Today, at the 39th meeting of the International Civil Aviation Organization, 191 countries reached a global climate deal to reduce carbon emissions from aviation. At the same time, NASA is working to create new experimental aircraft that will demonstrate new “green aviation” technology intended to dramatically reduce fuel use, emissions and noise – with the goal of cutting emissions from the nation’s commercial aircraft fleet by more than 50 percent, while also reducing perceived noise levels near airports to one-half the level of the quietest aircraft flying today.
To that end, NASA recently awarded six-month contracts to four companies, who will each define the technical approach, schedule, and cost for one or more large-scale, subsonic X-plane concepts. These concepts are in support of NASA’s ultra-efficient subsonic transport research goals.
The companies are Aurora Flight Sciences Corporation of Manassas, VA; Dzyne Technologies Incorporated of Fairfax, VA; Lockheed Martin Aeronautics Company of Ft. Worth, TX; and The Boeing Company of Hazelwood, MO.
“Engaging these contractors now to gather this information will help us move forward efficiently and expeditiously when we’re ready to commit to building the X-planes themselves,” said Ed Waggoner, NASA’s Integrated Aviation Systems Program director.
Each company is to detail their specific X-plane system requirements for a piloted experimental aircraft capable of sustained, two to three hours of powered high subsonic flight, as well as conducting at least two research flight sorties per week over the course of a year-long program.
The requested information is to be built around a plan that would see the selected experimental aircraft eventually flying no later than 2021.
NASA’s return to flying large-scale X-plane technology demonstrators – a staple of its aeronautical research heritage – is part of New Aviation Horizons, an ambitious 10-year accelerated research plan developed and announced by NASA earlier this year.
The five X-plane concepts envisioned for possible further development and the contractor responsible for providing NASA with the required information include:
- Aurora Flight Sciences for the D8 “Double Bubble,” a twin-aisle, largely composite airliner in which the fuselage is shaped to provide lift – enabling smaller wings – and the jet engines are mounted atop the rear tail area, which takes advantage of the air flow over the aircraft to both improve engine efficiency and reduce noise in the cabin and on the ground below.
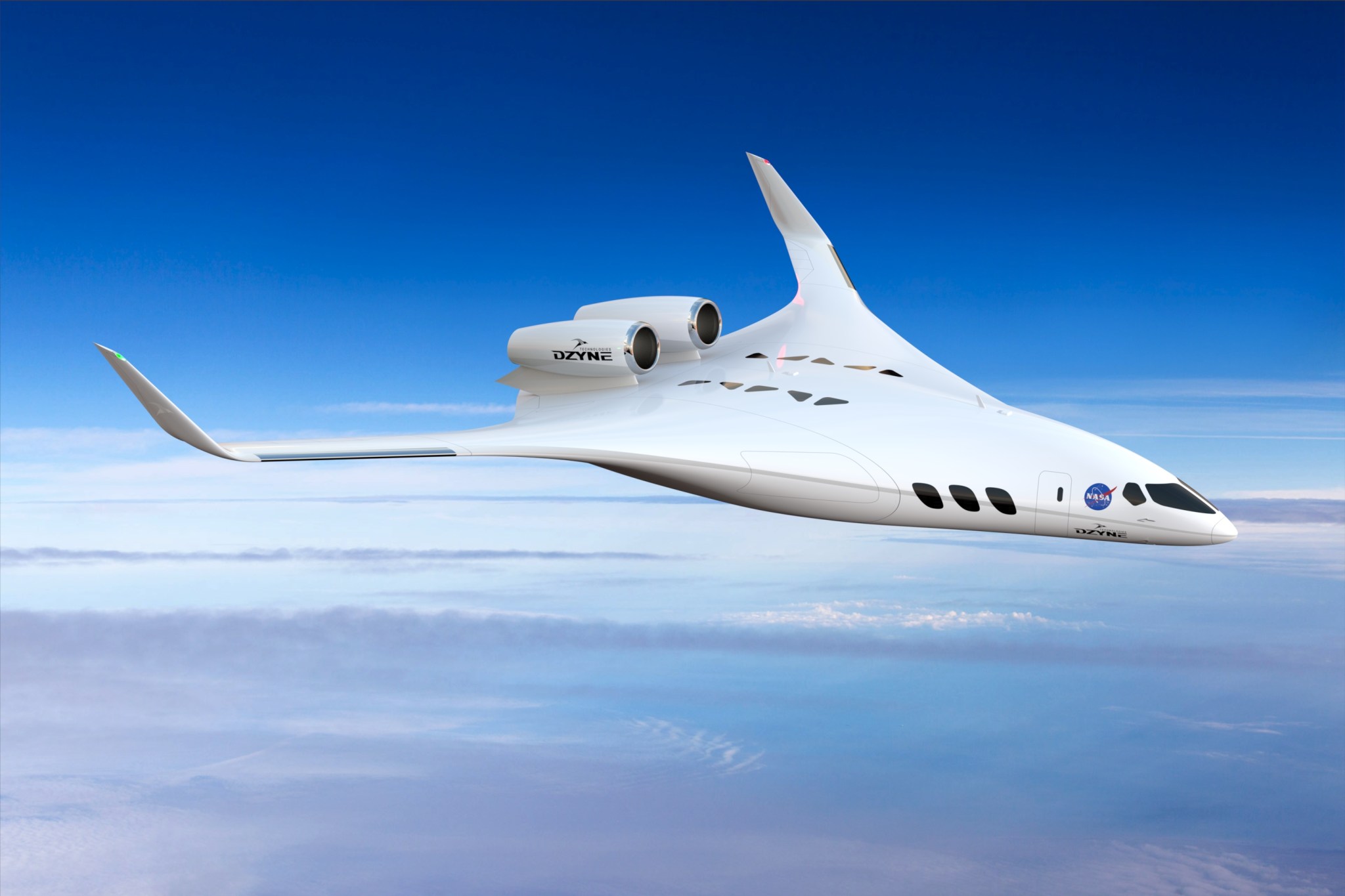
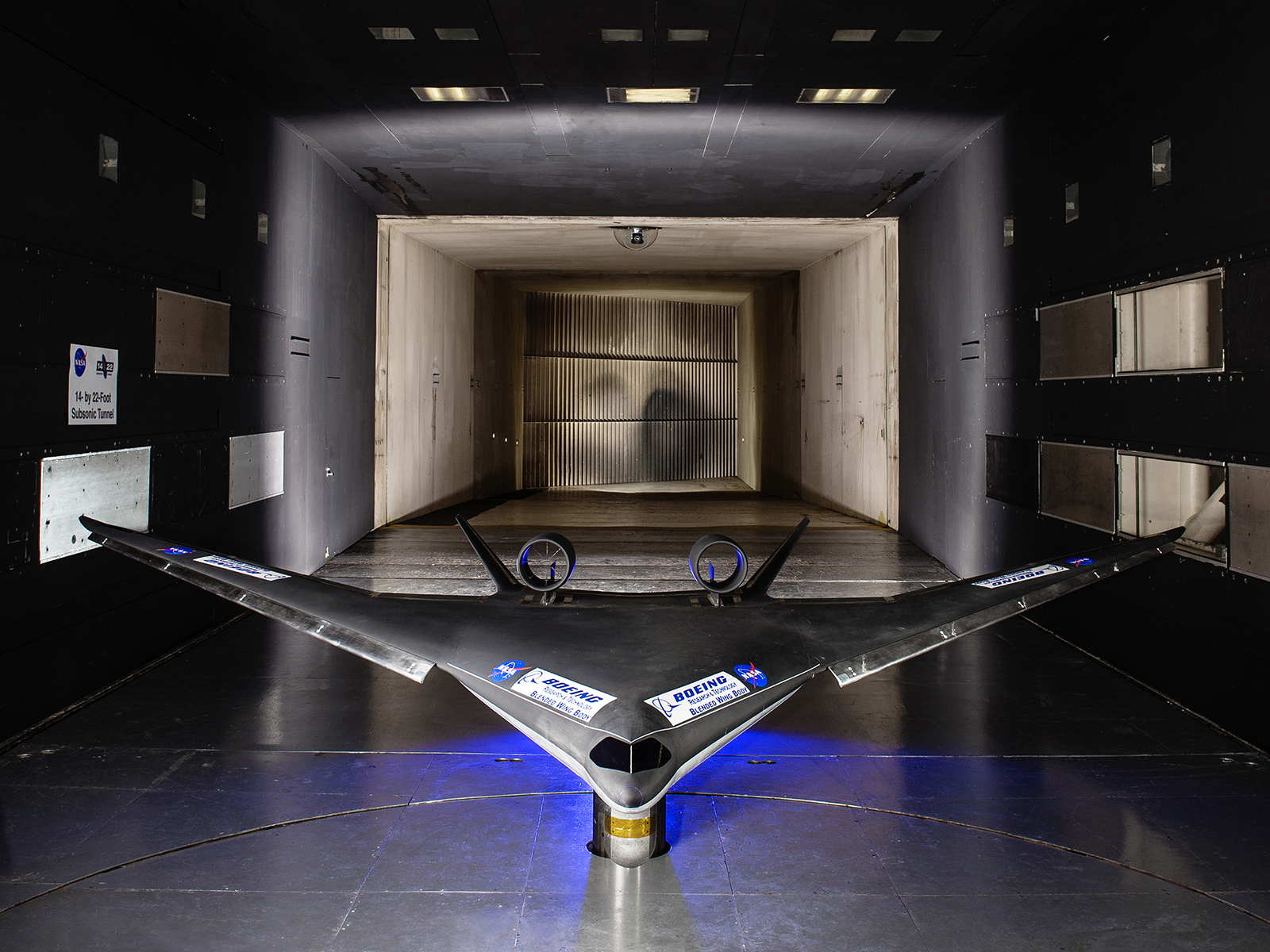
- Dzyne Technologies for a smaller regional jet-sized aircraft that features a blended wing body (BWB) design in which the lines of a traditional tube and wing airliner are shaped to become one continuous line in which the seam between the wing and fuselage is nearly indistinguishable. As an aerodynamic shape, this configuration increases lift and reduces drag.
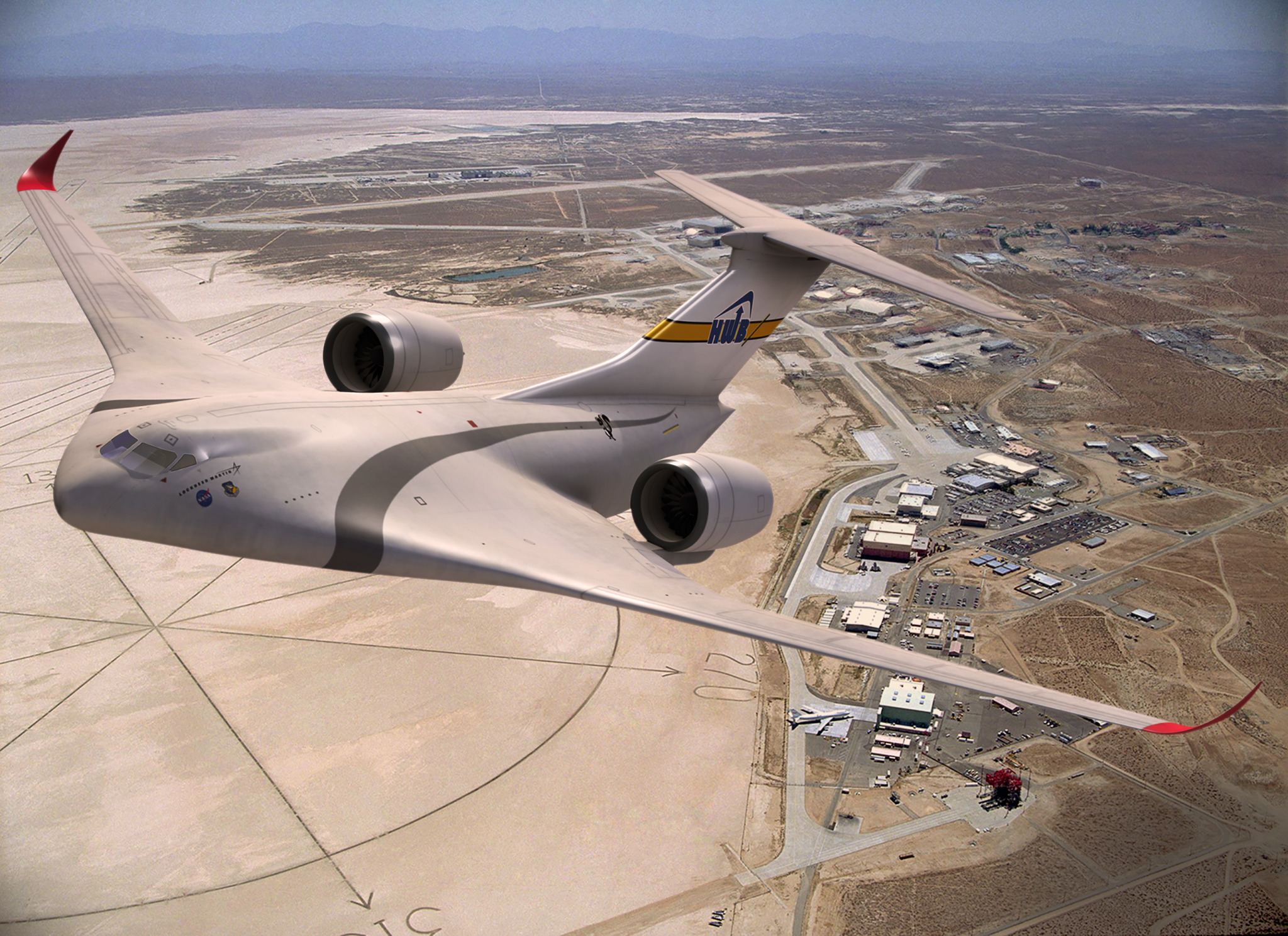
- Lockheed Martin for its Hybrid Wing Body, which includes features of the BWB on the forward part of the fuselage but has a more conventional looking T-shaped tail, with its jet engines mounted on the side of the hull but above the blended wing. Increased lift, reduced drag and quieter operations are all potential benefits.
- Boeing for both its BWB concept – versions of which the company has flight tested with its subscale X-48 program in partnership with NASA – and a Truss-Braced Wing concept, which features a very long, aerodynamically efficient wing that is held up on each side by a set of trusses connecting the fuselage to the wing. Otherwise the aircraft appears more conventional than the other X-plane concepts under consideration.
Preliminary design work already has begun on a half-scale X-plane called the Quiet Supersonic Technology, or QueSST, a piloted supersonic aircraft that generates a soft thump, rather than the disruptive boom currently associated with supersonic flight.
Work also is underway on the X-57 Maxwell, a general aviation-sized electric research airplane. Maxwell will fly for the first time in early 2018 and demonstrate battery powered, distributed electric propulsion. Transport-sized electric aircraft could reduce energy use by more than 60 percent and harmful emissions by more than 90 percent. This was the first project to get an X-plane number designation in a decade.
NASA’s other green aviation initiatives include reducing airline emissions and flight delays. Working in partnership with airlines and air traffic controllers at the Charlotte Douglas International Airport in North Carolina, NASA is beginning the first-of-a-kind demonstration of new technologies that coordinate operational schedules for aircraft arrivals, departures, and taxiing.