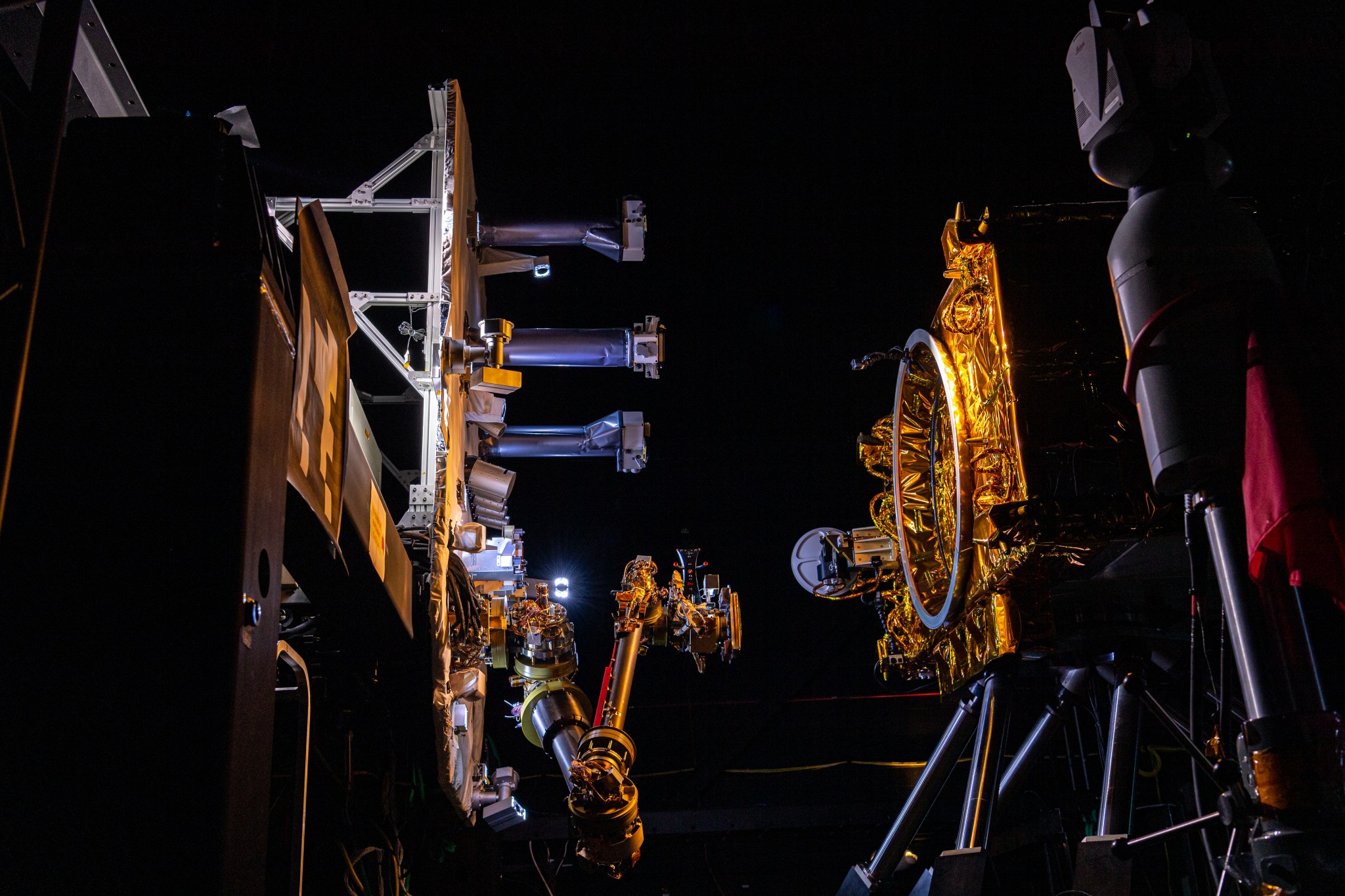
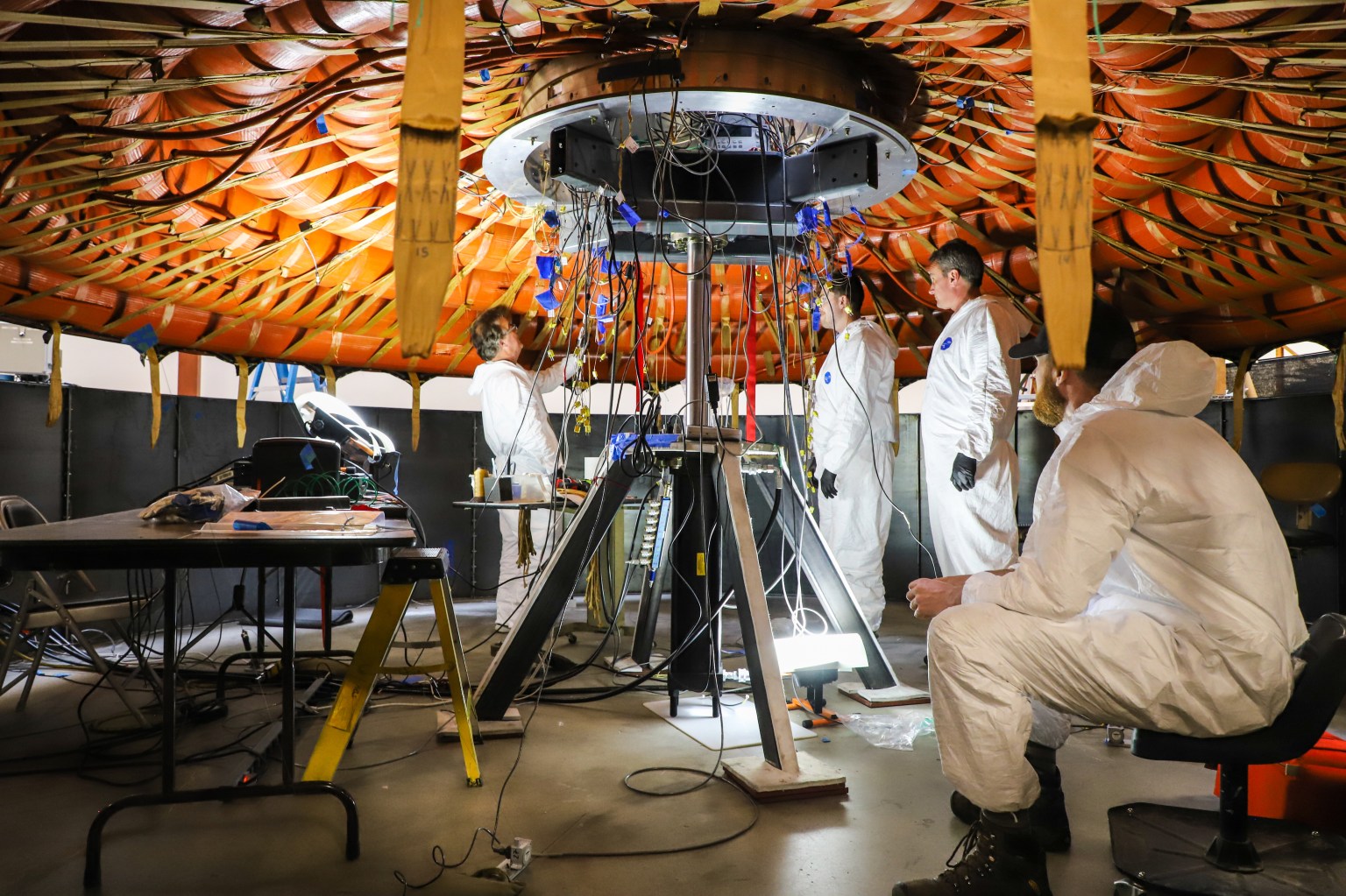
On-orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing 1 (OSAM-1)
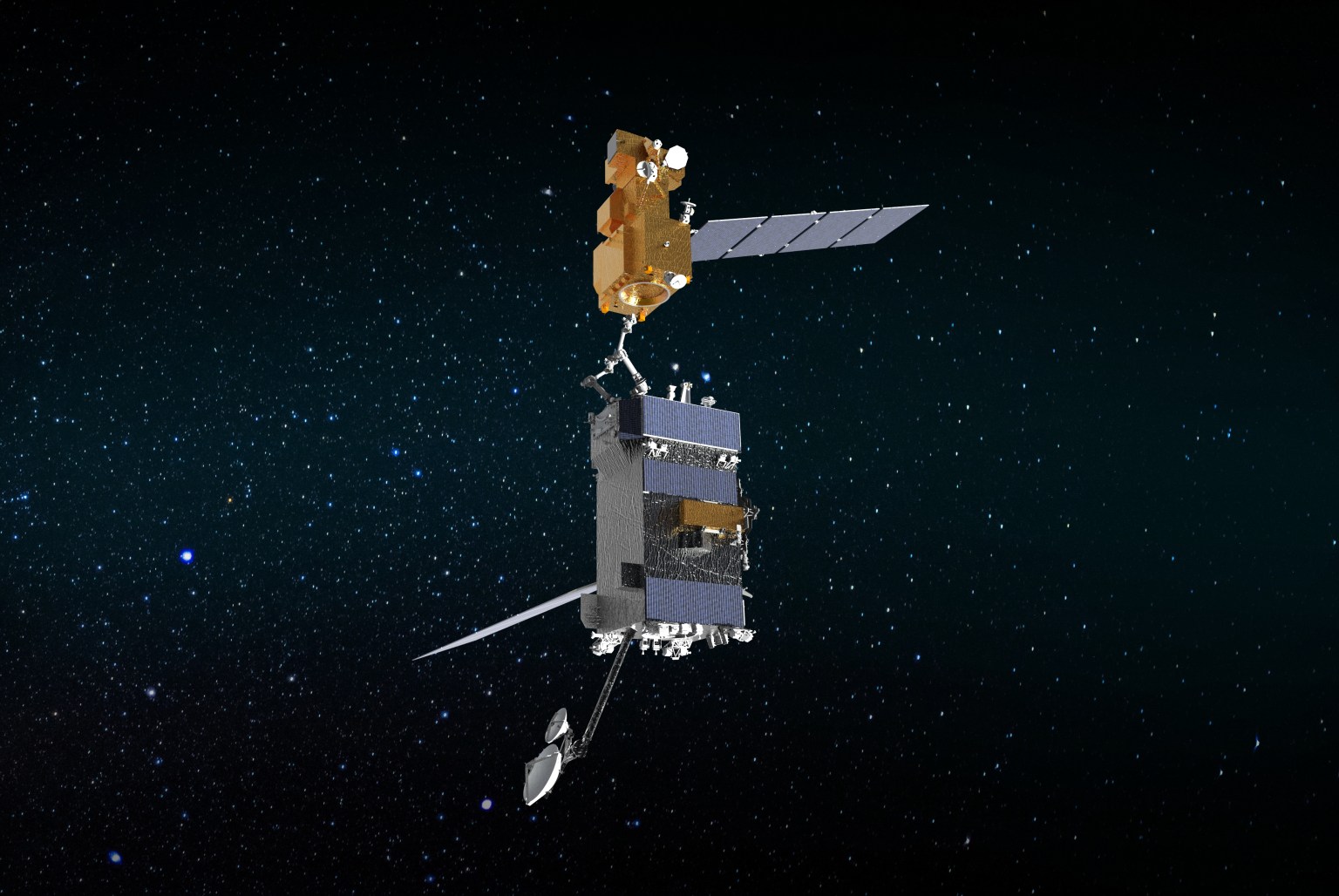

Announcement from NASA Headquarters:
Pursuant to appropriations law, NASA notified Congress on Sep. 4, of the intent to cancel OSAM-1. The agency confirmed with the Committees on Appropriations that there is no objection to cancellation, and on Oct. 1, began proceeding with an orderly shutdown.
Following an in-depth, independent project review, NASA initially decided on Feb. 29, to discontinue the On-orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing 1 (OSAM-1) project due to continued technical, cost, and schedule challenges and a broader community evolution away from refueling unprepared spacecraft, which has led to a lack of a committed partner. Shortly after NASA’s decision, Congress enacted the FY24 Consolidated Appropriations Act, providing $227 million for OSAM-1, and directing NASA to assess an OSAM-1 mission adjusted to ensure a 2026 launch within the cost profile assumed in the Fiscal Year 2024 budget, if possible.
Adhering to Congressional direction, NASA directed the OSAM-1 project to develop two potential forward plans for review: a descoped 2026 launch plan and an orderly shutdown plan. NASA conducted a rigorous review of the 2026 launch plan, including reviews by NASA’s independent technical authorities. Assessment of the 2026 launch plan found that the descoped plan introduced significant risk to mission success, significant remaining integration and test work which may result in further schedule and cost delays, low return on investment to the on-orbit servicing community, lack of a transition partner, and impacts on other NASA technology development efforts. Given these findings, NASA reconfirmed its earlier determination to cancel OSAM-1. NASA continues to be a champion of in-space servicing, assembly and manufacturing (ISAM) technology advancement and capability development. NASA funds a nationwide alliance dedicated to making ISAM a routine part of space architectures and mission lifecycles via the Consortium for Space Mobility and ISAM Capabilities. NASA also recently signed an interagency agreement with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency to provide subject matter expertise on its Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellites program. NASA released a Request for Information for OSAM-1 partnerships to further pursue the best and highest use of the project hardware and is reviewing the responses.
Establishing Satellite Servicing
Need extra gas or a tune-up for your satellite? For years, such services were outside the realm of possibility for most spacecraft. But now, one mission will break that paradigm.
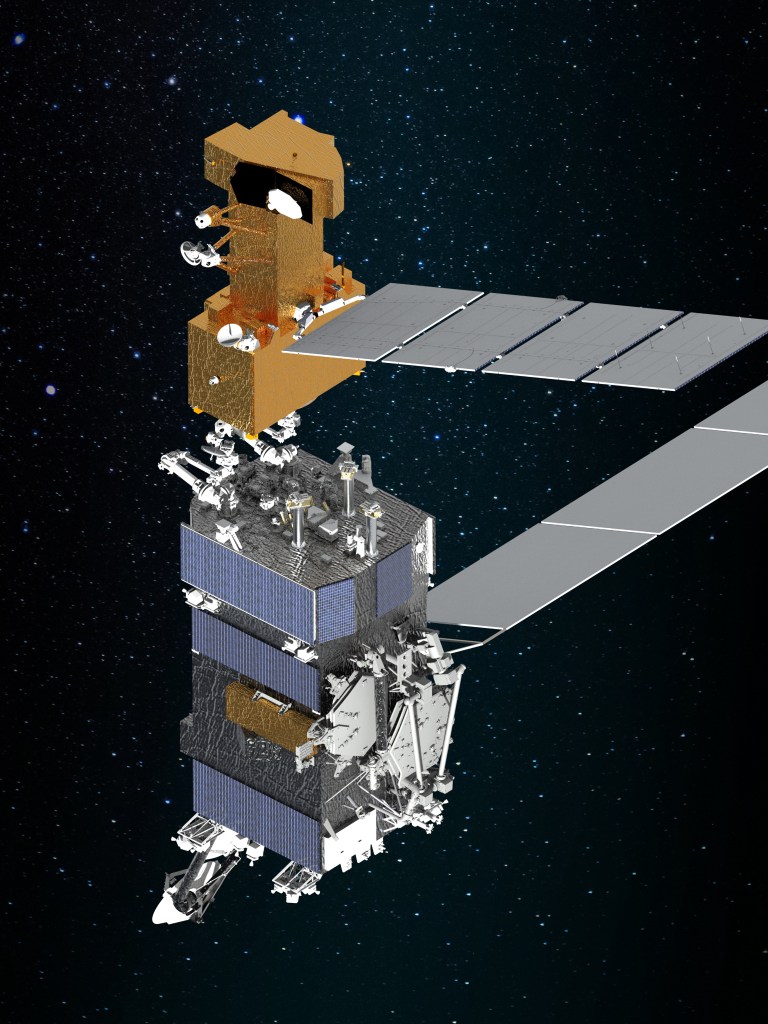
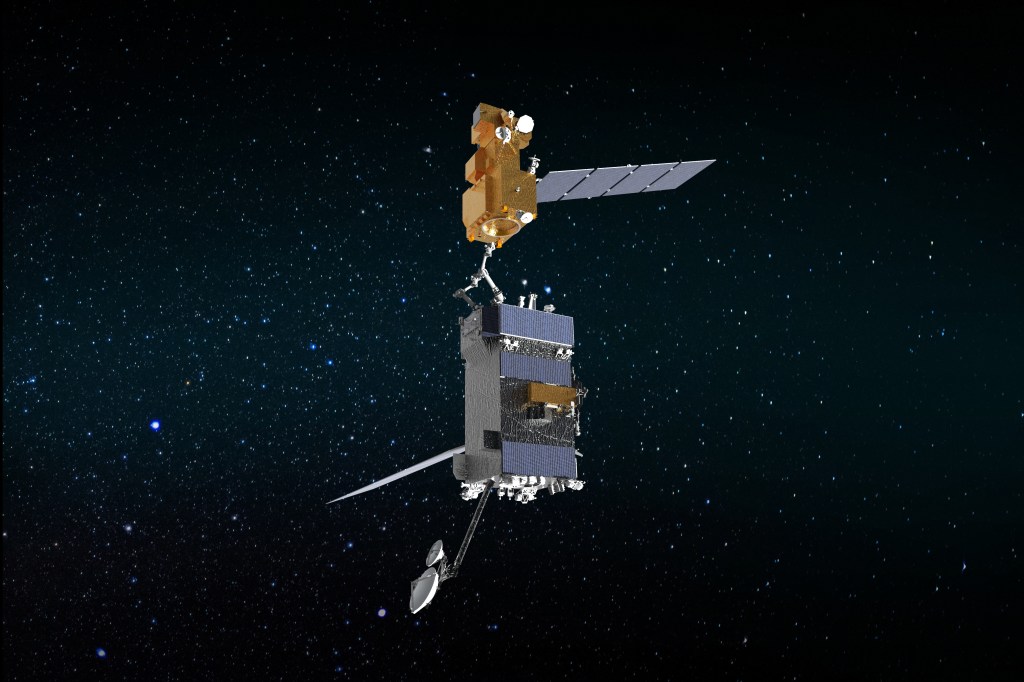
During its mission, the OSAM-1 servicer will rendezvous with, grasp, refuel and relocate a government-owned satellite to extend its life. However, OSAM-1’s effect will not end there.
The benefits are many. OSAM-1’s capabilities can give satellite operators new ways to manage their fleets more efficiently and derive more value from their initial investment. These capabilities could even help mitigate the looming issue of orbital debris.
Successfully completing this mission will demonstrate that servicing technologies are ready for incorporation into other NASA missions, including exploration and science ventures. NASA is also transferring OSAM-1 technologies to commercial entities to help jumpstart a new domestic servicing industry.
Space Infrastructure Dexterous Robot (SPIDER)
The OSAM-1 spacecraft will include an attached payload called Space Infrastructure Dexterous Robot (SPIDER).
SPIDER includes a lightweight 16-foot (5-meter) robotic arm, bringing the total number of robotic arms flying on OSAM-1 to three. Previously known as Dragonfly during the ground demonstration phase of the NASA Tipping Point partnership, SPIDER will assemble seven elements to form a functional 9-foot (3-meter) communications antenna. The robotically assembled antenna will demonstrate Ka-band transmission with a ground station.
The payload also will manufacture a 32-foot (10-meter) lightweight composite beam using technology developed by Tethers Unlimited of Bothell, Washington. The assembly and manufacturing element of the demonstration will verify the capability to construct large spacecraft structures in orbit.
SPIDER will help mature space technologies with many potential cross-cutting applications, including:
- Enabling new architectures and capabilities for a wide range of government and commercial missions
- Enabling In-space construction of large communications antennae and telescopes
- Eliminating volume limits imposed by rockets
- Replacing some astronaut extravehicular activity tasks with precision robotics
- Introducing the potential for longer mission durations enabled by planned or unplanned maintenance
Bringing OSAM-1 to Life
It takes years of testing, countless hours of design, and five new technologies to make robotic satellite servicing a reality. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of OSAM-1.
Servicing Technologies
1. AUTONOMOUS, REAL-TIME RELATIVE NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Sensors, algorithms and a processor join forces, allowing OSAM-1 to rendezvous safely with its client.
2. SERVICING AVIONICS
In addition to ingesting and crunching sensor data, these elements control OSAM-1’s rendezvous and robotic tasks.
3. DEXTEROUS ROBOTIC ARMS
Two nimble, maneuverable arms precisely execute servicing assignments. Software comes included.
4. ADVANCED TOOL DRIVE AND TOOLS
Sophisticated, multifunction tools are manufactured to execute each servicing task.
5. PROPELLANT TRANSFER SYSTEM
This system delivers measured amounts of fuel to the client at the right temperature, pressure and rate.
OSAM-1 News

Following an in-depth, independent project review, NASA has decided to discontinue the On-orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing 1 (OSAM-1) project…

Spacecraft Bus for Satellite Servicing Mission Arrives at NASA Goddard

NASA’s On-orbit Servicing, Assembly, and Manufacturing 1 (OSAM-1), a mission that will be the first to robotically refuel a satellite…
NASA Creates ISAM Consortium
NASA announced a new consortium focused on making in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing (ISAM) capabilities a routine part of space architectures and mission lifecycles.
Learn More about NASA Creates ISAM Consortium