This article is for students grades 5-8.
Orion /o-rie-un/ is a NASA spacecraft that carries astronauts during Artemis missions to the Moon
What Does Orion Do?
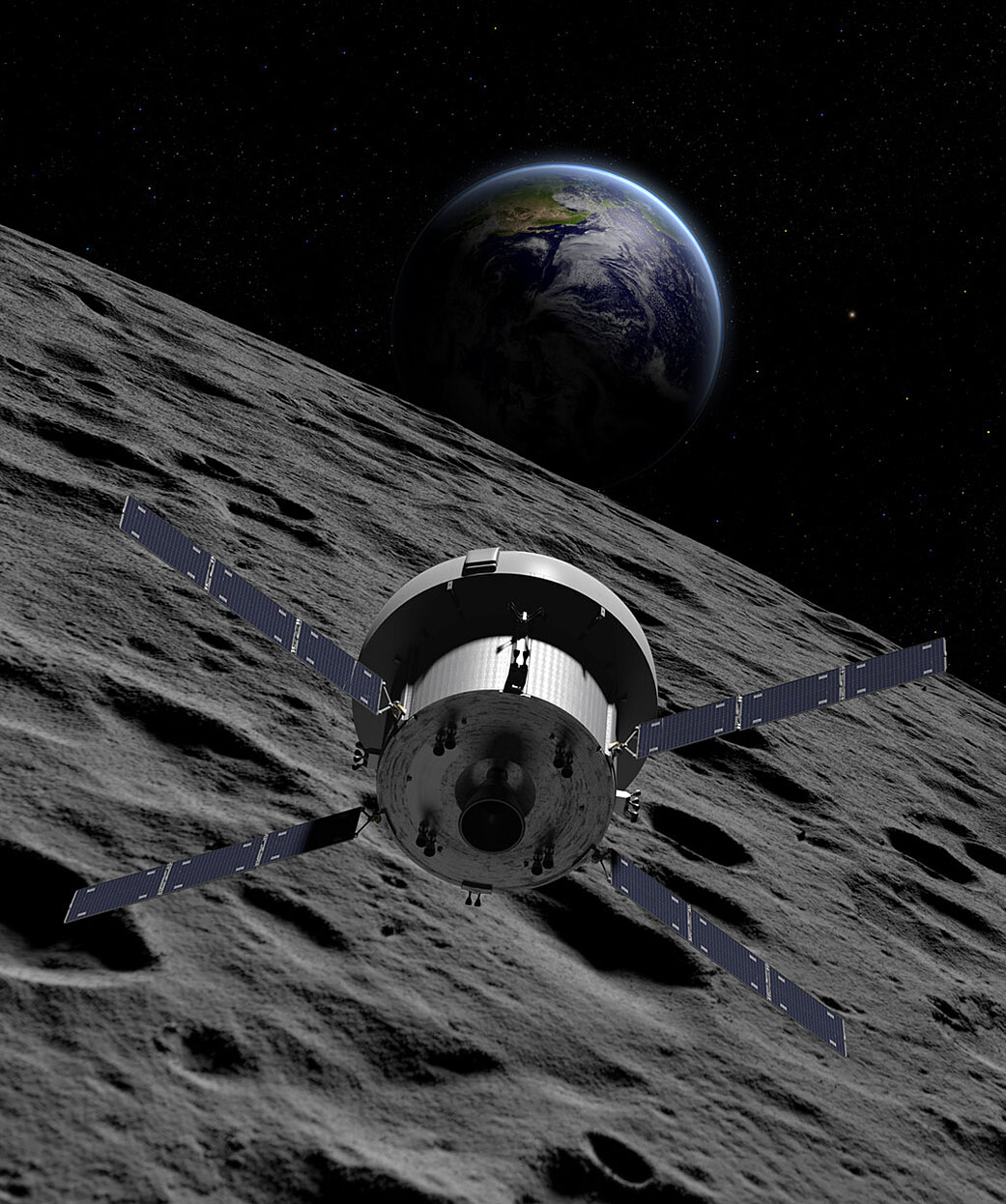
Orion is designed to carry up to four astronauts into deep space and then return them safely to Earth. Artemis astronauts will travel to lunar orbit in Orion. On future missions that involve landing on the lunar surface, Orion will dock with Gateway, a new spacecraft that will orbit the Moon.
Orion will take astronauts farther than they have ever gone. Orion will:
- Carry the crew safely to space.
- Serve as a home while the crew is traveling.
- Allow the crew to return to Earth safely from speeds as fast as 25,000 miles per hour.
- Be a “lifeboat” if the crew has to return to Earth in an emergency.
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Words to Know
deep space: the vast region of space that extends beyond the Moon and across the solar system
jettison: to drop from an aircraft or spacecraft in flight
propulsion: the force that pushes forward or drives an object forward
____________________________________________________________________________________________
What Are the Parts of Orion?
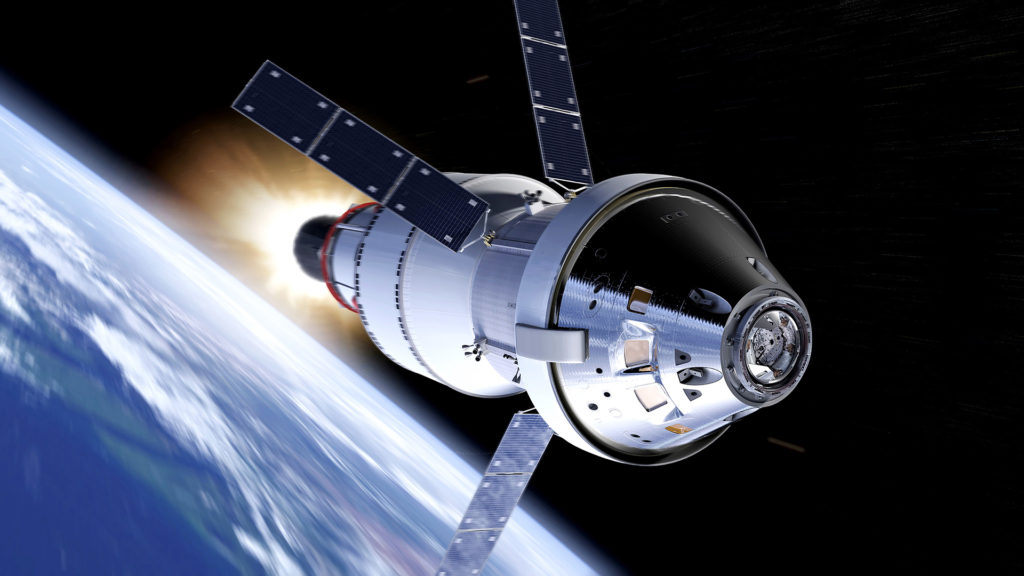
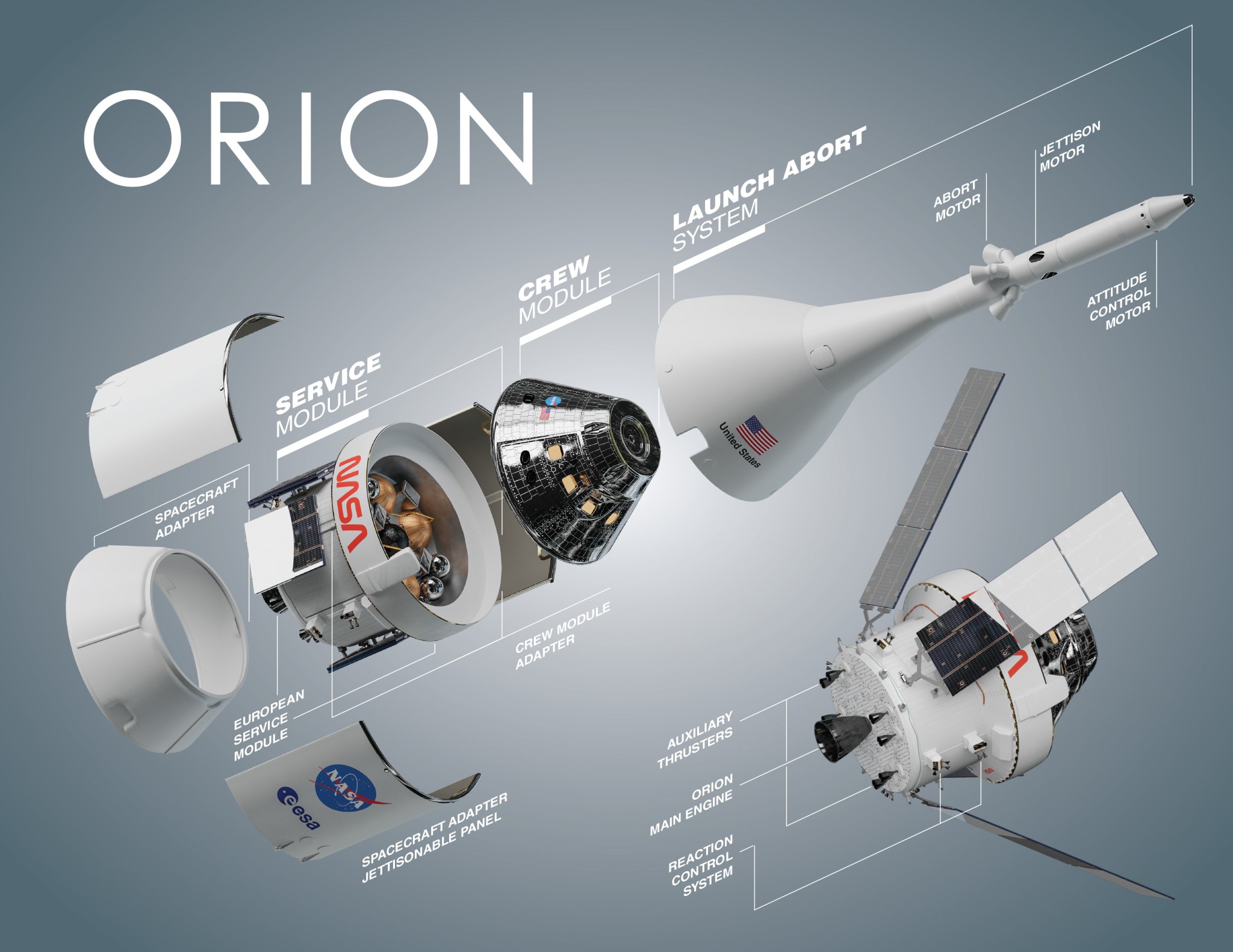
Orion has three main parts:
- The launch abort system (LAS) is at the top. If there is an emergency during launch, the LAS will pull the crew capsule away from the rocket for a safe landing.
- The crew module is in the center. This is the pressurized capsule where the astronauts will live and work on their journey to the Moon and back.
- The service module is at the bottom. This module carries life support systems that provide water and oxygen to the crew. Once in space, it has four solar array wings that expand to generate electricity. This module also provides in-space propulsion and regulates temperatures in the crew module.
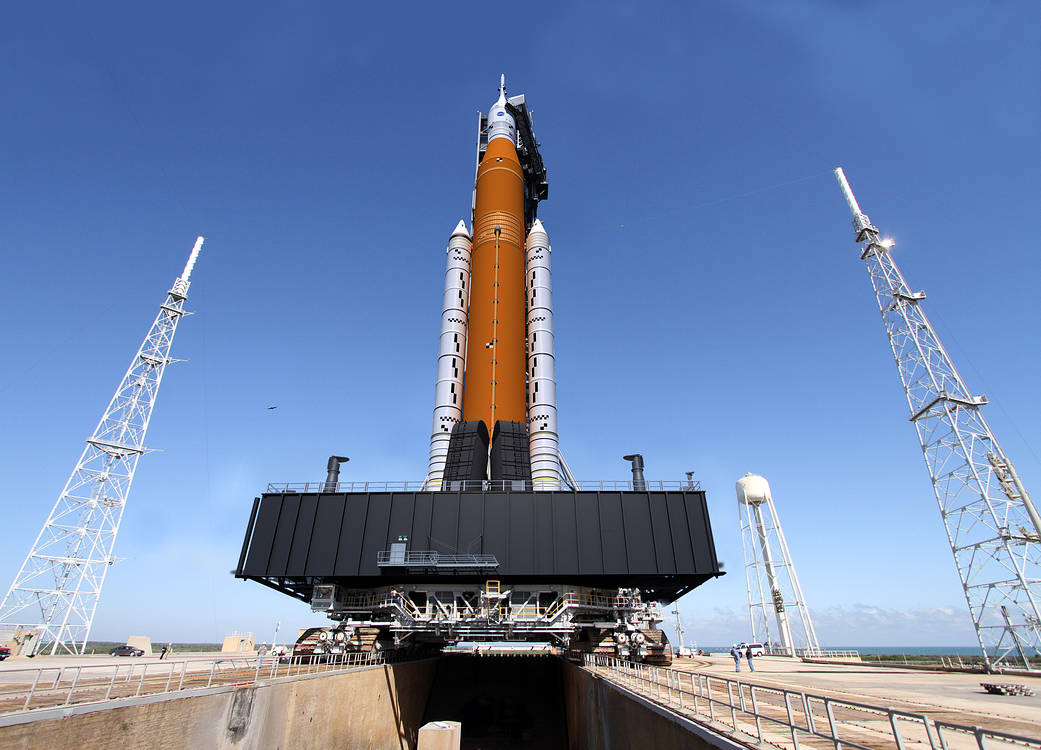
How Does Orion Launch and Land?
Orion launches from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It rides atop NASA’s heavy-lift rocket, the Space Launch System (SLS). After traveling through most of Earth’s atmosphere safely, the LAS is jettisoned. The crew module and service module remain together throughout the mission to the Moon and back.
During Orion’s return to Earth, the crew module separates from the service module. The crew module turns its heat shield toward Earth and begins entry. The capsule is traveling nearly 25,000 miles per hour when it reaches Earth. Friction with Earth’s atmosphere begins to slow the capsule and creates extreme temperatures up to around 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit. After a fiery re-entry through Earth’s upper atmosphere, parachutes slow Orion down even more for a safe splashdown in the Pacific Ocean near the coast of California.
Has Orion Flown Yet?
Orion has flown on two test flights. There were no astronauts on these flights.
The first flight was in 2014 and tested Orion in orbit around Earth. The second test flight was the Artemis I mission in 2022. This was the first test of the Orion spacecraft and the SLS rocket together. During Artemis I, Orion successfully orbited the Moon and returned to Earth.

What’s Next for Orion?
In early 2026, Orion will launch on the Artemis II mission. This will be the first Artemis mission with a crew. Four astronauts will spend 10 days testing the Orion spacecraft. Their mission will take them around the Moon and back. The flight will be the farthest humans have ever traveled into space.
Career Corner
Are you interested in a career that is related to space vehicles like Orion? Many different types of jobs make crewed spaceflight possible. Here are a few examples:
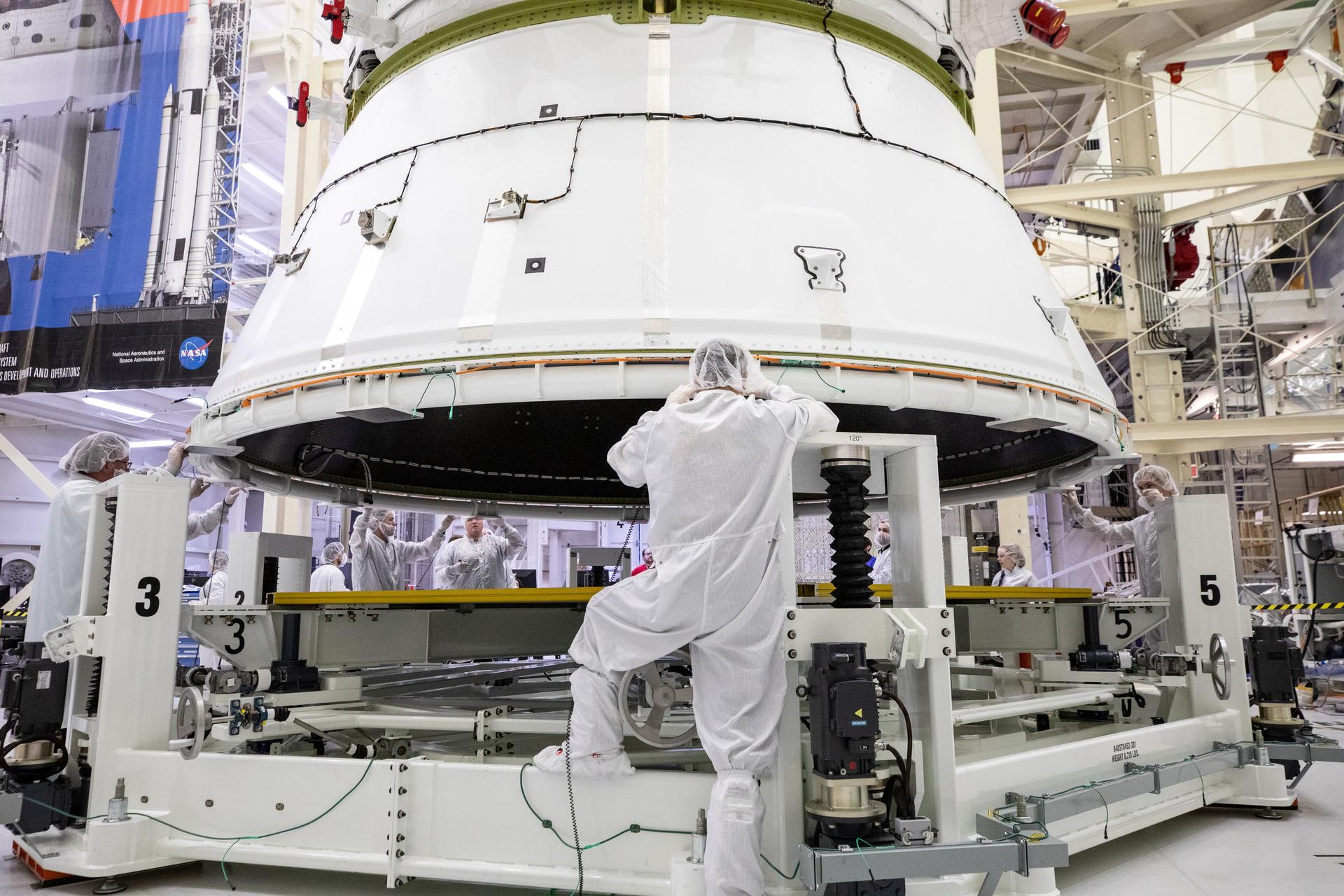
Manufacturing Engineer: Thousands of pieces and parts come together to build complex spacecraft like Orion. Manufacturing engineers fabricate the different pieces. They must follow precise instructions and measurements. This career requires trade school training or a college degree.
Radiation Scientist: When Artemis astronauts travel to the Moon, they will be exposed to increased levels of space radiation. This can lead to health problems. Radiation scientists study how space radiation affects the human body. This helps them find ways to protect astronauts on deep space missions. This career requires a good understanding of biology and physics.
Human Factors Engineer: Spending long periods of time in a small spacecraft can take a toll on astronauts. Human factors engineers design and test systems and equipment to make sure astronauts stay safe and comfortable. This includes things like making sure control panels are easy to use. This career includes tasks relating to engineering and psychology.
More About Orion
Orion Quick Facts (PDF)
Orion Crew Vehicle
What Is the Artemis Program?
What Is the Space Launch System?
Infographic: Orion—Designed for Deep Space