Integrated Vehicle Performance
Integrated vehicle performance is paramount for human spaceflight as it ensures seamless coordination and optimal function of various spacecraft components and mission elements, guaranteeing the safety, efficiency, and success of space missions. With expertise and capabilities in mission design, detailed end-to-end trajectory optimization, high performance computing and data analytics, mission management product analysis, metrics production, and mission trades, Johnson Space Center (JSC) is shaping the future of space exploration missions. JSC experts play key roles in the development and analysis of human spaceflight architectures, mission plans, spacecraft functional decomposition, and mission design and analysis across the exo-LEO human spaceflight portfolio. NASA JSC invites our partners to leverage our cutting-edge capabilities in integrated vehicle performance for diverse human spaceflight missions.
Exploration Mission Data Analytics
The Exploration Mission Planning Office (EMPO) provides high performance computing and data analytics expertise for enhanced data science and production capabilities.
- Trajectory database and post-processing tooling development
- Analysis and production of mission management products and mission metrics
- High performance computing improvements and data management
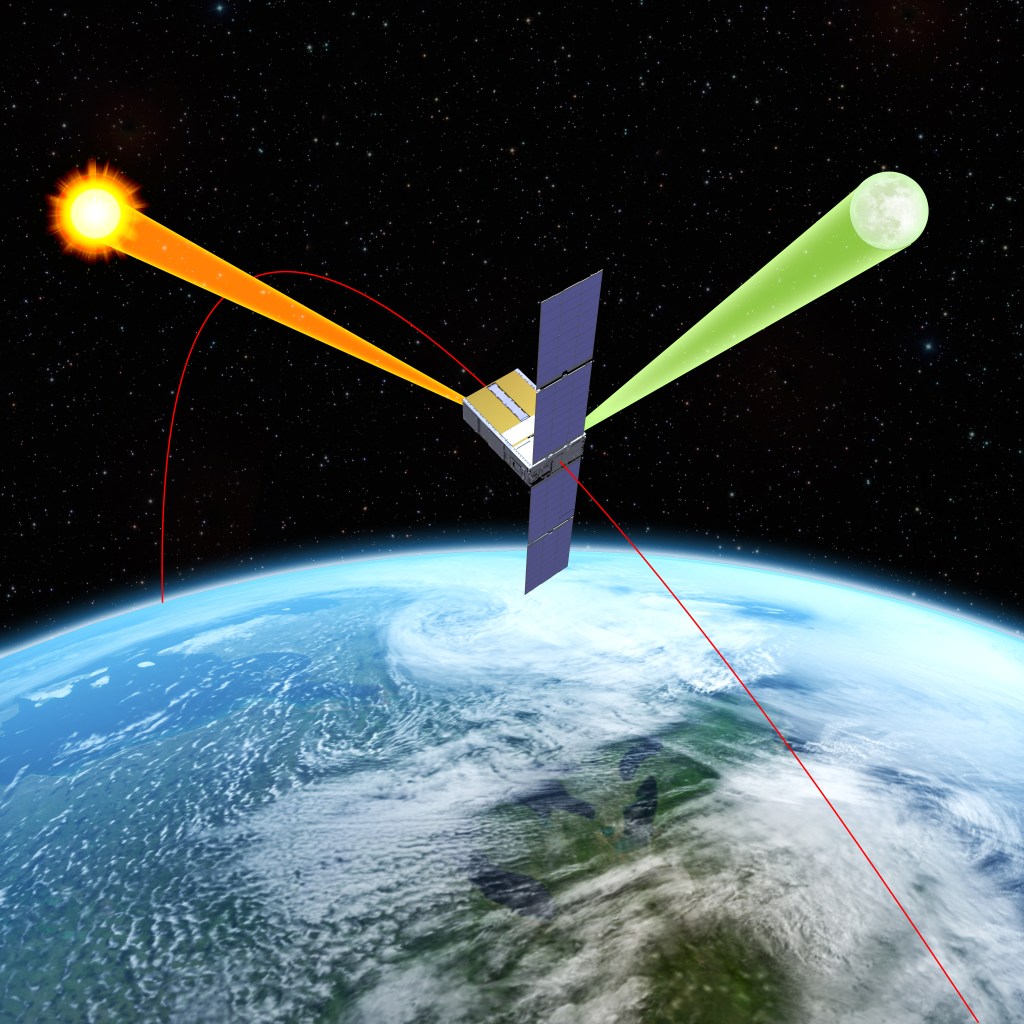
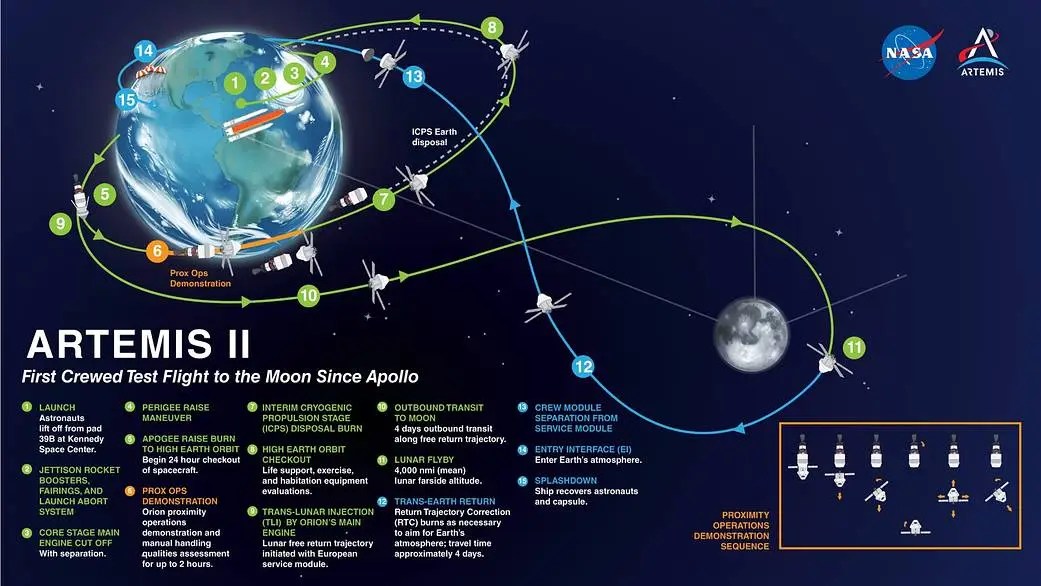
Astrodynamics, Mission Design, and Integrated Vehicle Performance
NASA JSC analyzes and designs optimal spacecraft orbits and trajectories for human spaceflight missions.
NASA JSC provides design analysis and evaluation of mission concepts, vehicle flight performance capabilities and requirements, and preliminary guidance, navigation, and control (GN&C) requirements. This includes flight envelopes and trajectories for ascent, targeting and profiles for on-orbit rendezvous, interplanetary trajectories, and entry through landing trajectory designs. JSC can optimize end-to-end trajectories and vehicle performance for Low Earth Orbit, cislunar, and planetary missions.
Exploration Mission Design, Integration, and Analysis
The Exploration Mission Planning Office (EMPO) provides Agency leadership for the development and analysis of human spaceflight architectures, mission plans, and spacecraft and surface system definitions. EMPO integrates mission design and planning from concept through transition to the flight operations phase. They develop and recommend near term mission options reflecting the capabilities of the program elements and provide iterative mission planning to respond to actual constraints, priorities, and contingency needs.
- Mission design, integration, and analysis across the exo-LEO human spaceflight portfolio
- Establishing mission objectives, ground rules and constraints
- Conducting mission trades for conditions, objectives, and design solutions
- Identification of cross-program constraints and definition of mission achievability
- Landing site identification, analysis, and selection
- Mission availability assessments
- End-to-end trajectory design, optimization, and cross-agency implementation of mission design
- Coordination, integration and analysis of cross-program design constraints, product deliveries, and flight development