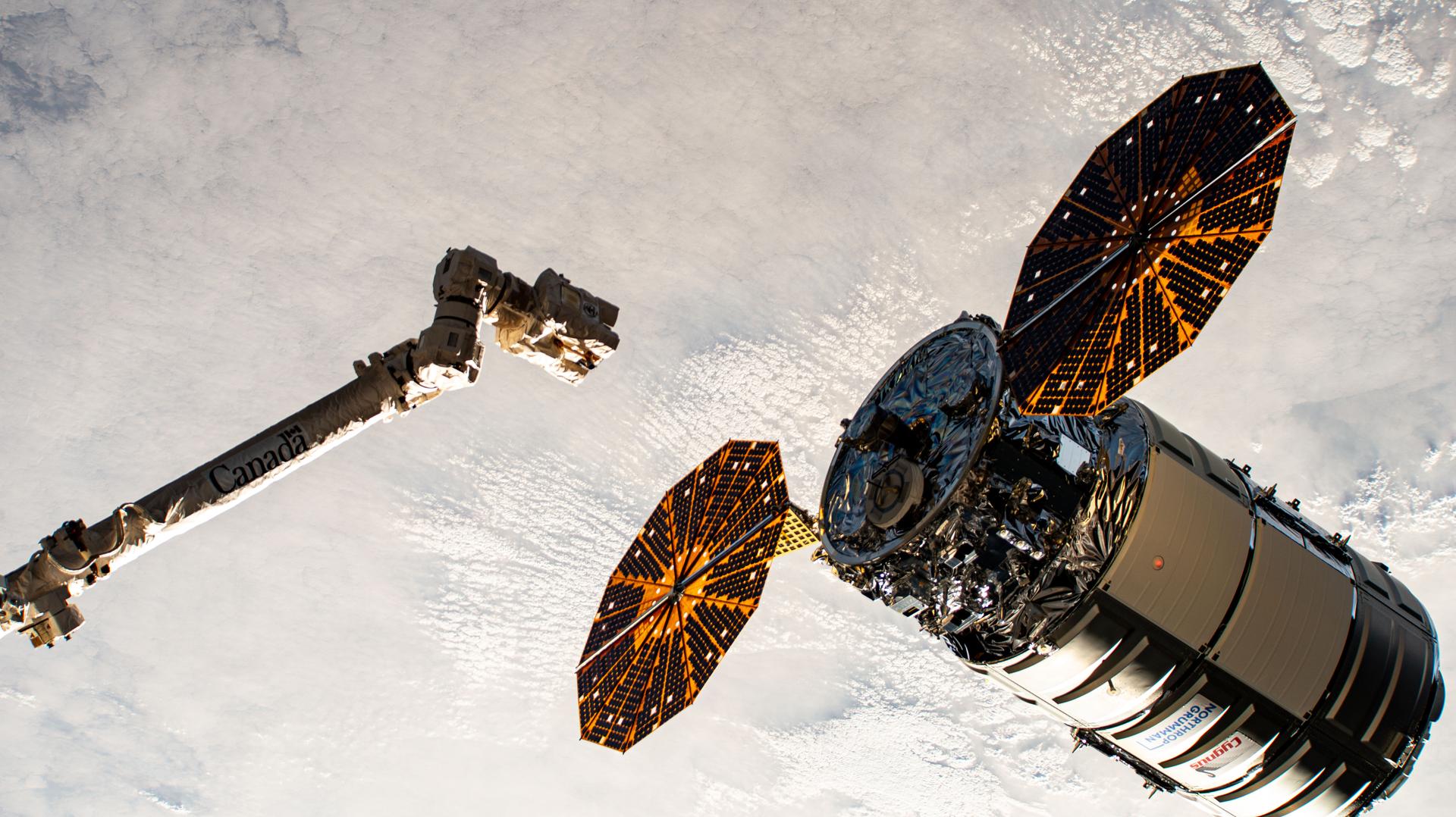
NASA’s Northrop Grumman Commercial Resupply Services 23, or Northrop Grumman CRS-23, will deliver more than 11,000 pounds of science and supplies to the International Space Station. This mission will be the first flight of the Cygnus XL, the larger, more cargo-capable version of the company’s solar-powered spacecraft.
The Cygnus XL will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Following arrival, astronauts aboard the space station will use the Canadarm2 to grapple Cygnus XL before robotically installing the spacecraft to the Unity module’s Earth-facing port for cargo unloading. Stream live launch and arrival coverage on NASA+, Amazon Prime, YouTube.
Mission Infographics

Mission Hardware
IDA Planar Reflector – This is a reflective element used by visiting spacecraft during docking. The spacecraft bounces a laser off the reflector to compute relative range, velocity, and attitude on approach to the International Space Station. Due to degradation found on the installed reflector, this unit will launch to support a future spacewalk to replace the damaged reflector.
Urine Processing Assembly (UPA) Distillation Assembly – The urine processor on the space station uses filtration and distillation to separate water from wastewater to produce potable water. This unit is launching as a spare.
Reactor Health Sensor – Part of the Environmental Control and Life Support System – Water Processing Assembly, includes two sensors with inlet and outlet ports to measure reactor health. This unit is being launched as a spare.
Pressure Management Device – This is an intravehicular activity system for performing pressurization and depressurization of the space station vestibules between the space station hatch and the hatch of a visiting spacecraft or other module, like the NanoRacks Airlock. During depressurization, most of the air will be added to the space station cabin air to save the valuable resource.
Air Selector Valve – This electro-mechanical assembly is used to direct airflow through the Carbon Dioxide Removal Assembly. Two units are launching as spares.
Major Constituent Analyzer Mass Spectrometer Assembly – This assembly monitors the partial pressure levels of nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, methane, water vapor, and carbon dioxide aboard station. This unit is launching as a contingency spare.
Major Constituent Analyzer Mass Sample/Series Pump Assembly – This contains plumbing and a pair of solenoid valves to direct sample gas flow to either of the redundant sample pumps. It draws sample gas from the space station’s atmosphere into the analyzer. This unit is launching as a contingency spare.
Major Constituent Analyzer Sample Distribution Assembly – This isolates the gas sample going to the Mass Spectrometer Assembly. The purpose is to distribute gas samples throughout the analyzer. This unit is launching as a contingency spare.
Charcoal Bed – The bed allows the Trace Contaminant Control System to remove high molecular weight contaminants from the station’s atmosphere. This unit is launching as a spare.
Common Cabin Air Assembly Heat Exchanger – This assembly controls cabin air temperature, humidity, and airflow aboard the space station. This unit is launching as a spare.
Sequential Shunt Unit – This regulates the solar array wing voltage when experiencing high levels of direct sunlight; in doing so, it provides usable power to the station’s primary power system. This unit is launching as a spare.
Solid State Lighting Assembly – This is a specialized internal lighting assembly aboard station. NASA will use one lighting assembly to replace a failed unit and will keep the others as spares.
Remote Power Control Module Type V – This module distributes 120V/DC electrical power and provides current-limiting and fault protection to secondary loads aboard the orbiting laboratory. This module is launching as a spare.
Treadmill Isolator Assembly – The Upper, X, Y, and Z Isolator Assemblies are launching as spares for the space station’s treadmill, where they work together to reduce vibration and force transfer when astronauts are running.
Pump Fan Motor Controller – The controller is an electronic controller to modulate the power to the motor windings, which are coils of conductive wire that are wrapped around its core carrying electric current to drive the motor. Windings are commonly used in household appliances, cars (power steering), pumps, and more.
Quick Don Mask Assembly – This mask is used by the crew, along with the Pre-Breath Assembly, in emergency situations. This unit is launching to replace a unit aboard station.
Anomaly Gas Analyzer – This analyzer senses various gases, like oxygen, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, ammonia, and others, along with cabin pressure, water vapor and temperature. Two units are launching as an upgrade to the current analyzer system used on board.
Nitrogen, Oxygen Resupply Maintenance Kit – One tank of nitrogen and one tank of oxygen used for gas replenishment aboard the space station are launching to maintain gas reserves.
Crew and Equipment Translation Aid Luminaire – This is a lighting unit used aboard station to illuminate the astronauts’ equipment cart and surrounding work areas during spacewalks.