Microstructural analysis is used extensively in failure investigations and supplements material performance tests such as environmental degradation studies and welding qualification testing. Our metallurgists routinely section and examine materials to understand their building blocks, from simple grain size to complex structures of a broad spectrum of metals. This understanding helps identify potential problems and give insight into the effects of processes such as welding and machining on a materials microstructure. Conventional metallographic techniques, supplemented by our fully equipped machining and fabrication facility, are used to prepare specimens for microstructural analysis using a research-grade optical metallograph and scanning electron microscope.
Fractography
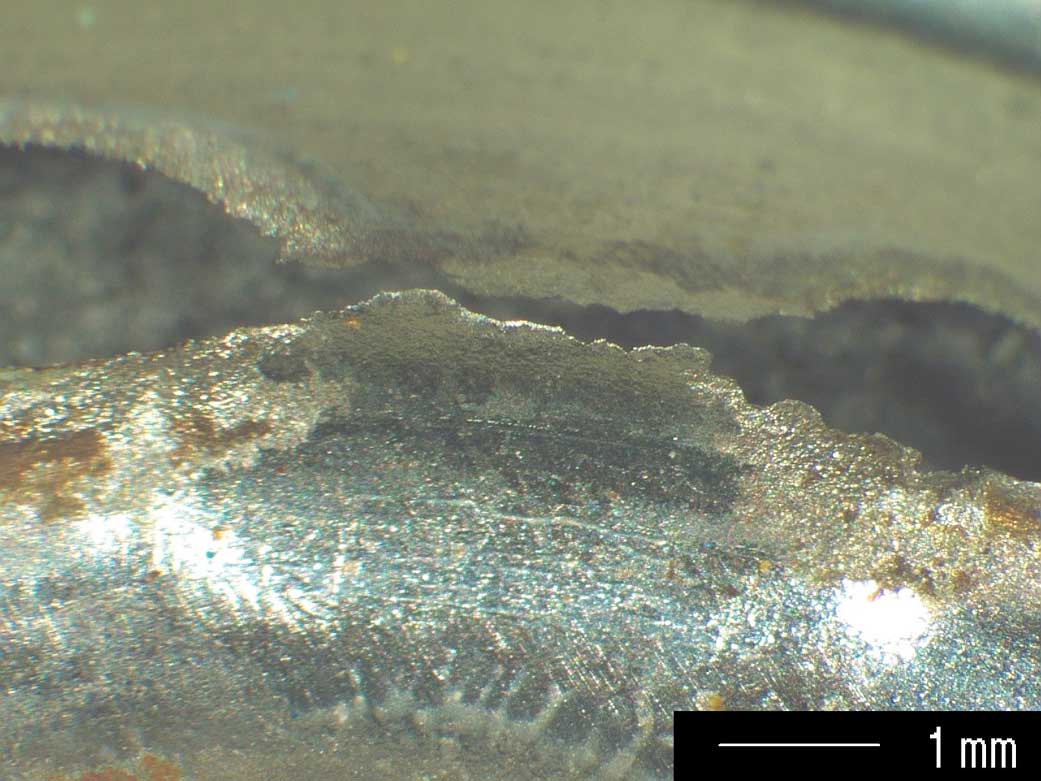
Fracture surfaces can reveal specific information about the conditions and cause of a fracture. An examination can determine information such as the location and nature of flaws including material or manufacturing defects, the crack initiation site and direction of propagation, and the type of stress and load direction that were applied. This information is fundamental to determining the cause of the fracture as part of a failure analysis.
Metallography
In support of failure analysis and materials evaluation, metallographic examination of the constitution and structure of metals and alloys can detect material microstructures, flaws, and abnormalities, which may be critical to determining metal failure and preventing future failures. Often a critical tool for characterizing the extent of pits and cracks in metal material, metallographic examination can also detect changes to metals due to welding, machining, heat treating, chemical exposure, environmental effects, etc.