environment for direct contact regolith simulant testing.
- 48” x 96” surface area for larger test articles or mobility testing
- 8” maximum fill depth
- Interior baffles for partial filling at full depth and efficient use of simulant
- Filled and prepared in dust containment and prep lab to keep other equipment clean
Simulant Test Consulting and Development
On-site expertise available for successful vacuum operations with prepared simulant samples and test articles.
Subject Matter Expert development of specialized analog Lunar and Mars soil simulants for hardware and system testing, end-to-end from soil development to test execution.
Simulant Development Lab
Simulant and Feedstock Material Processing
The NASA JSC Simulant Development Lab (SDL) is a multifunction collaborative lab space that supports the analysis, curation, development, distribution, and testing of planetary simulants (Lunar and Martian) and granular materials. Housing over 30 metric tons of simulants and feedstock materials, the SDL can provide an end-to-end process of simulant production, from crushing rocks into micron-sized particles, adding in the appropriate particle types (glass, agglutinates, volatiles, etc.), and sieving to match accurate particle size distributions of the simulant analog.
- 12. Gilson BO-350S 7ft³ Stainless Steel Interior Bench Oven – heating and drying applications
- Various Rock Crushers, Pulverizers, Mills – for reducing rock sizes to specified diameters
- Multiple Sieve Shakers – for particle separations, accommodates various sieve sizes
- Readco Kurimoto RK Labmaster Mixer: facilitates dry powder blending and processing
- Mechanical Soil Compactor: used to compact soils in an accurate and systematic manner to achieve desired soil properties
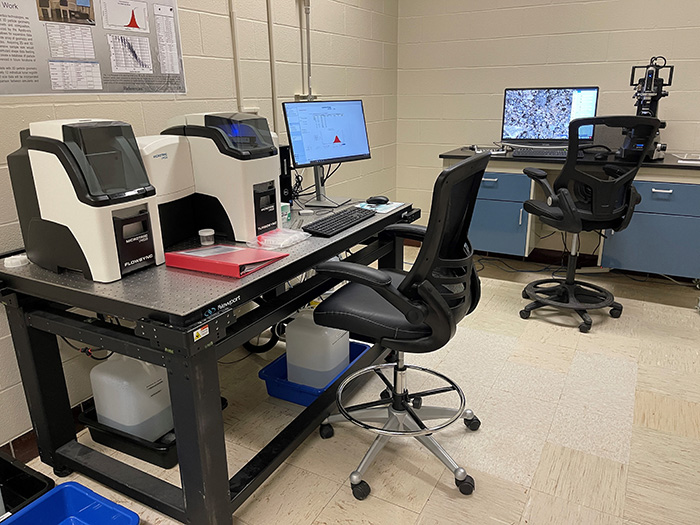
Analytical Instruments for Granular Material Characterization
The SDL also contains a suite of instruments used to characterize simulants and granular materials. Particle size distributions, particle counting, magnification, magnetic susceptibility, and shear values are capabilities.
- Microtrac Sync Wet/Dry Multi Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer (Range: 0.01 – 2,000 microns): The Sync particle size analyzer is used to characterize size distribution and particle shape of granular materials (e.g., simulated extraterrestrial dust and regolith).
- Keyence VHX-7000 Series Digital Microscope: The Keyence Digital Microscope is a fully automated 4K Ultra-High Accuracy Microscope with a fully integrated head which accommodates smooth magnification transitions from 20x up to 1000x.
- Bartington MS2B Dual Frequency Sensor + MS3 Meter (Magnetic Susceptibility): Magnetic Susceptibility measurements on soils, powders, or liquids, can be made with the coupled system of the MS3 meter and MS2B sensor.
- Gilson Standard Pneumatic Direct Shear Machine: The Gilson Standard Pneumatic Direct Shear Machine is used to evaluate the strength and stability of soils and provides direct or direct/residual shear values.
Ambient Dust Testing
The SDL is a first-ask place for running dust-ingress and dusty environments testing at ambient pressure conditions. The lab space is proximal to the bake-out oven, simulant processing tools, and the analytical suite.
Several gloveboxes and simulant test beds can be set up to run customers’ dust testing needs. Gloveboxes contain fans that disburse simulant in the enclosed space.
To learn more about the Simulant Development Lab, visit ARES | Exploration Science Projects | Lunar Regolith Simulants | Simulant Development Lab.
Connect With Us
Whether you are a public agency, private company, or academic institution, we look forward to hearing from you. Fill out the Statement of Interest form to submit your inquiry.