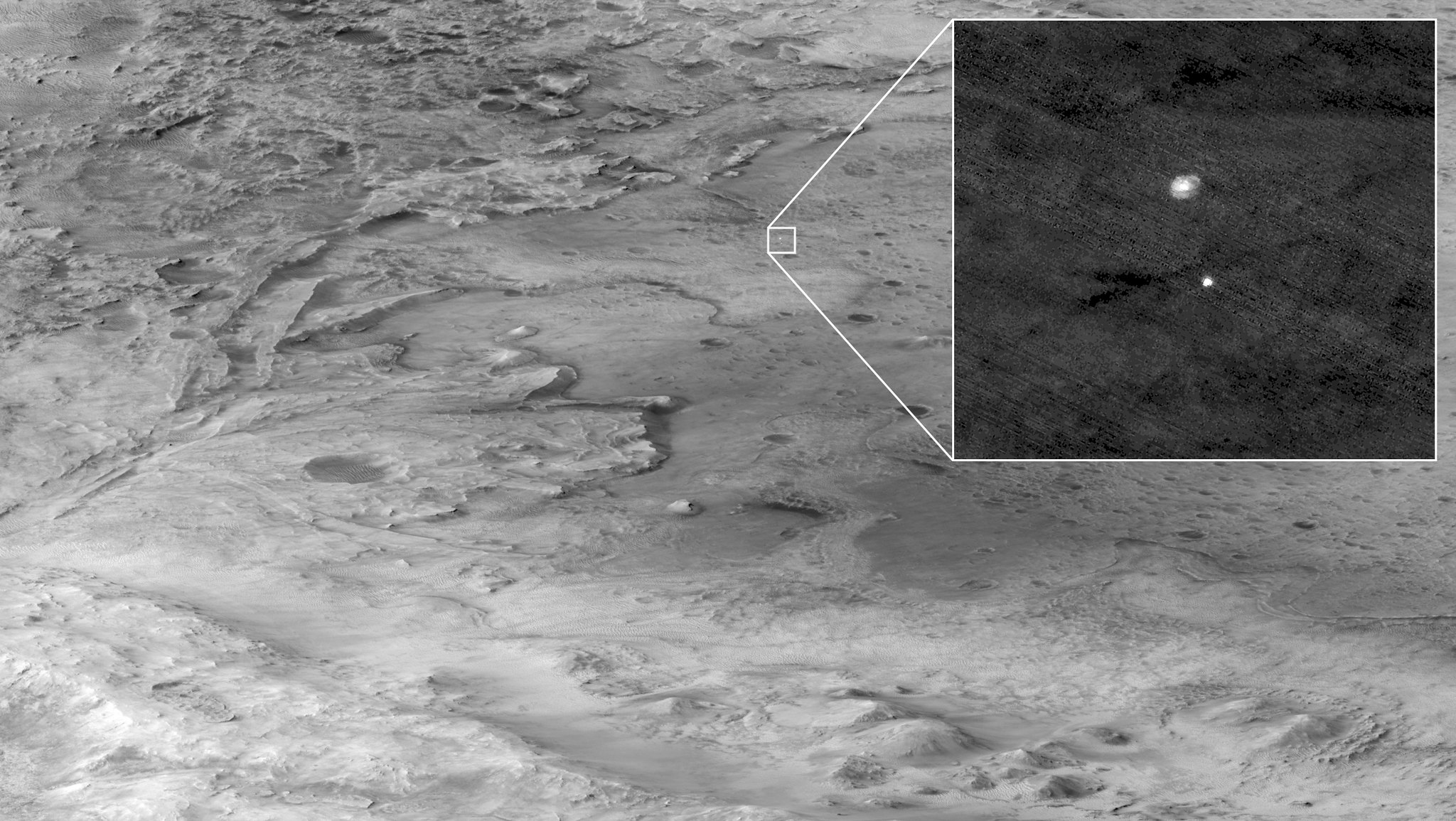
Mesas and dunes stand out in the view snapped by HiRISE, one of the imagers aboard the agency’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
After nearly 20 years at the Red Planet, NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has snapped its 100,000th image of the surface with its HiRISE camera. Short for High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment, HiRISE is the instrument the mission relies on for high-resolution images of features ranging from impact craters, sand dunes, and ice deposits to potential landing sites. Those images, in turn, help improve our understanding of Mars and prepare for NASA’s future human missions there.
Captured Oct. 7, this milestone image from the spacecraft shows mesas and dunes within Syrtis Major, a region about 50 miles (80 kilometers) southeast of Jezero Crater, which NASA’s Perseverance rover is exploring. Scientists are analyzing the image to better understand the source of windblown sand that gets trapped in the region’s landscape, eventually forming dunes.
“HiRISE hasn’t just discovered how different the Martian surface is from Earth, it’s also shown us how that surface changes over time,” said MRO’s project scientist, Leslie Tamppari of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “We’ve seen dune fields marching along with the wind and avalanches careening down steep slopes.”
The subject of the 100,000th image was recommended by a high school student through the HiWish site, where anyone can suggest parts of the planet to study. Team members at University of Arizona in Tucson, which operates the camera, also make 3D models of HiRISE imagery so that viewers can experience virtual flyover videos.
“Rapid data releases, as well as imaging targets suggested by the broader science community and public, have been a hallmark of HiRISE,” said the camera’s principal investigator, Shane Byrne of the University of Arizona in Tucson. “One hundred thousand images just like this one have made Mars more familiar and accessible for everyone.”
More about MRO
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California manages MRO for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington as part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program portfolio. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver built MRO and supports its operations.
The University of Arizona in Tucson operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information, visit:
https://science.nasa.gov/mission/mars-reconnaissance-orbiter
News Media Contacts
Andrew Good
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-2433
andrew.c.good@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Molly Wasser
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / molly.l.wasser@nasa.gov
2025-140