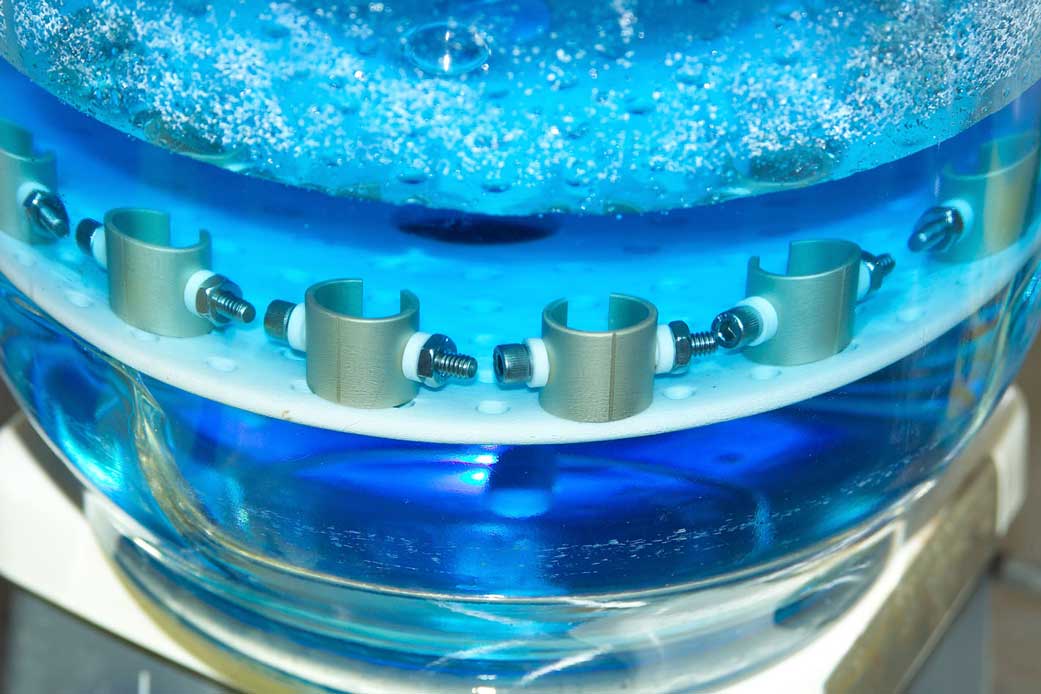
Supported by our in-house Materials Testing and Materials Flight Acceptance expertise, our team assess the compatibility of various materials including metal alloys, polymer composites, elastomers, and fabrics that are expected to come into contact with propellants and aerospace fluids. The use of devices that are not compatible with a liquid may damage the equipment and cause a leak that could result in property damage or personal injury. Our testing not only determines the compatibility of materials but can also provide data for hazards evaluation, failure analysis, and safe system design to name a few. Materials are evaluated for compatibility with oxidizers, propellants, and other hazardous fluids such as
- Aerozine 50,
- AF-M315E,
- Ammonia,
- Gaseous Oxygen (GOX),
- Hydrazine,
- Hydrogen Peroxide,
- Liquid Methane,
- Liquid Oxygen (LOX),
- Monomethylhydrazine (MMH),
- Nitrous Oxide,
- Nitrogen Tetroxide and mixed oxides of nitrogen,(MON-3 and others), and
- Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine.
Reactivity Assessment
We conduct testing to identify changes resulting from exposure to fluids that degrade either the material or the fluid or produce a reaction potentially causing a pressure increase in a closed system.
Material Degradation
Material degradation may be evaluated using mechanical testing, surface analysis, or optical and electron microscopy by our in-house materials testing group.
Fluid and Material Composition
Immersion testing can be performed at specified use temperatures or the standard temperatures of 30 and 71°C (303 and 344 K) followed by posttest analysis of the fluid and material for any changes in composition.