Overview
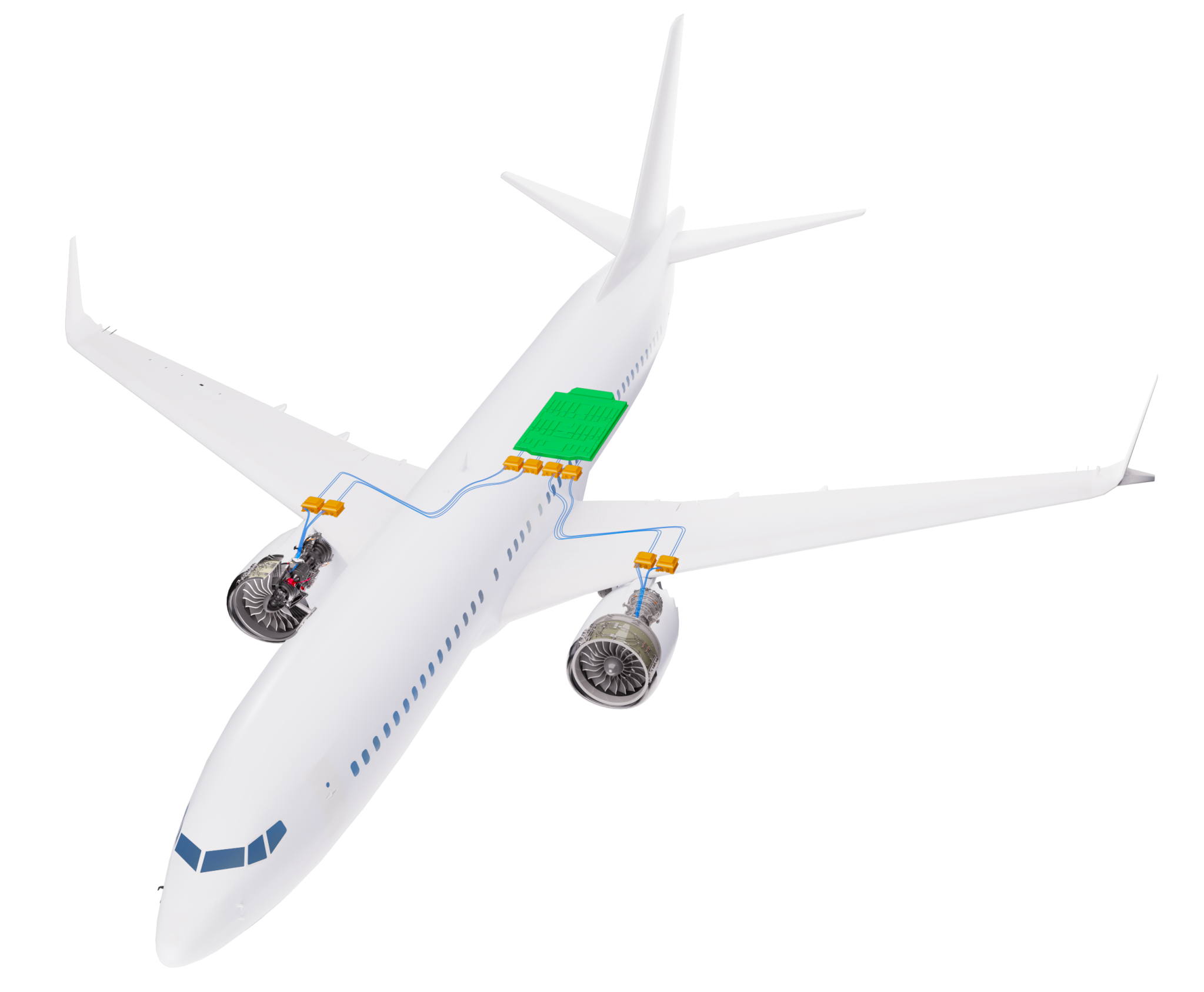
To keep future electrified aircraft systems operating safely at high altitudes, lightweight electrical insulation can help transport electricity while keeping cables cool.
While a key role for electrical machine insulation is to isolate different electrical power flows, thermal conductivity is equally impactful in the design process. Trapped heat increases the electrical resistance of conductors, resulting in reduced efficiency, greater fuel consumption, and a greater overall thermal management burden.
The Challenge
As electrical currents run through wires and cables, buildup of heat can negatively impact reliability and safety. Current state-of-the-art insulation does not effectively remove excess heat, which occurs when an electrical current flows in the cable and can have breakdowns that result in arcing through the air between two conductors. This creates a potential safety hazard, especially as electric aircraft operate at high altitudes with high-voltage electricity.
New Design Technologies
New electrical insulation development explores the use of fillers, such as boron nitride, to help make insulation thinner and more lightweight. These fillers offer high thermal conductivity, enabling better transfer of heat, and are electrically insulating to prevent electrical arcing events. Research and development will play a key role in improving safety measures and ensuring optimal performance as electric aircraft take flight.