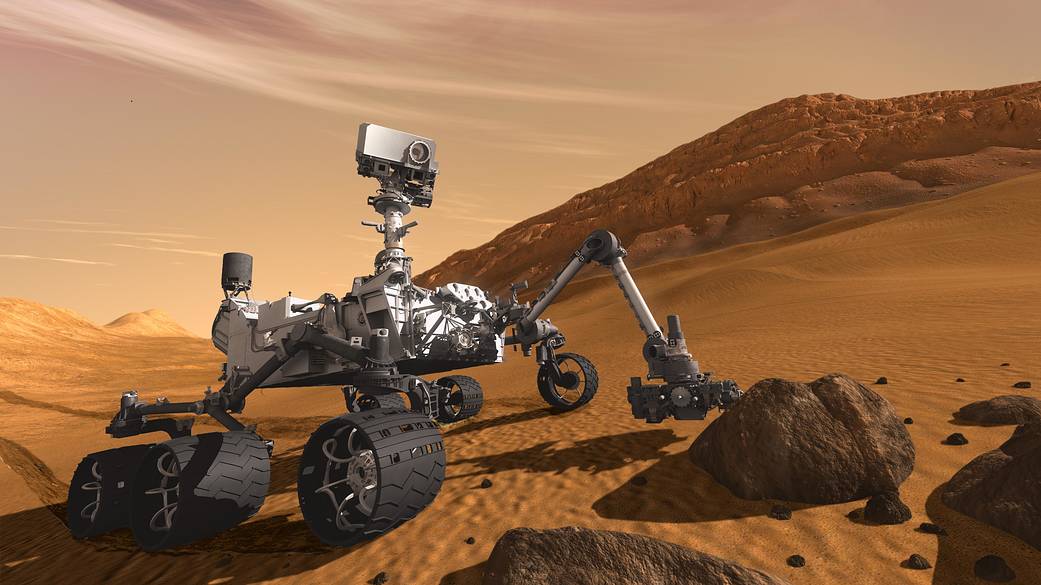
Ames’ Involvement in Mars Science Laboratory / Curiosity
NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley made key contributions both to the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission and the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter mission.
TODAY
45
Active NASA Astronauts
08
Days Until Next Crewed Mission
Curiosity, carrying laboratory instruments to analyze samples of rocks, soil and atmosphere, is investigating whether Mars has ever offered environmental conditions favorable for microbial life. Ames is contributing to this exciting mission in a variety of ways.
Science
- CheMin: Ames is the lead for the Chemical and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument which will identify and quantify the minerals in Martian rocks and soils.
Ames is also support other science instruments on Curiosity, including:
- ChemCam: Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) is a rock-zapping laser instrument that observes the resulting flash through a telescope to identify the chemical elements in the target.
- SAM: The Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument has three laboratory tools for analyzing gases pulled from rocks and soil samples, as well as from the Martian atmosphere.
- REMS: The Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS) will provide daily weather reports from the Red Planet using a suite of meteorological instruments.
Entry, Descent and Landing
- Arc Jet testing: The MSL heat shield was tested at Ames’ Arc Jet Complex, which reproduces heating and pressure conditions similar to those experienced by spacecraft during atmospheric re-entry.
- Parachute testing: Wind tunnel engineers conducted a full-scale MSL parachute deployment, small-scale verification tests and supersonic tests to study the interaction between the MSL Capsule and parachute during atmospheric entry.
- PICA: Researchers invented the unique thermal protection system consisting of tiles made of Phenolic Impregnated Carbon Ablator (PICA) that the MSL spacecraft will use to safely reach the surface of the Red Planet.
- MEDLI: The Mars Science Laboratory Entry, Descent, and Landing Instrument (MEDLI) contains multiple sophisticated temperature sensors to measure atmospheric conditions and performance of the capsule’s heat shield.†li>
Operations
- MSLICE: Engineers developed the Mars Science InterfaCE (MSLICE) software tool in collaboration with engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory to plan the actions of the Mars rover and maximize scientific research.
- Antares: Ames engineers and computer scientists in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, Calif., and JPL developed visualization and simulation software to plan and generate command sequences for the rover science cameras.
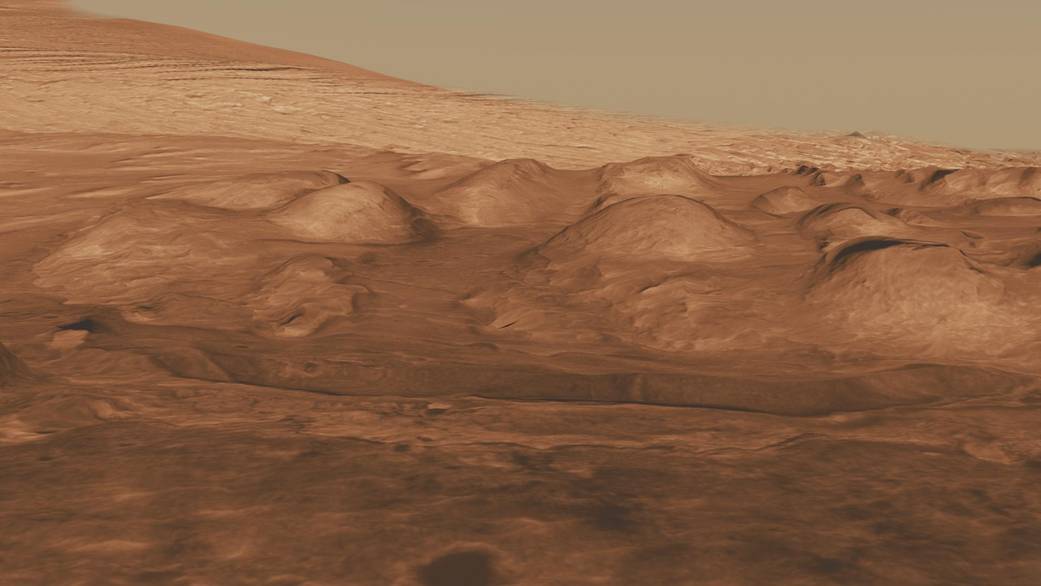

This oblique view of the lower mound in Gale Crater shows layers of rock that preserve a record of environments on Mars. Here, orbiting instruments have detected signatures of both clay minerals and sulfate salts, with more clay minerals apparent in the foreground of this image and fewer in higher layers.