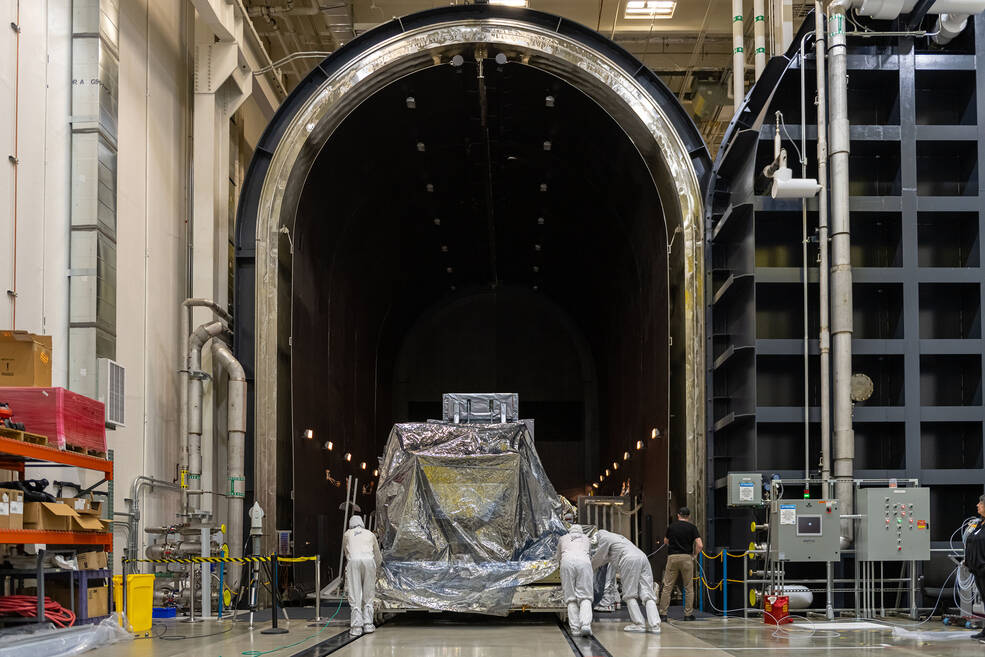
A team of engineers and technicians at Ball Aerospace, one of the industry partners for NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, and NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, have finished assembling the spacecraft’s giant camera. Called the Wide Field Instrument (WFI), this state-of-the-art tool will enable astronomers to explore the cosmos from the outskirts of our solar system to the edge of the observable universe.
“The year-long integration effort culminates in the instrument’s first baseline performance testing, where we turn on the instrument to ensure it’s working as expected,” said Mary Walker, Roman’s WFI instrument manager at Goddard. “Now the team is ready to take the instrument through key environmental testing to show it can withstand the harsh conditions of launch and in space.”
The Ball team provided four components for the WFI: the stable optical structure, element wheel assembly, thermal management system, and alignment compensation mechanism. The Goddard team provided the critical optical elements, focal plane system, relative calibration system, and the instrument command and data handling electronics. Then engineers from both teams put all these building blocks together in a clean room in Boulder, Colorado, mechanically and electrically integrating the components into one system. Now, the team will complete full environmental testing in space-like conditions before delivering the WFI to Goddard in summer 2024. Once there, it will join other observatory systems for integration and testing, as the mission gets ready to launch no later than May 2027.
The WFI is a 288-megapixel infrared camera that will give Roman the same angular resolution as the Hubble Space Telescope but with at least 100 times Hubble’s field of view. Its sweeping cosmic surveys will help scientists discover new and uniquely detailed information about planets beyond our solar system, untangle mysteries like dark energy, and map how matter is structured and distributed throughout the cosmos. The mission’s broad, crisp view will produce an extraordinary resource for a wide range of additional investigations.
“Overall, Roman’s camera greatly exceeds the mission’s performance requirements, including the operational capabilities of the camera detectors,” said Julie McEnery, Roman’s project scientist at Goddard. “So now we get to explore how much better Roman’s surveys will be, and what we’ll be able to do with the extra scientific riches they produce.”
For more information about the Roman Space Telescope, visit: roman.gsfc.nasa.gov or www.nasa.gov/roman. To virtually tour an interactive version of the telescope, visit: https://roman.gsfc.nasa.gov/interactive/.
By Ashley Balzer
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
301-286-1940