Exploration Technology Projects
The Exploration Technology Directorate leads and supports NASA projects across all mission areas – Human Exploration, Aeronautics, Earth and Space Science, and Technology. The following are current projects.

ARMADAS
The Automated Reconfigurable Mission Adaptive Digital Assembly Systems (ARMADAS) project is developing modular space systems infrastructure with distributed robotics for autonomous in-space servicing, assembly, and maintenance (ISAM) of instruments, habitats, support structures, and more.

ASRS / C3RS
The Aviation Safety Reporting System (ASRS) and the Confidential Close Call Reporting System (C3RS) are voluntary, confidential, non-punitive safety reporting systems, operated by NASA in partnership with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) respectively.

Astrobee
NASA’s free-flying robotic system on the International Space Station (ISS) that serves as a research platform that can be outfitted and programmed to carry out experiments in microgravity, helping us learn more about how robotics can benefit astronauts in space.
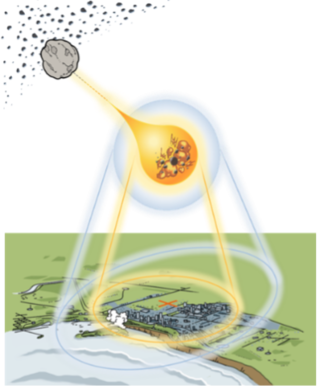
ATAP
The Asteroid Threat Assessment Project (ATAP) produces quantitative estimates of asteroid impact risk through a combination of expertise in planetary science, entry systems, high-fidelity modeling and simulation, and engineering risk assessment.

Dragonfly EDL
The Dragonfly mission will send a mobile robotic rotorcraft lander to Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, to study prebiotic chemistry and habitability at various locations. The Entry, Descent, and Landing (EDL) element includes aerothermal analysis and thermal protection system (TPS) sizing for entry into Titan’s atmosphere.
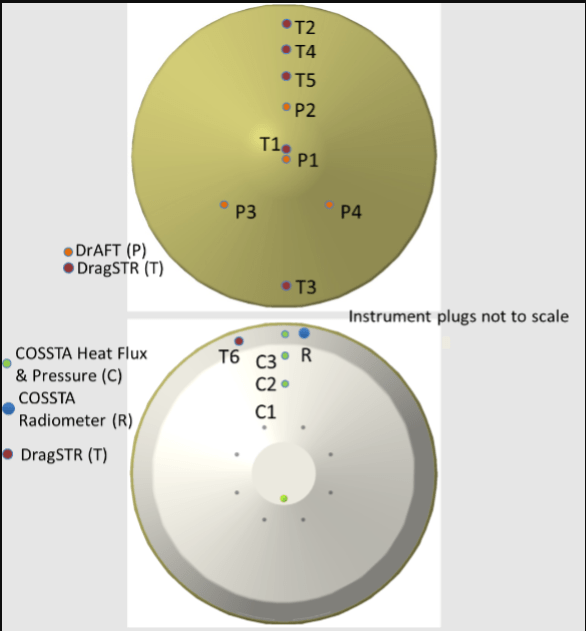
DrEAM
DrEAM (Dragonfly Entry Aerosciences Measurements) is the instrumentation project that will measure pressures, temperatures, and heat fluxes on the Dragonfly entry vehicle as it passes through Titan’s atmosphere.

DSA
The Distributed Spacecraft Autonomy (DSA) project is maturing technology required for larger, autonomous spacecraft constellations through orbital deployments and simulation studies. DSA software on the Starling mission will demonstrate command and control of distributed spacecraft as a single entity.

HECC
The High-End Computing Capability (HECC) project supports scientists and engineers in effectively utilizing high-end computing resources for large-scale modeling, simulation, machine learning, and data analysis to advance scientific understanding and enhance NASA mission achievements.

ISAAC
Integrated System for Autonomous and Adaptive Caretaking (ISAAC) is building software for caretaking of exploration vehicles, focusing on uncrewed phases which enables autonomous operation of the integrated system consisting of intra-vehicular robots (IVR) and other vehicle subsystems.

LOFTID
NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) successfully demonstrated a 6-meter inflatable aeroshell technology, a type of deployable heat shield for atmospheric re-entry.

MAS
Mission Assurance Systems (MAS) employs human-centered design processes to research, design, develop, test, and maintain a suite of interconnected software solutions supporting engineering, safety, operations, and support teams across multiple centers, programs, and projects such as Common Exploration Systems Development (CESD), Artemis Campaign Development ACD), and International Space Station (ISS).
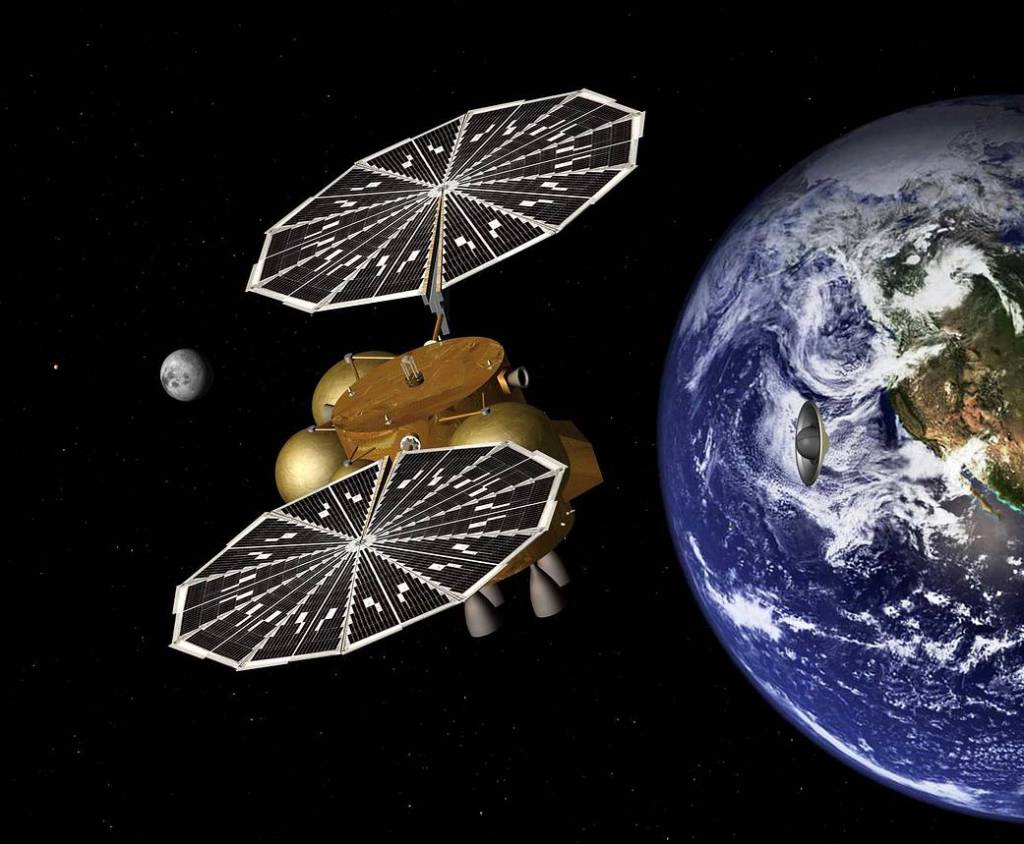

MSR EES Heat Shield
The Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission will return Martian rocks, soils and atmosphere to Earth for analysis. The MSR Earth Entry System (EES) carries the samples through Earth’s atmosphere to the ground. We are developing the heat shield and providing design and analysis support for MSR EES.
NTTS
NASA Technology Transfer System (NTTS) is an enterprise web framework for streamlining the Agency’s technology transfer process, including reporting new technologies, protecting intellectual property, and commercializing technologies through licenses, software releases, spinoffs, partnerships, and success stories.
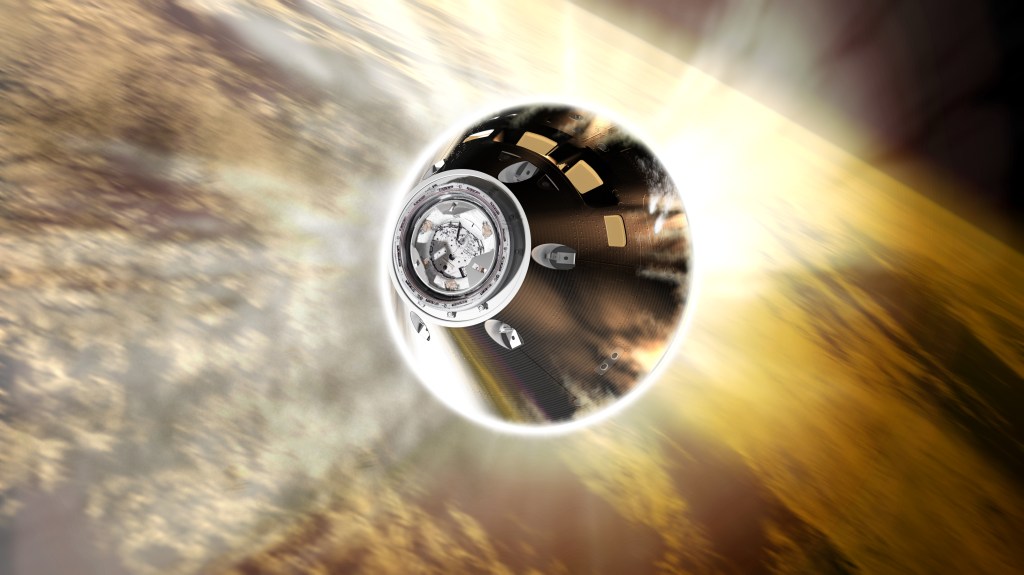

Orion TPS
The TS Division provides nearly all Orion TPS arc jet testing, supports thermal analysis, executes post-flight heat shield sampling, provides at-sea support for Orion recovery, and hosts Orion TPS team leadership personnel. Since 2005, the division has been the center of gravity for development of both Orion's ablative heat shield and the spacecraft's insulative tiles.

QuAIL
NASA’s Quantum Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (QuAIL) is the agency’s hub for assessing and advancing the potential of quantum computing to impact computational challenges and enable more ambitious aeronautics, Earth, and space missions in future decades.

SLS Analysis
The Space Launch System (SLS) is NASA’s super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle, designed to launch the crewed Orion spacecraft to the Moon. For SLS, we are conducting aerodynamics and acoustics wind tunnel testing, risk analyses and assessments, and high-fidelity computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations.

Starling 1.5
Starling 1.5 is an extension to the Starling mission, which is flying four Cubesats in low Earth orbit (LEO). The goal of Starling 1.5 is to demonstrate enhanced space traffic management using the Starling swarm and the SpaceX Starlink constellation.

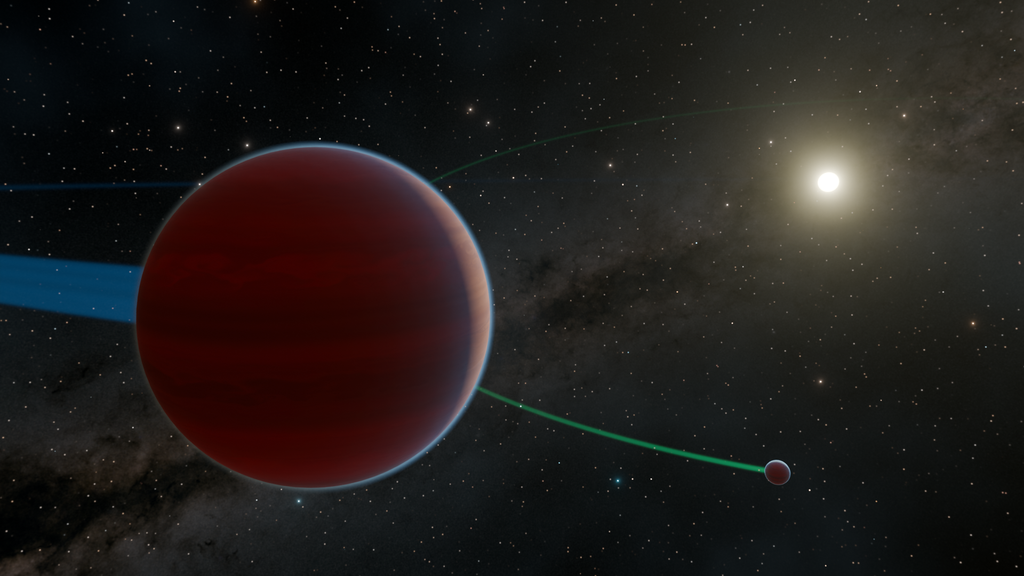
TESS SPOC
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) Science Processing Operations Center (SPOC) processes the raw pixels, extracts photometry and astrometry for each target star, identifies and removes systematic errors, flags transiting planet signatures, and performs a suite of diagnostic tests in order to help detect exoplanets.

VIPER Software
Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) will land at the Moon’s South Pole in late 2024 to find and characterize the water ice that could sustain human exploration on the Moon and Mars. For VIPER, we lead operating system and Ground Data System software development.