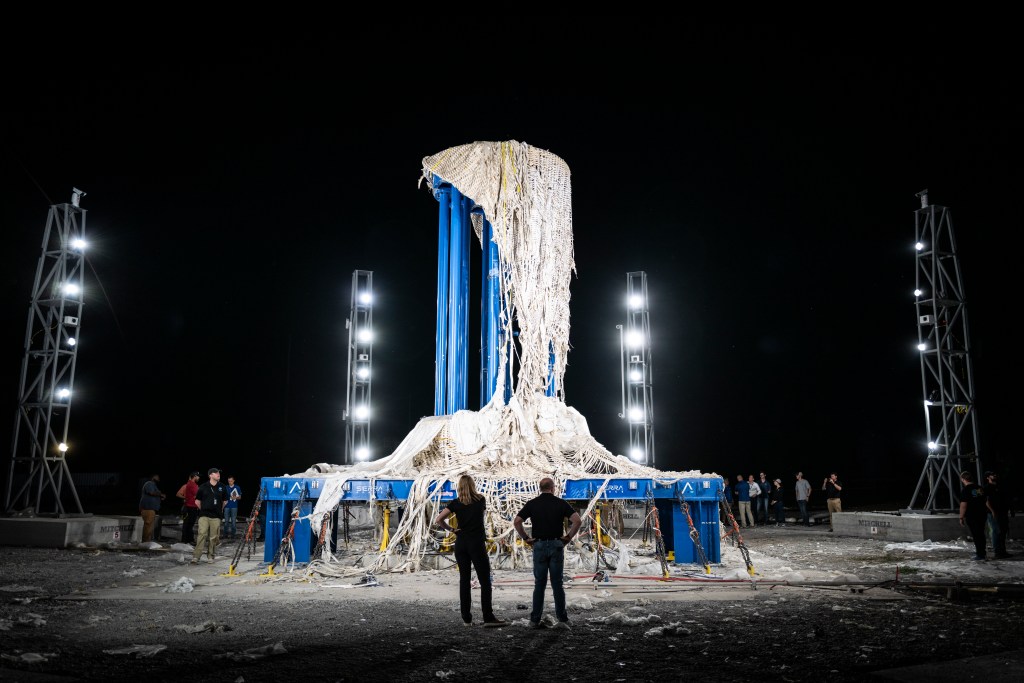
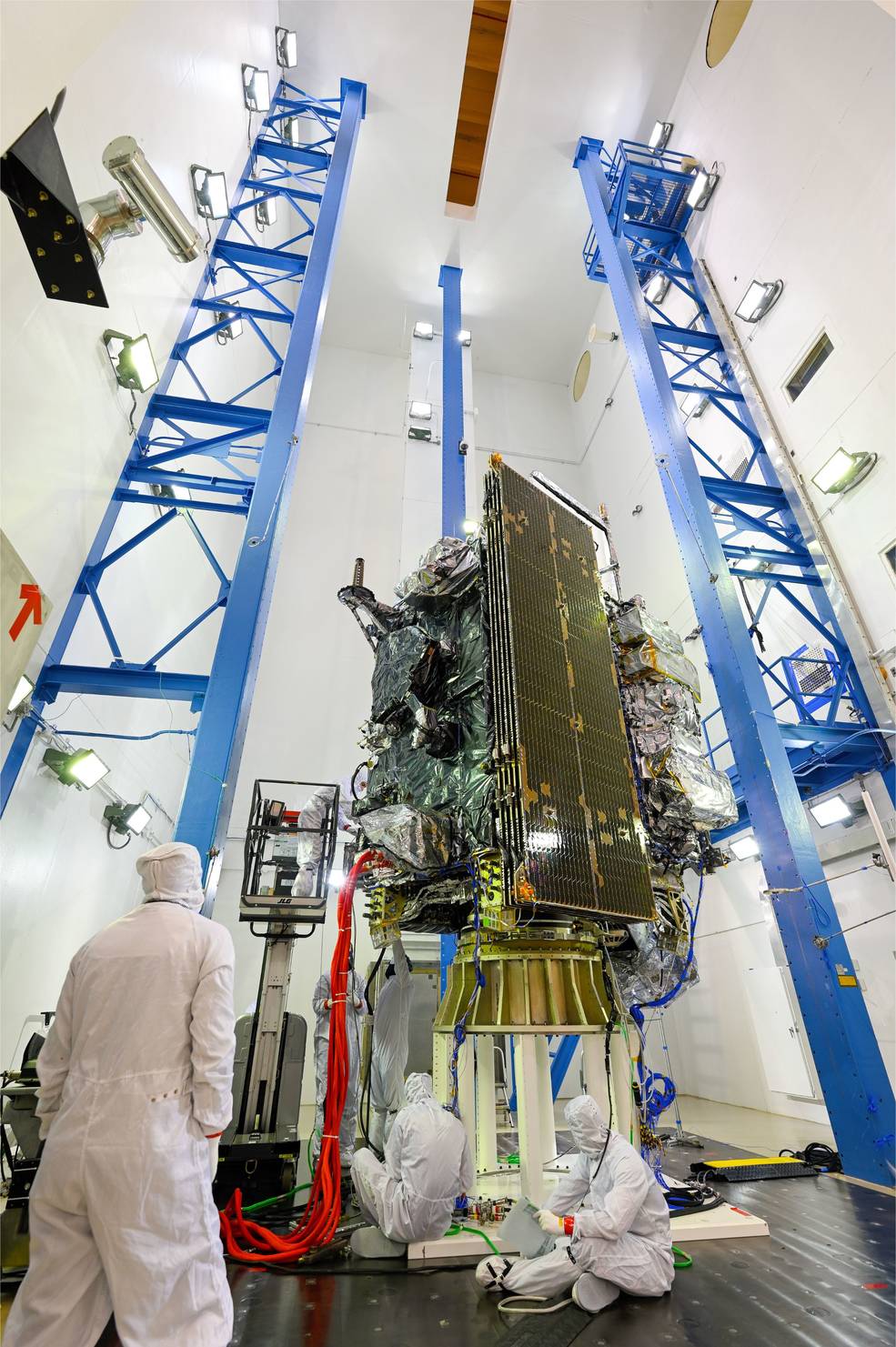
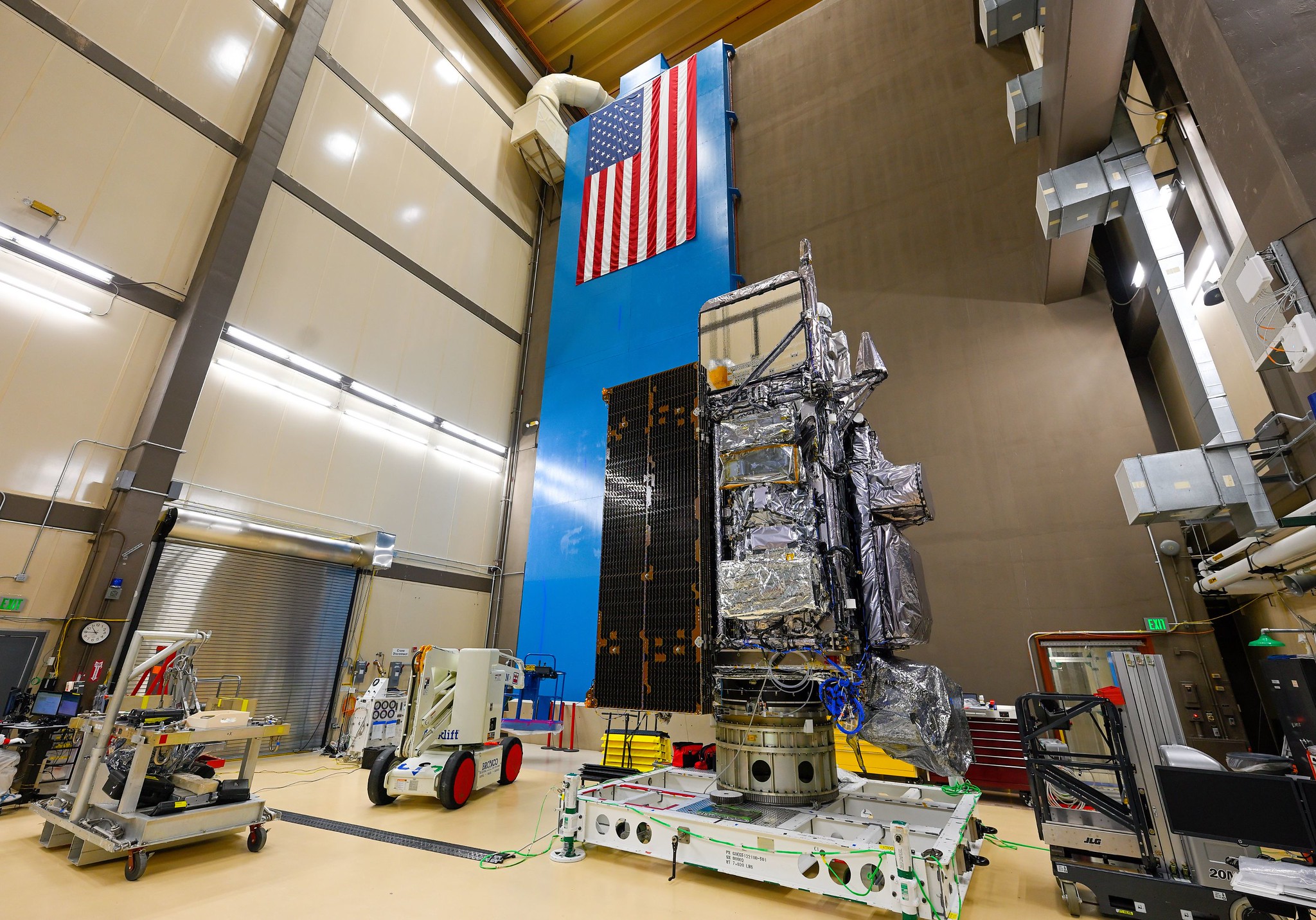
GOES-U, the fourth and final satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series, recently completed acoustics testing as part of a rigorous testing program to ensure it can withstand the harsh conditions of launch and orbiting in space 22,236 miles above Earth.
GOES-U, the fourth and final satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series, recently completed acoustics testing as part of a rigorous testing program to ensure it can withstand the harsh conditions of launch and orbiting in space 22,236 miles above Earth.
During acoustic testing, GOES-U endured extremely high sound pressure of 138.4 decibels from high-intensity horns. This testing simulated the noises GOES-U will experience when it is launched.
The testing was conducted at Lockheed Martin Space’s Littleton, Colorado, facility, where GOES-U was built. GOES-U is scheduled to launch in April 2024.
The GOES-R program is a collaborative effort between the National Aeronautics and Space Agency (NASA) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NASA builds and launches the satellites for NOAA, which operates them and distributes their data to users worldwide. The satellites provide critical data for weather forecasts and warnings, detecting and monitoring environmental hazards like fire, smoke, fog, volcanic ash, and dust, and monitoring solar activity and space weather.
Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
robert.j.gutro@nasa.gov