STS-79
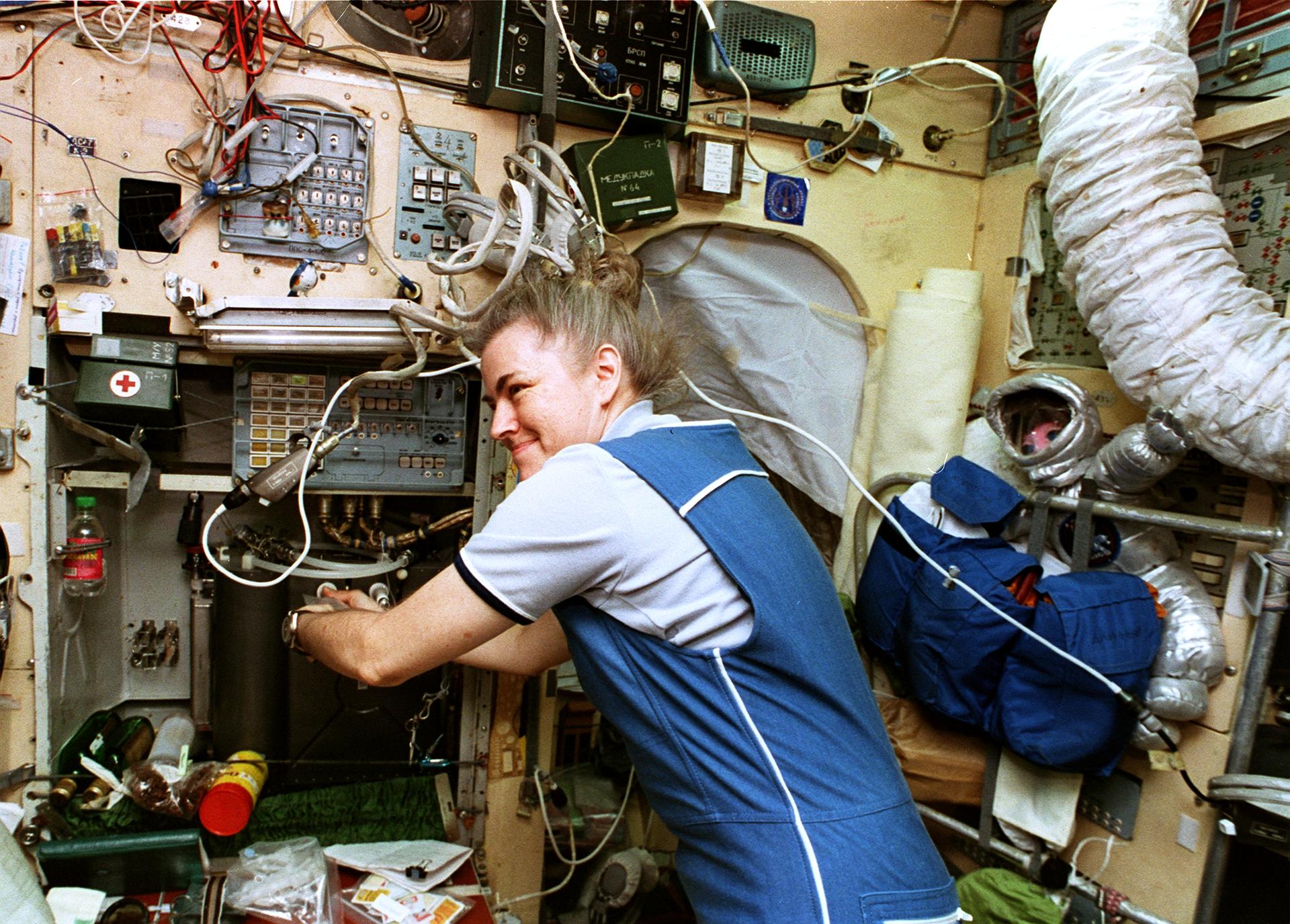
STS-79 brought back to Earth U.S. astronaut Shannon Lucid after her 188 days in space, a new U.S. spaceflight record and a world record for a woman. Astronaut John Blaha succeeded Lucid on Mir, joining Mir-22 commander Valeri Korzun and flight engineer Alexander Kaleri.
Orbiter
Mission Duration
Launch
Landing

Mission Facts
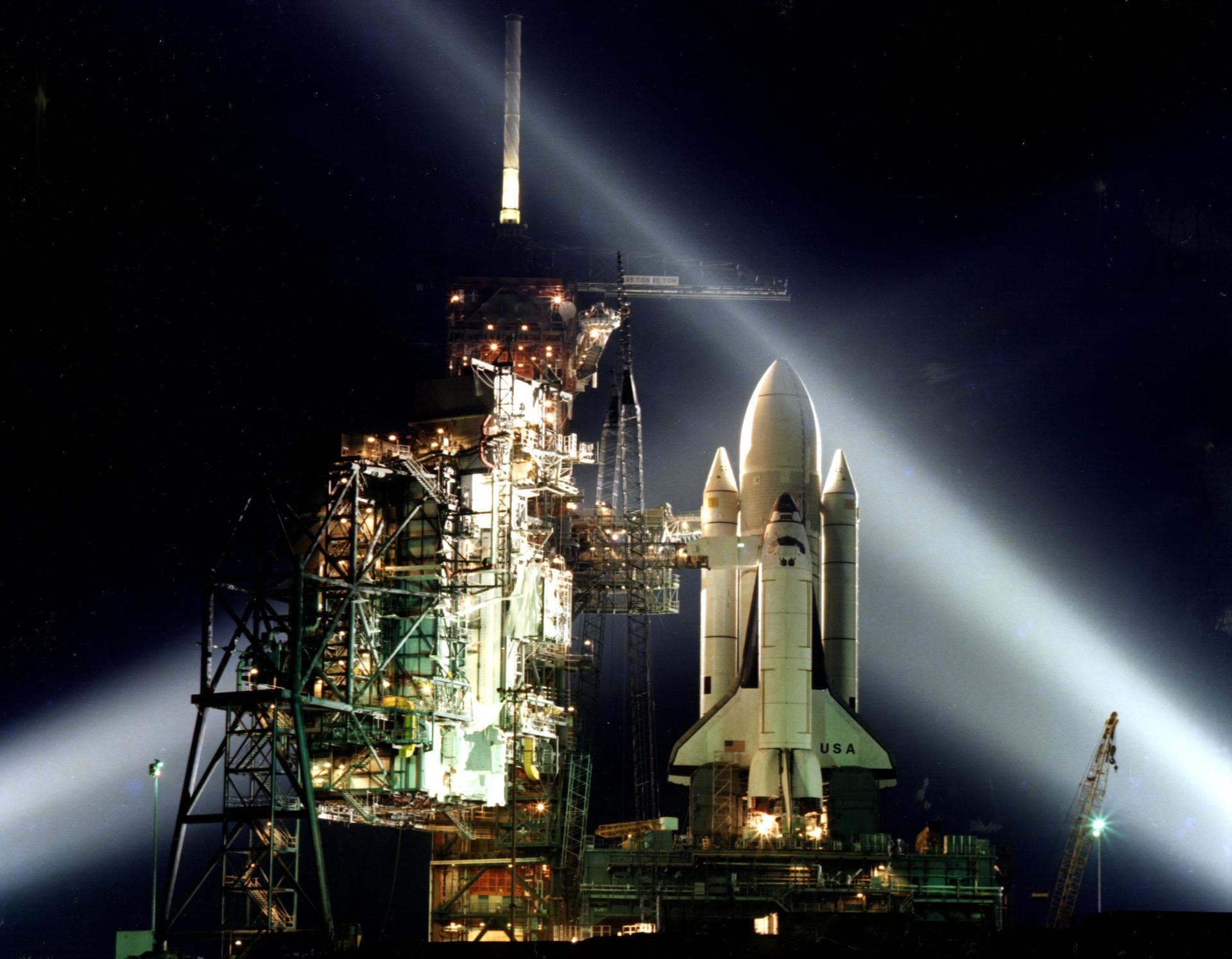
Mission: Fourth Shuttle-Mir Docking
Space Shuttle: Atlantis
Launch Pad: 39A
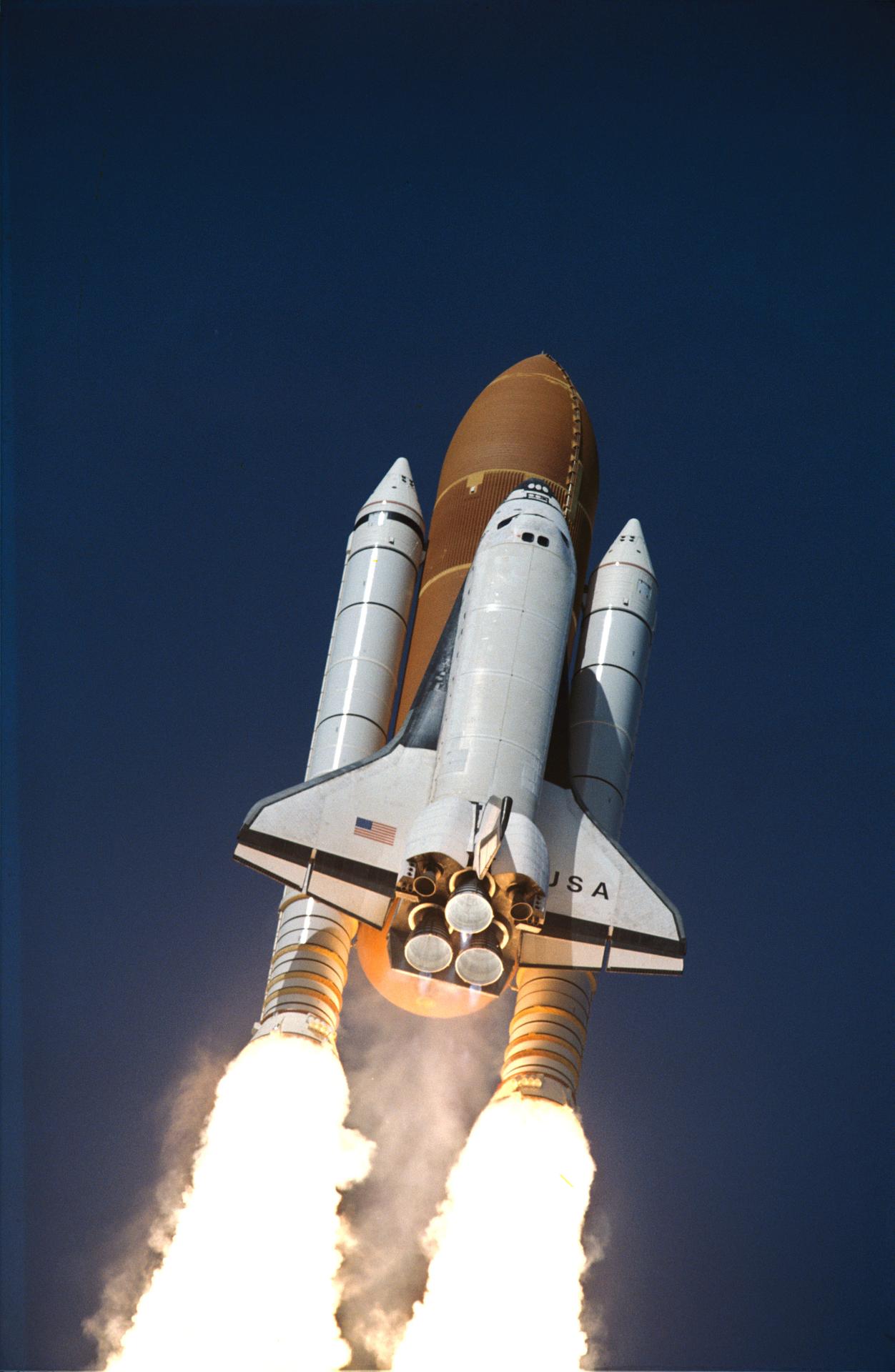
Launched: September 16, 1996, 4:54:49 a.m. EDT
Landing Site: Kennedy Space Center, Florida
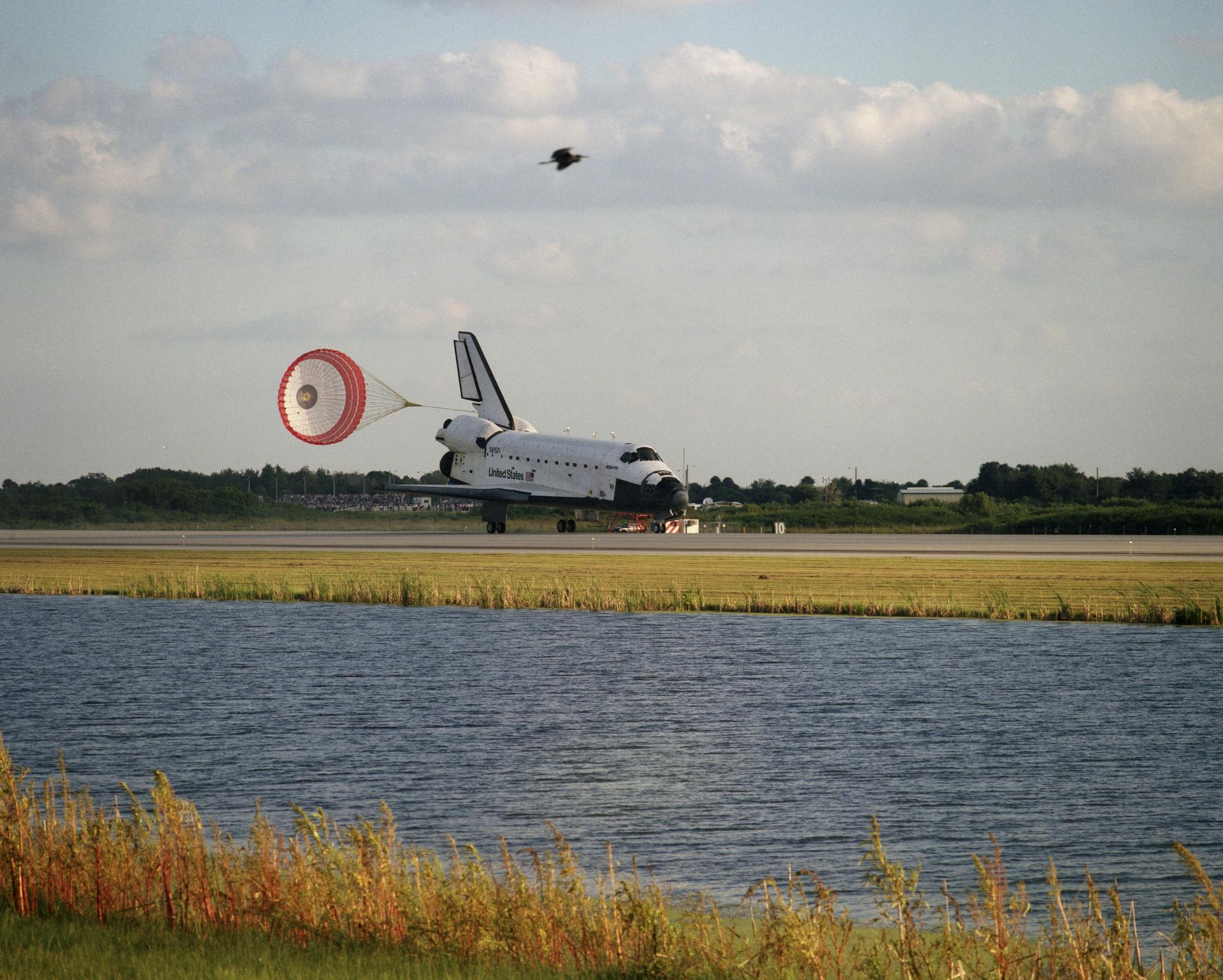
Landing: September 26, 1996, 8:13:15 a.m. EDT
Runway: 15
Rollout Distance: 10,981 feet
Rollout Time: 62 seconds
Revolution: 160
Mission Duration: 10 days, 3 hours, 18 minutes, 26 seconds
Orbit Altitude: 196-245 statute miles
Orbit Inclination: 51.6 degrees
Miles Traveled: 3.9 million
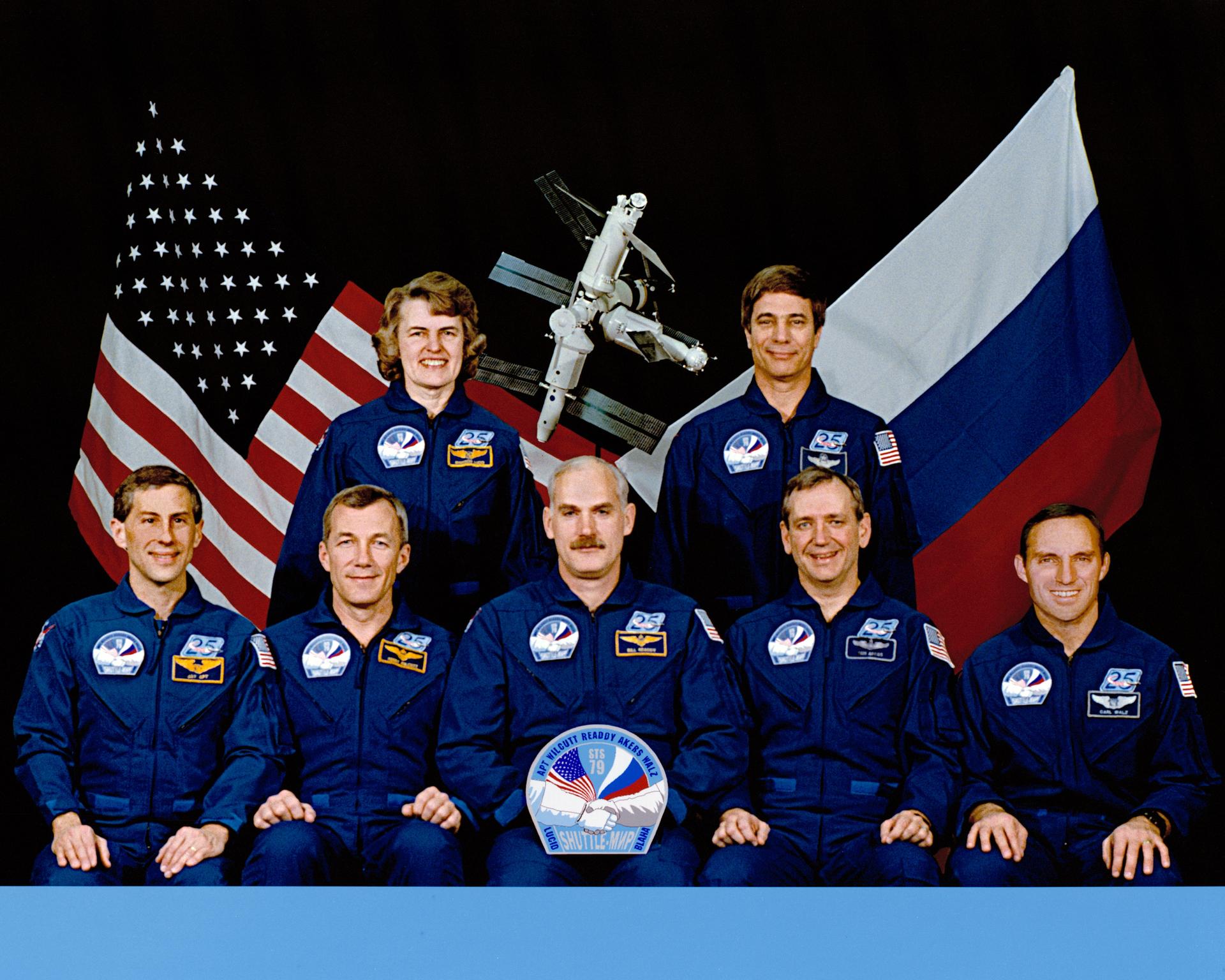
Crew
William F. Readdy, Commander
Terrence W. Wilcutt, Pilot
Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mission Specialist
Thomas D. Akers, Mission Specialist
Carl E. Walz, Mission Specialist
Shannon W. Lucid, Mission Specialist
John E. Blaha, Mission Specialist
Launch Highlights
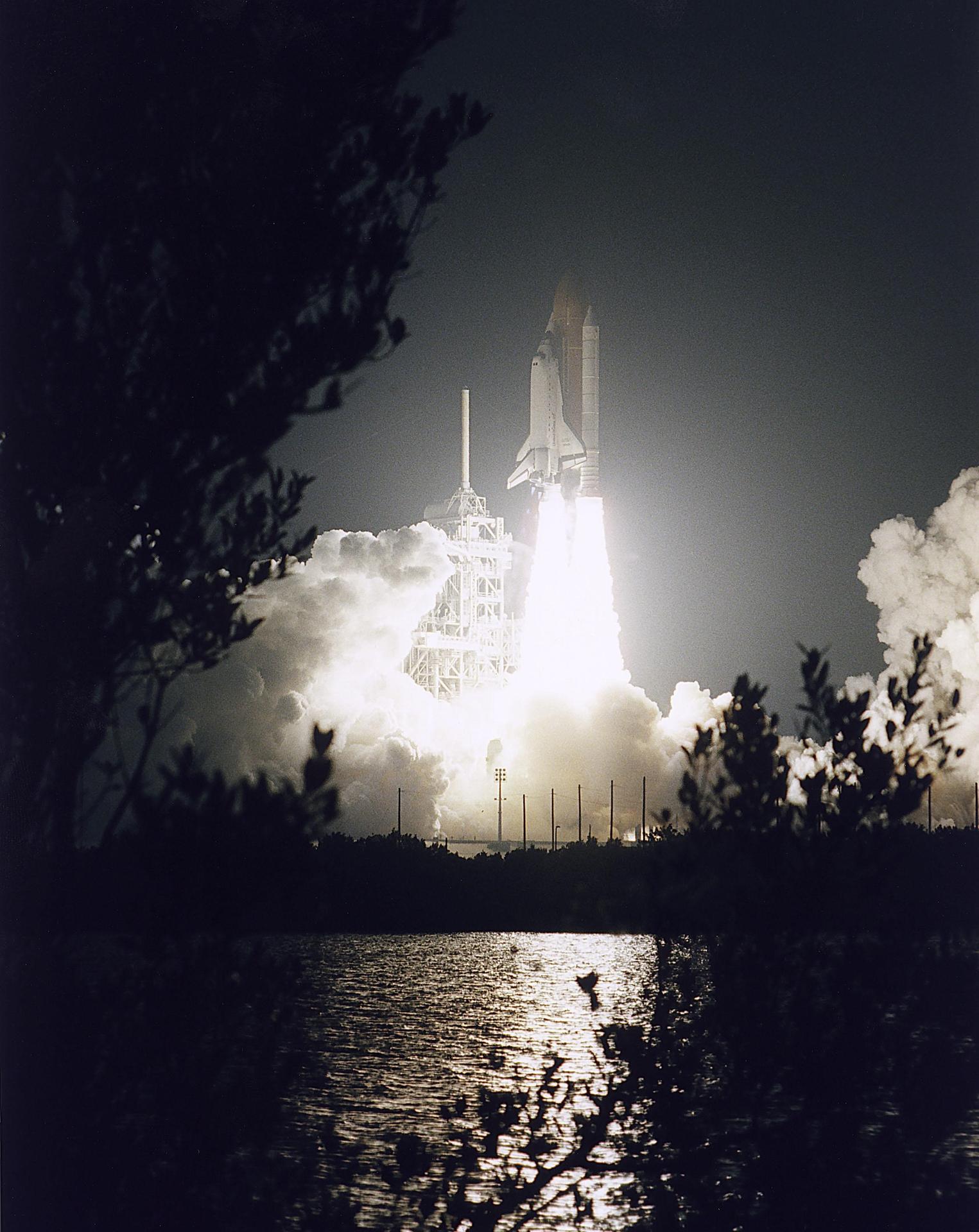
Launch originally set for July 31 slipped when mission managers decided to switch out Atlantis’ twin solid rocket boosters. STS-79 boosters assembled using same new adhesive as boosters flown on previous mission, STS-78, in which hot gas path into J-joints of motor field joints was observed post-retrieval. Although managers concluded original STS-79 boosters were safe to fly, they decided to replace them with a set slated for STS-80 that used original adhesive. Booster changeout took place after Atlantis was already back in Vehicle Assembly Building due to threat from Hurricane Bertha. New launch date of Sept. 12 targeted and Atlantis returned to pad. Launch date delayed to Sept. 16 when shuttle was returned to the VAB due to threat from Hurricane Fran, marking first time shuttle rolled back twice in single processing flow due to hurricane threats. Countdown proceeded smoothly to ontime liftoff Sept. 16. Approximately 13 minutes into flight, auxiliary power unit no. 2 went down prematurely. After review and analysis, the Mission Management Team concluded mission could proceed to nominal end-of-mission as planned.
Mission Highlights
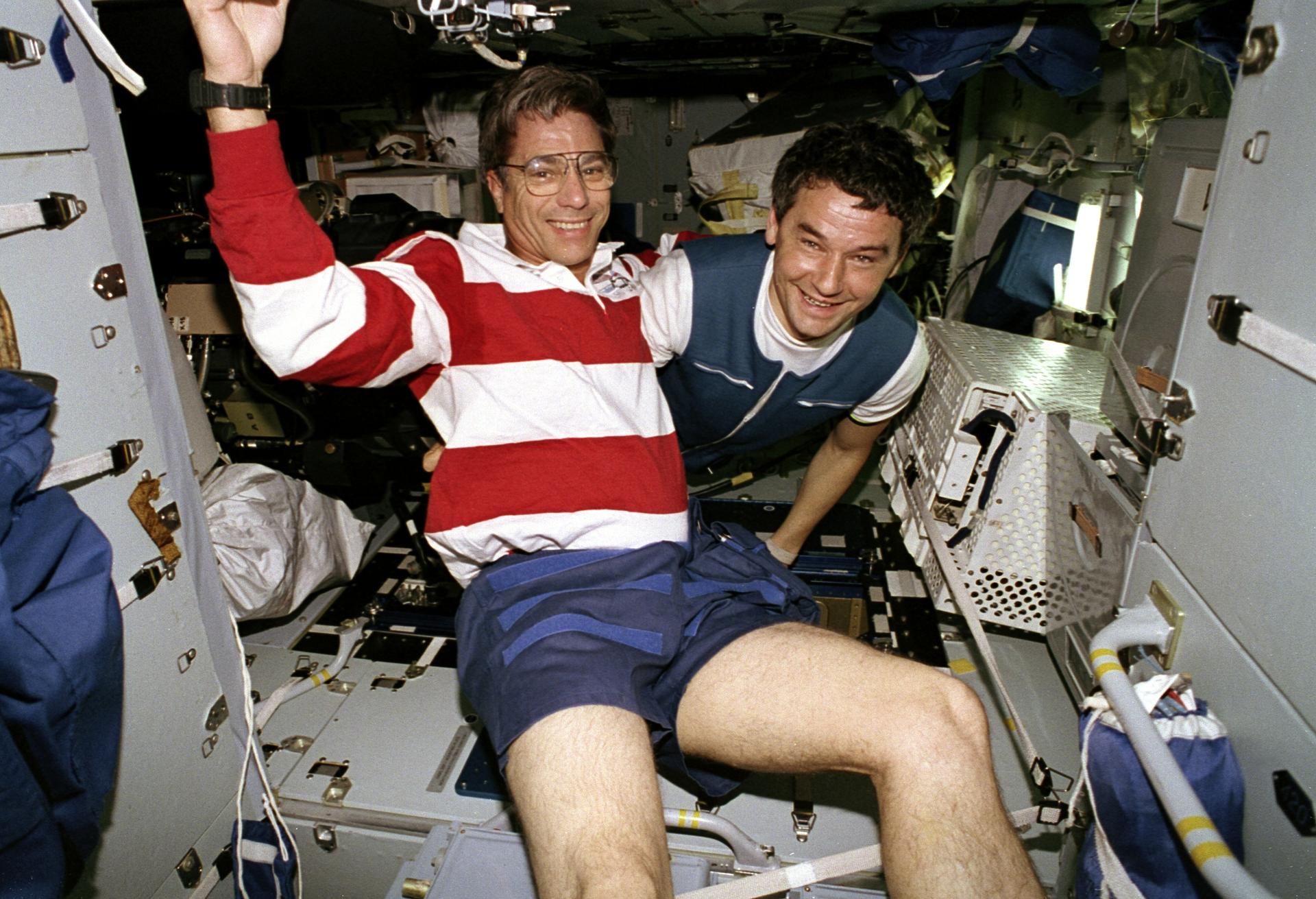
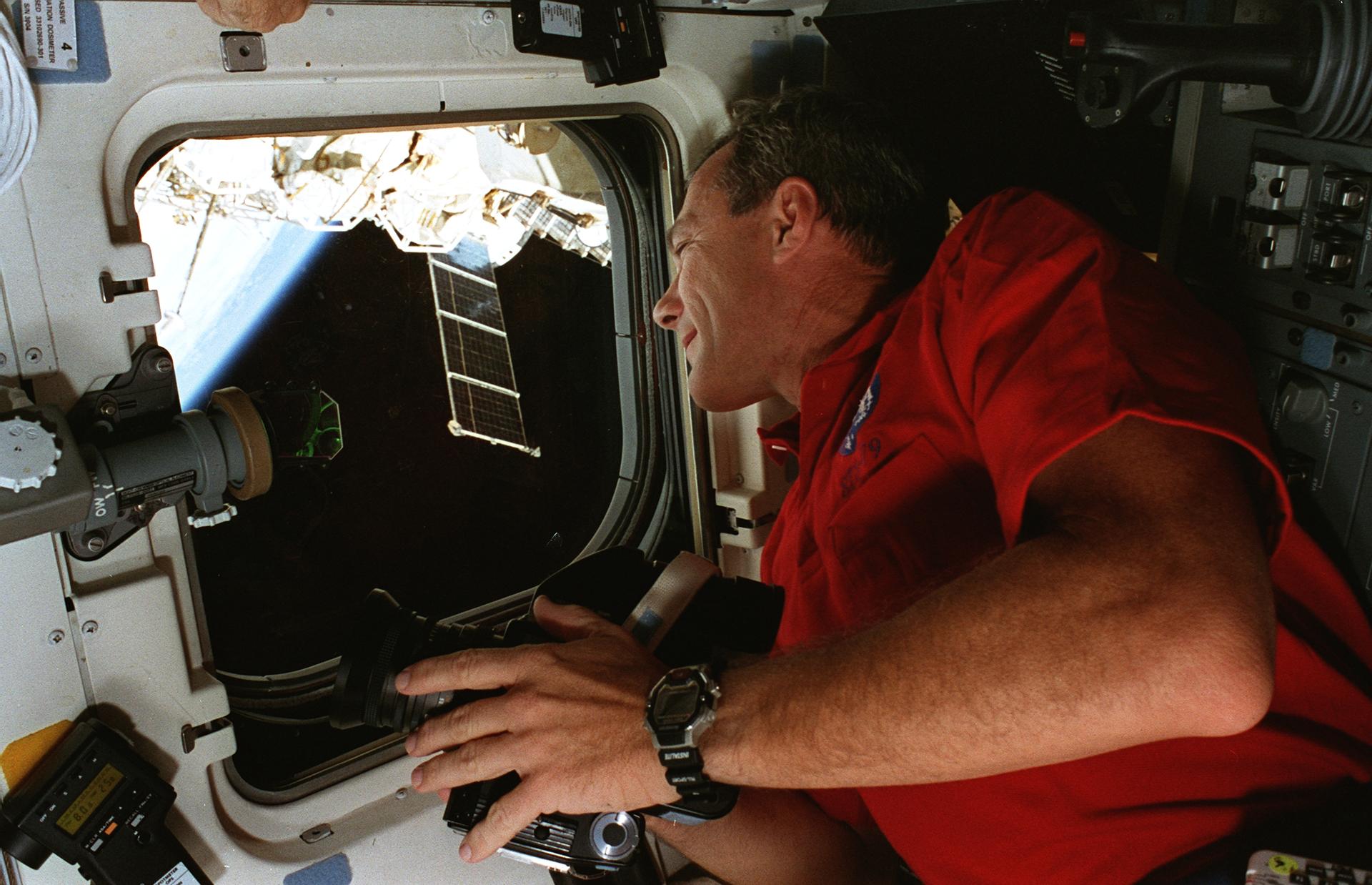
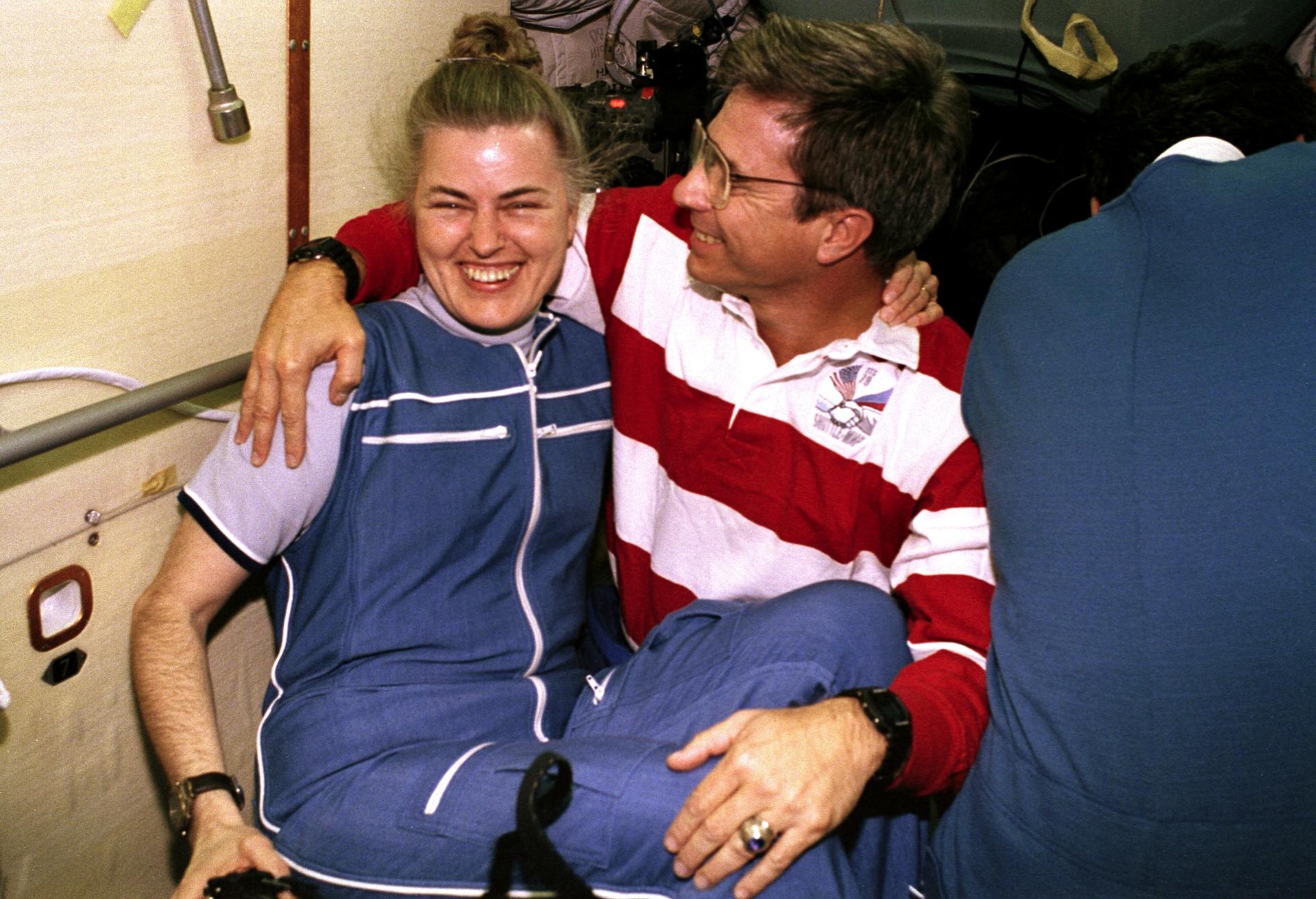
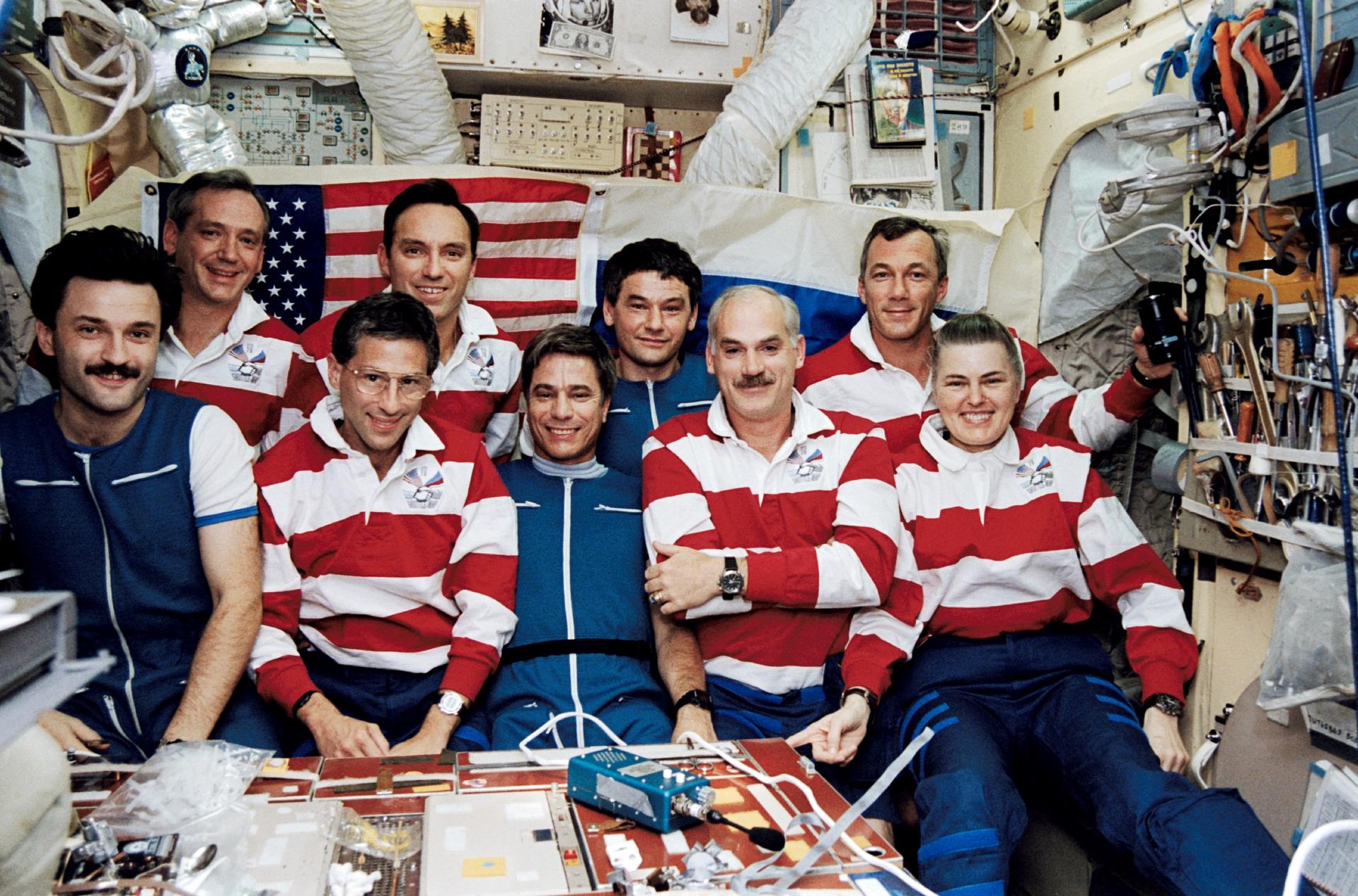
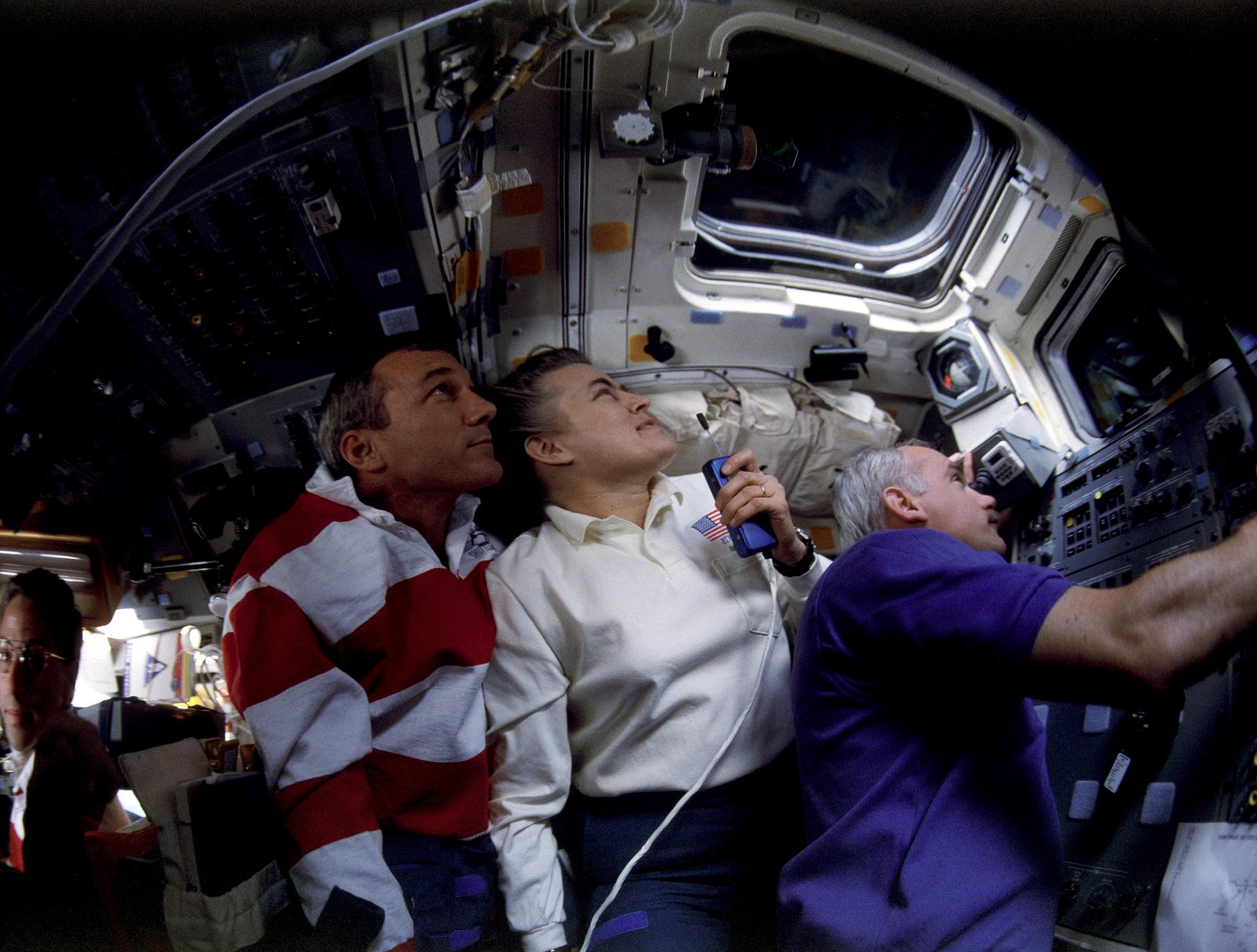
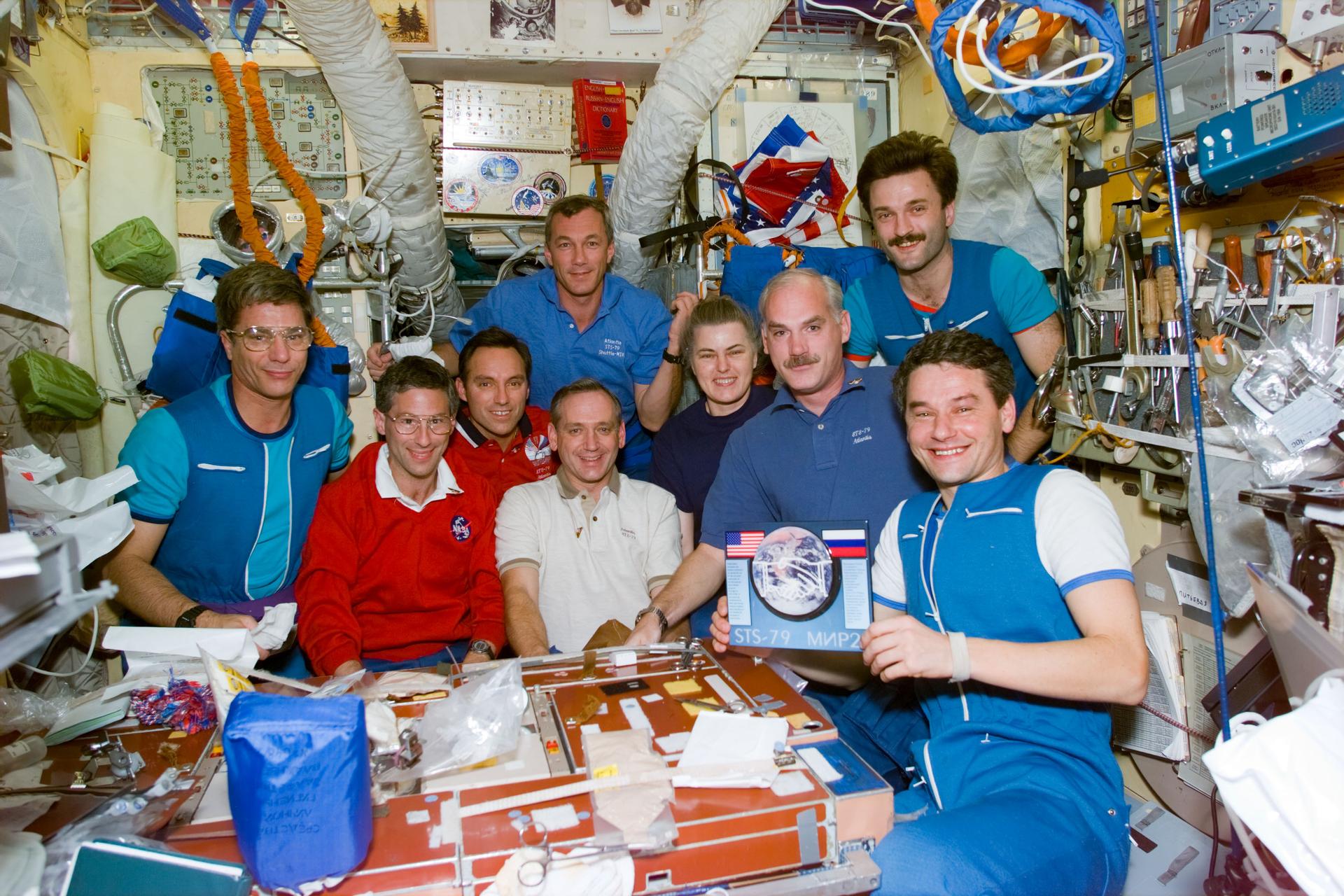
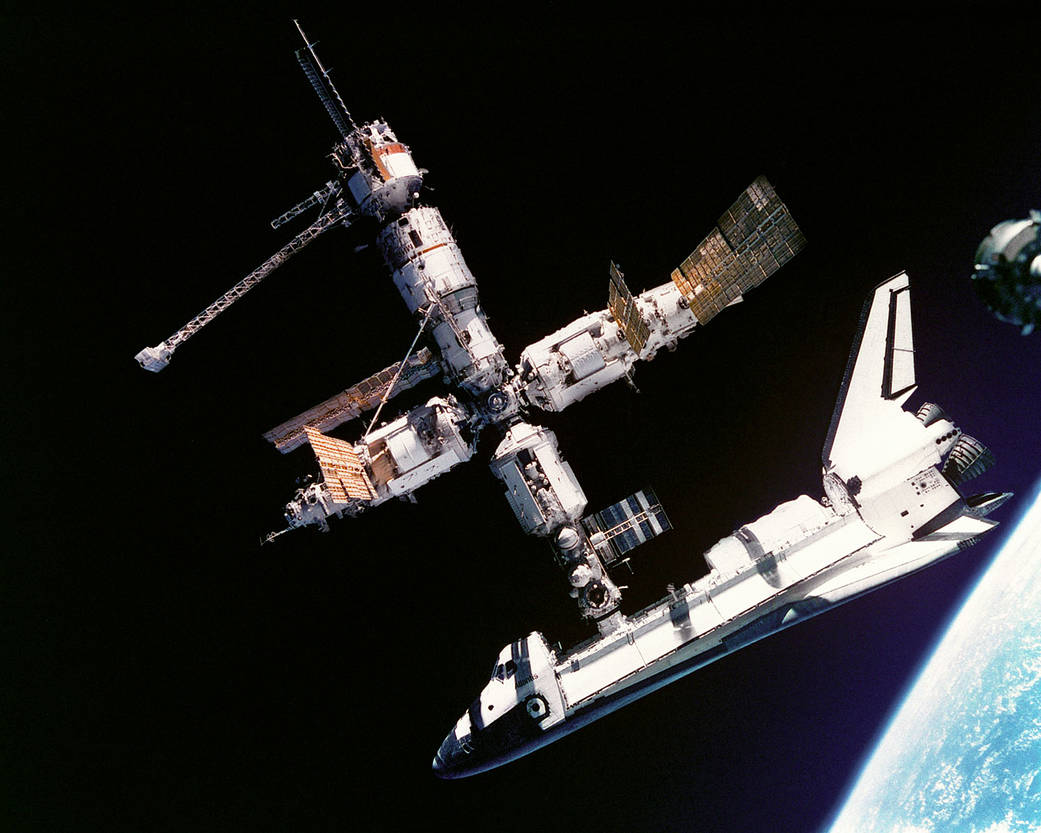
STS-79 highlighted by return to Earth of U.S. astronaut Lucid after 188 days in space, first U.S. crew exchange aboard Russian Space Station Mir, and fourth Shuttle-Mir docking. Lucid’s long-duration spaceflight set new U.S. record as well as world record for a woman. She embarked to Mir March 22 with STS-76 mission. Succeeding her on Mir for an approximately four-month stay is Blaha, who will return in January 1997 with STS-81 crew; U.S. astronaut Jerry Linenger will replace him.
STS-79 also marked second flight of SPACEHAB module in support of Shuttle-Mir activities and first flight of SPACEHAB Double Module configuration. Shuttle-Mir linkup occurred at 11:13 p.m. EDT, Sept. 18, following R-bar approach. Hatches opened at 1:40 a.m., Sept. 19, and Blaha and Lucid exchanged places at 7 a.m. EDT. Awaiting Blaha on Mir were Valery Korzun, Mir 22 commander, and Alexander Kaleri, flight engineer.
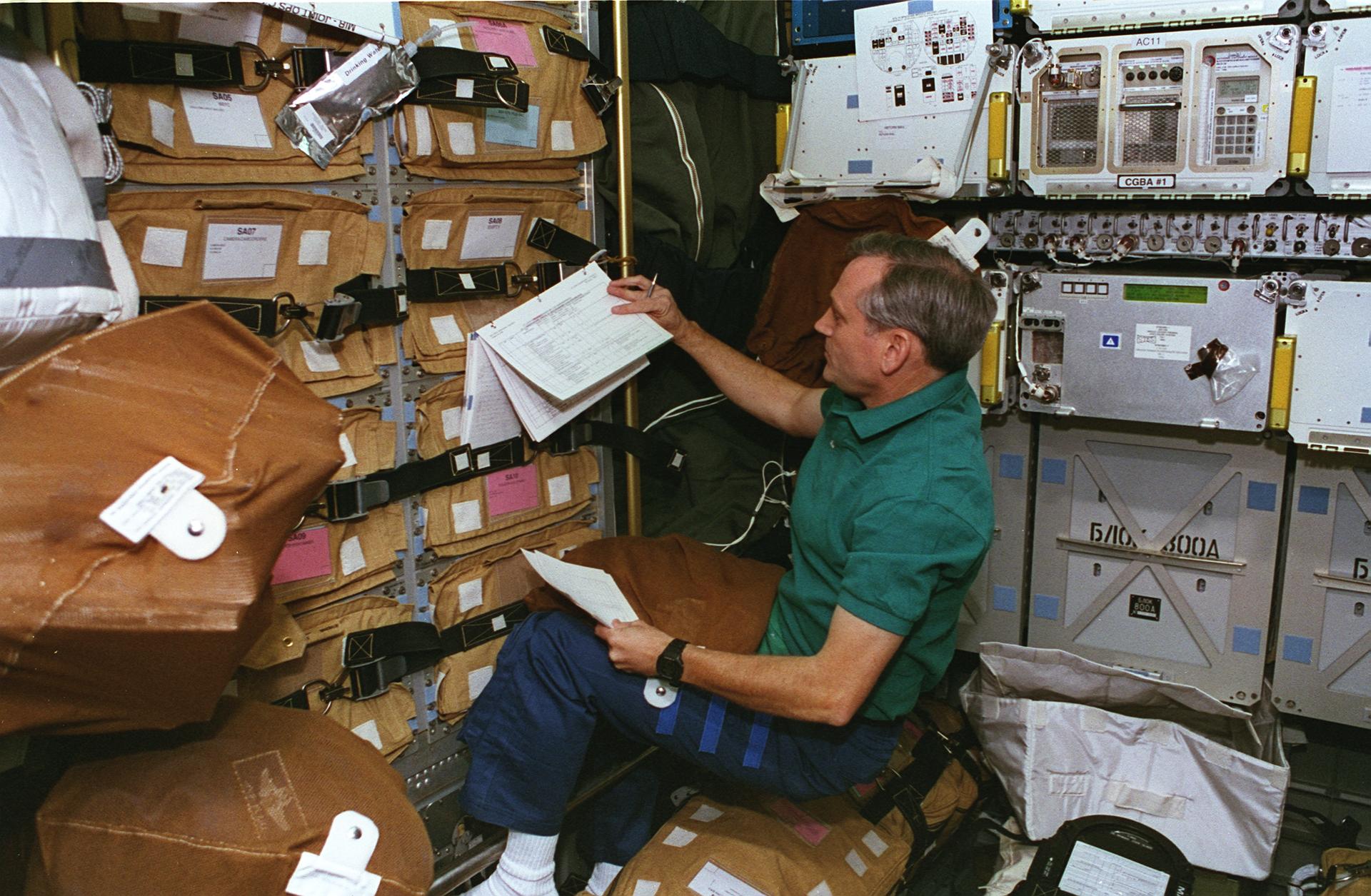
During five days of mated operations, two crews transferred more than 4,000 pounds (1,814 kilograms) of supplies to Mir, including logistics, food and water generated by orbiter fuel cells. Three experiments also were transferred: Biotechnology System (BTS) for study of cartilage development; Material in Devices as Superconductors (MIDAS) to measure electrical properties of high-temperature superconductor materials; and Commercial Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (CGBA), containing several smaller experiments, including self-contained aquatic systems.
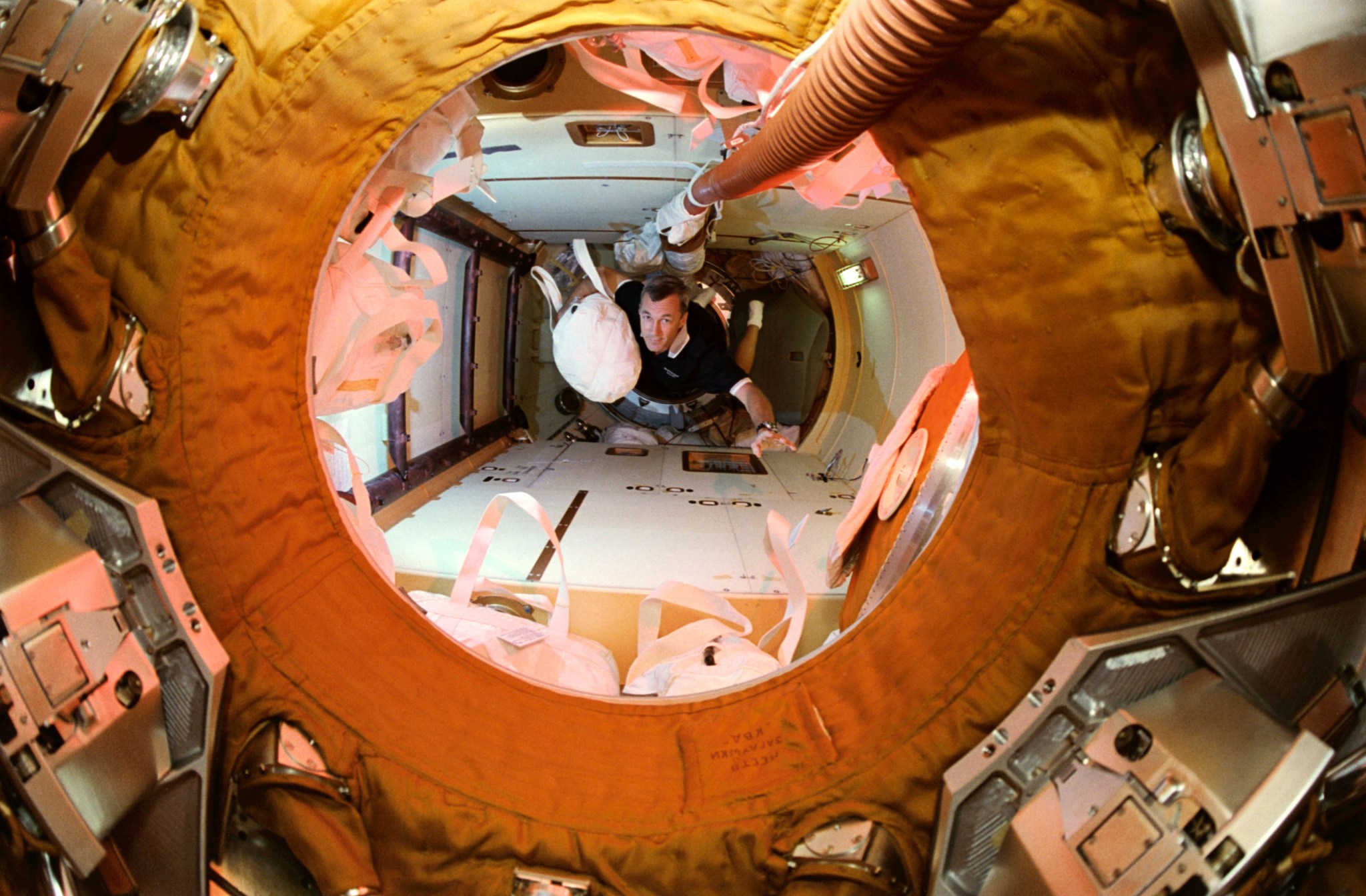

About 2,000 pounds (907 kilograms) of experiment samples and equipment transferred from Mir to Atlantis; total logistical transfer to and from station of more than 6,000 pounds (2,722 kilograms) was most extensive to date. During her approximately six-month stay on Mir, Lucid conducted research in following fields: advanced technology, Earth sciences, fundamental biology, human life sciences, microgravity research and space sciences. Specific experiments included: Environmental Radiation Measurements to ascertain ionizing radiation levels aboard Mir; Greenhouse-Integrated Plant Experiments, to study effect of microgravity on plants, specifically dwarf wheat; and Assessment of Humoral Immune Function During Long-Duration Space Flight, to gather data on effect of long-term spaceflight on the human immune system and involving collection of blood serum and saliva samples. Some research conducted in newest and final Mir module, Priroda, which arrived at station during Lucid’s stay.
Three experiments remained on Atlantis: Extreme Temperature Translation Furnace (ETTF), a new furnace design allowing space-based processing up to 871 degrees Fahrenheit (1,600 degrees Centigrade) and above; Commercial Protein Crystal Growth (CPCG) complement of 128 individual samples involving 12 different proteins; and Mechanics of Granular Materials, designed to further understanding of behavior of cohesionless granular materials, which could in turn lead to better understanding of how Earth’s surface responds during earthquakes and landslides.
As with all Shuttle-Mir flights, risk-mitigation experiments were conducted to help reduce development risk for the International Space Station. Flying for first time was the Active Rack Isolation System (ARIS), an experiment rack designed to cushion payloads from vibration and other disturbances.
Conducted near end of flight was test using orbiter’s small vernier jets to lower Atlantis’ orbit. A similar maneuver may be employed at the end of the second Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission, STS-82, to re-boost Hubble to a higher orbit while still in the orbiter payload bay.
STS-79
Shuttle News
Retired Space Shuttle Locations
Shuttle Atlantis – Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex Shuttle Discovery – Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center Shuttle Endeavour – California Science…
Read the Story