This article is for students grades K-4.
The word “rocket” can mean different things. Most people think of a tall, thin, round vehicle. They think of a rocket that launches into space. “Rocket” can mean a type of engine. The word also can mean a vehicle that uses that engine.
How Does a Rocket Engine Work?
Like most engines, rockets burn fuel. Most rocket engines turn the fuel into hot gas. The engine pushes the gas out its back. The gas makes the rocket move forward.
A rocket is different from a jet engine. A jet engine needs air to work. A rocket engine doesn’t need air. It carries with it everything it needs. A rocket engine works in space, where there is no air.
There are two main types of rocket engines. Some rockets use liquid fuel. The main engines on the space shuttle orbiter use liquid fuel. The Russian Soyuz uses liquid fuels. Other rockets use solid fuels. On the side of the space shuttle are two white solid rocket boosters. They use solid fuels. Fireworks and model rockets also fly using solid fuels.
Why Does a Rocket Work?
In space, an engine has nothing to push against. So how do rockets move there? Rockets work by a scientific rule called Newton’s third law of motion. English scientist Sir Isaac Newton listed three Laws of Motion. He did this more than 300 years ago. His third law says that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The rocket pushes on its exhaust. The exhaust pushes the rocket, too. The rocket pushes the exhaust backward. The exhaust makes the rocket move forward.
This rule can be seen on Earth. Imagine a person standing on a skateboard. Imagine that person throwing a bowling ball. The ball will go forward. The person on the skateboard will move, too. The person will move backward. Because the person is heavier, the bowling ball will move farther.
When Were Rockets Invented?
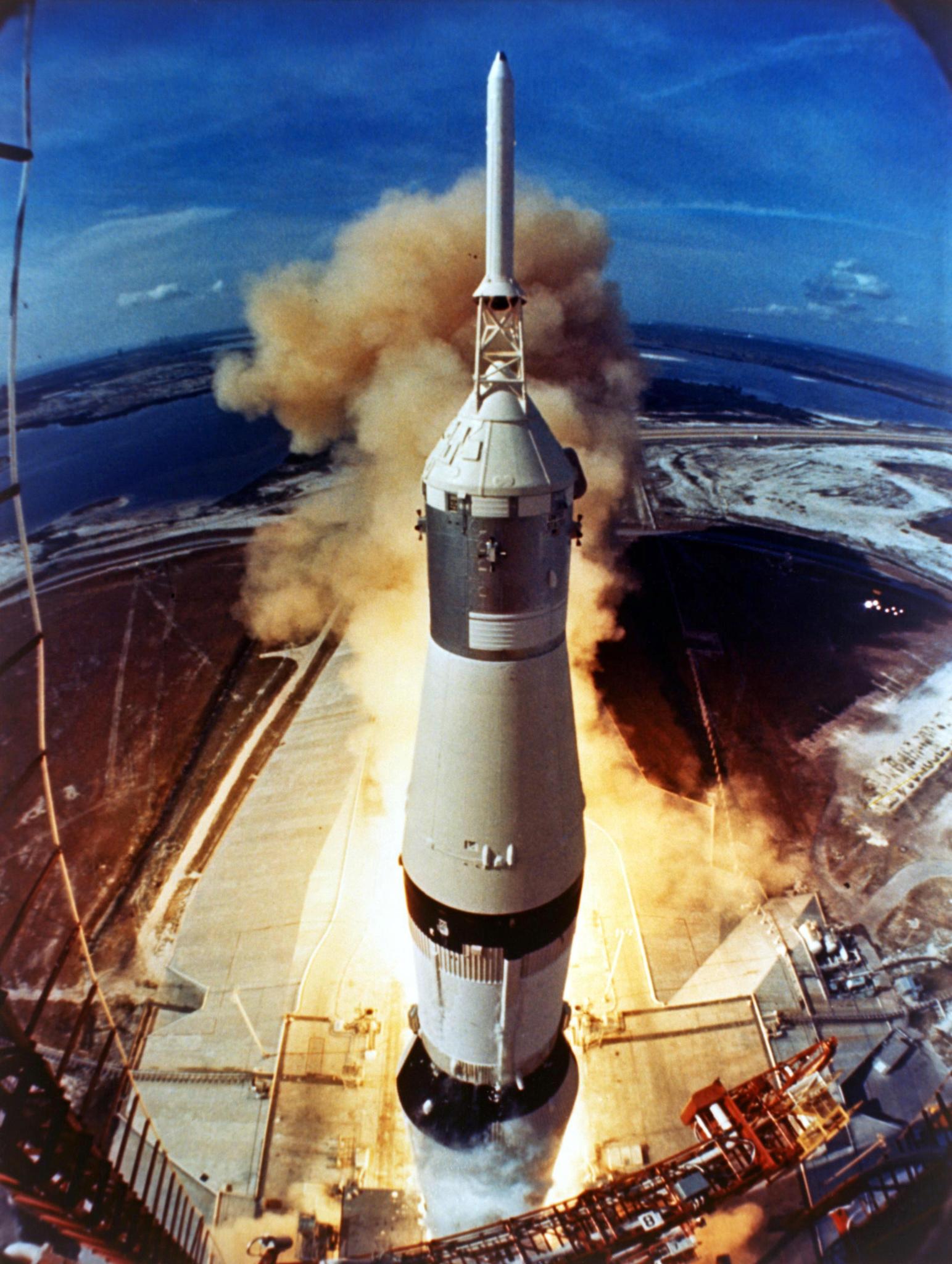
The first rockets we know about were used in China in the 1200s. These solid rockets were used for fireworks. Armies also used them in wars. In the next 700 years, people made bigger and better solid rockets. Many of these were used for wars too. In 1969, the United States launched the first men to land on the moon using a Saturn V rocket.
How Does NASA Use Rockets?
Early NASA missions used rockets built by the military. Alan Shepard was the first American in space. He flew on the U.S. Army’s Redstone rocket. John Glenn was the first American in orbit. He flew on an Atlas rocket. NASA’s Gemini missions used the Titan II rocket. The first rockets NASA built to launch astronauts were the Saturn I, the Saturn IB and the Saturn V. These rockets were used for the Apollo missions. The Apollo missions sent men to the moon. A Saturn V also launched the Skylab space station. The space shuttle uses rocket engines.
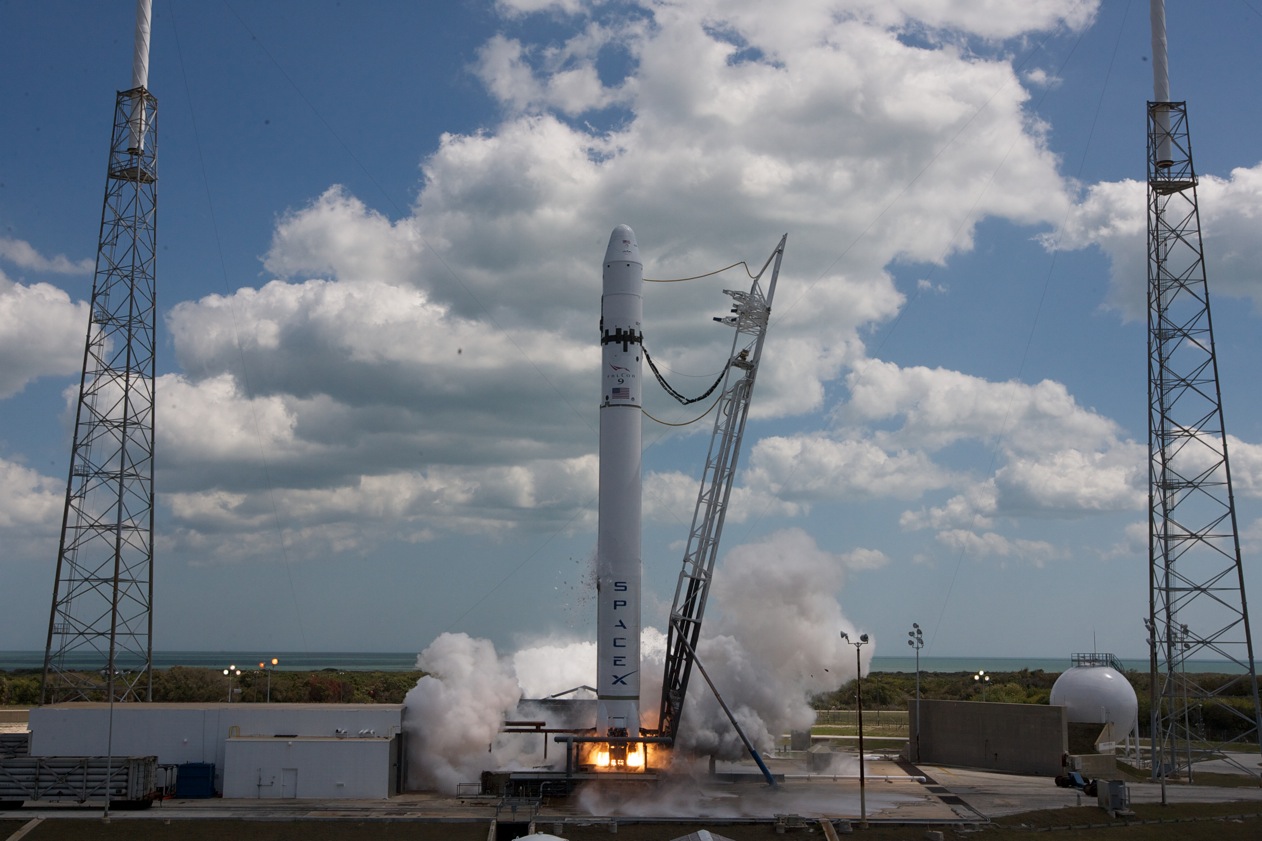
NASA uses rockets to launch satellites. It also uses rockets to send probes to other worlds. These rockets include the Atlas V, the Delta II, the Pegasus and Taurus. NASA uses smaller “sounding rockets” for scientific research. These rockets go up and come back down. They do not fly into orbit.
How Will NASA Use Rockets in the Future?
New rockets are being developed today. They will launch astronauts on future missions.
The new rockets will not look like the space shuttle. These rockets will look more like earlier ones. They will be tall and round and thin. These rockets will take astronauts into space. They will take supplies to the International Space Station. NASA also is working on a powerful new rocket called a heavy lift vehicle. This rocket will be able to take big loads into space.
Together, these new rockets will make it possible to explore other worlds. Someday they may send humans to Mars.