Jet Propulsion Laboratory – Current Missions
Missions and instruments built or managed by JPL have visited every planet in our solar system and the sun and have entered interstellar space.

NISAR
Using advanced radar imaging that will provide an unprecedented, detailed view of Earth, the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar, or NISAR, satellite is designed to observe and take measurements of some of the planet's most complex processes.

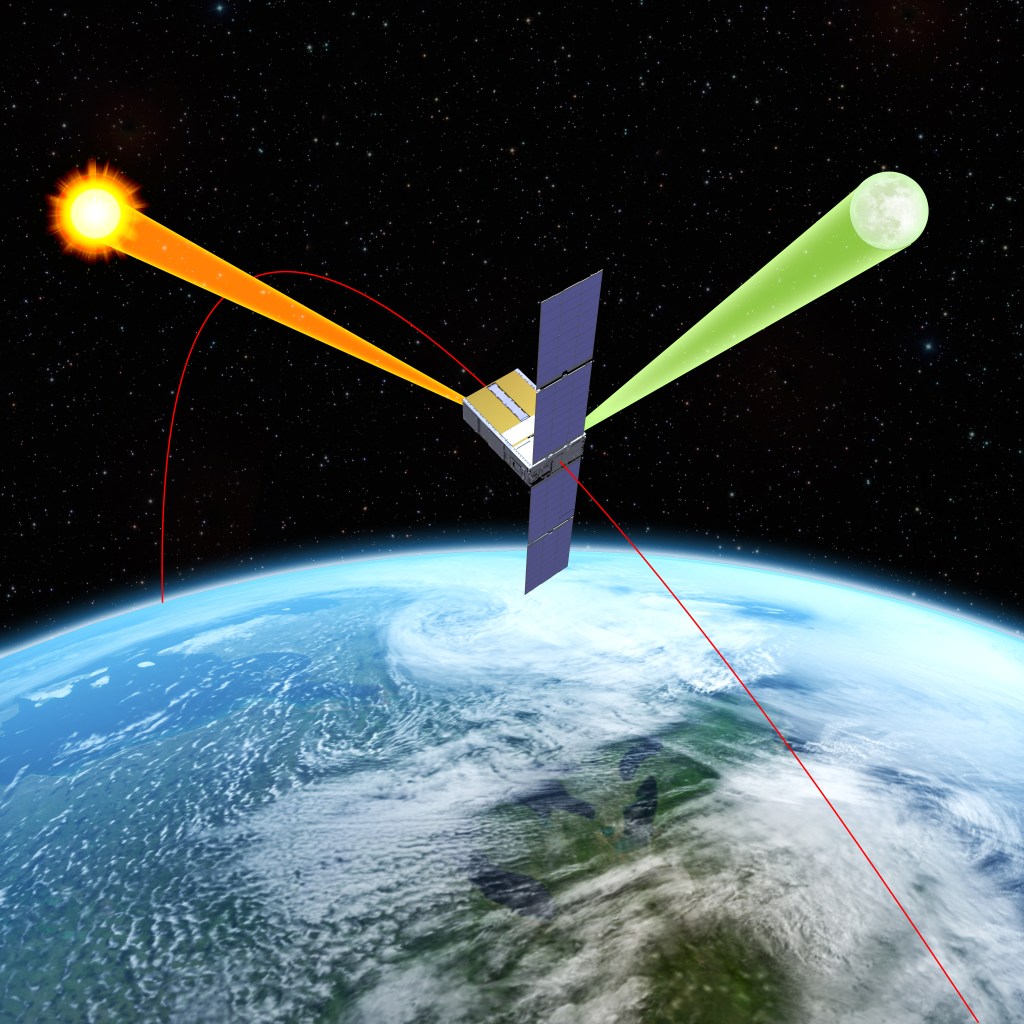
Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC)
The experiment will aim to demonstrate high-bandwidth communications in deep space for the first time.
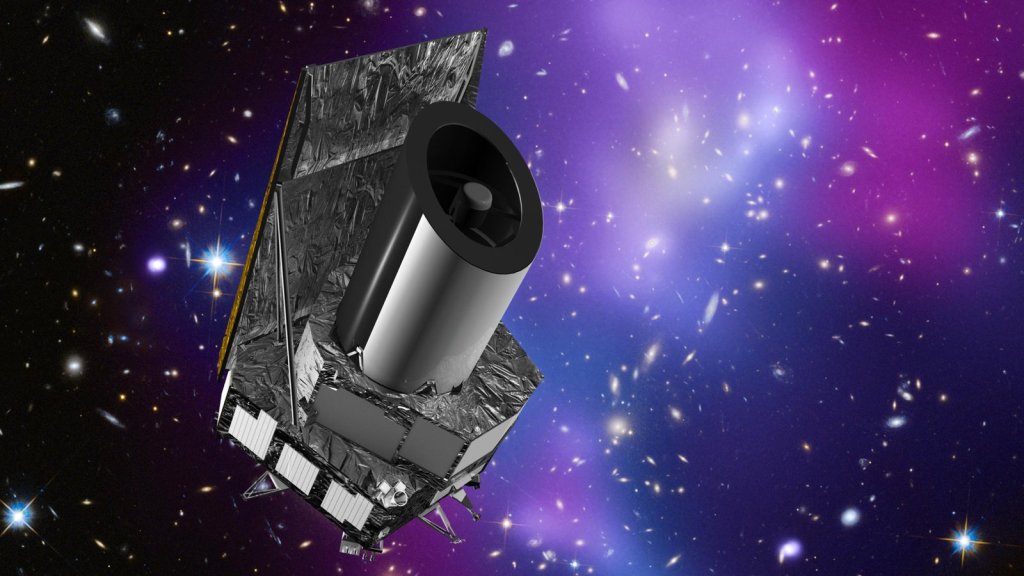

Euclid
Euclid will investigate the profound cosmic mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, both thought to be key components of our cosmos.
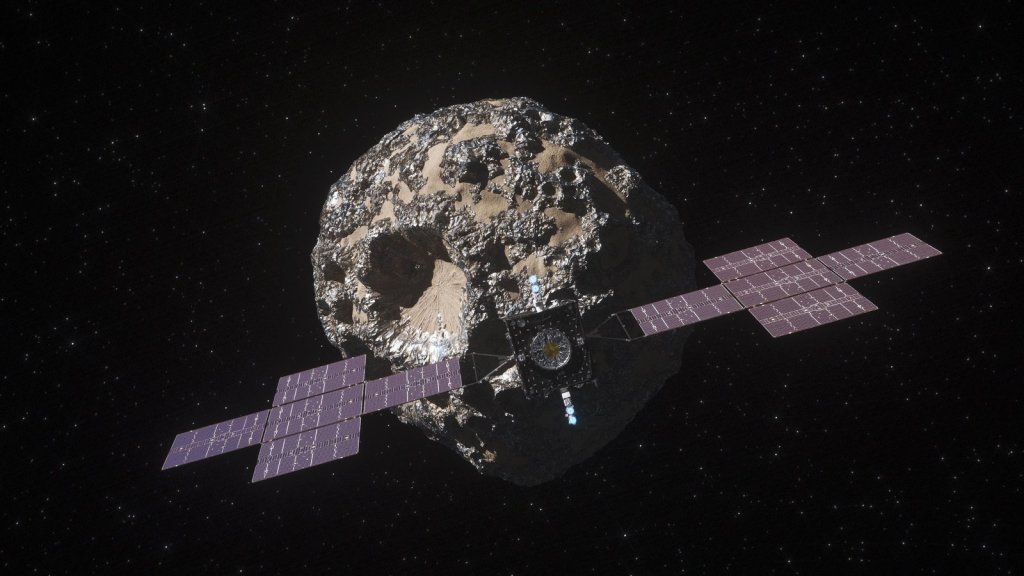

Psyche
The Psyche mission is a journey to a unique metal-rich asteroid orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter.
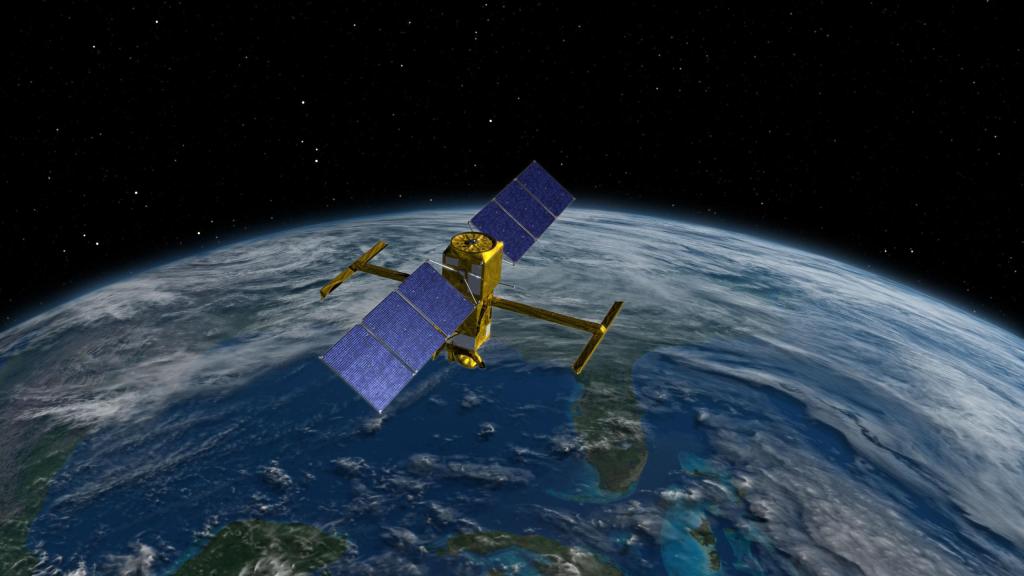

Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT)
Designed to make the first-ever global survey of Earth's surface water, the Surface Water and Ocean Topography, or SWOT, satellite will collect detailed measurements of how water bodies on Earth change over time.
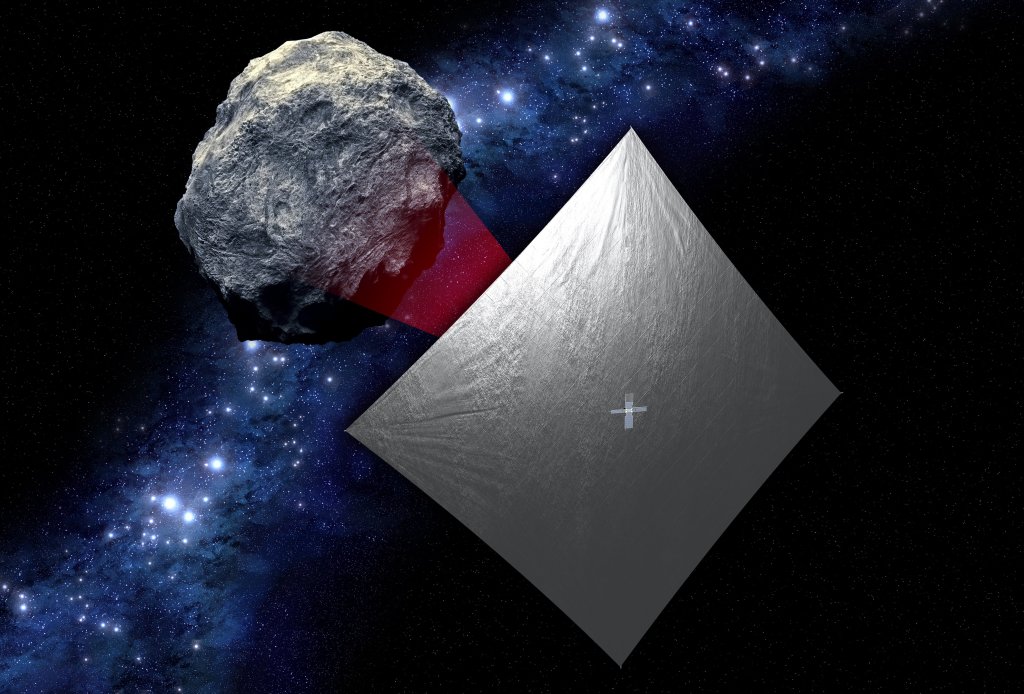
Near Earth Asteroid Scout (NEA Scout)
NEA Scout is an exciting new mission that was recently selected by NASA's Advanced Exploration Systems (AES) by a team from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Marshall Space Flight Center.

Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT)
The Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) is an Earth Ventures-Instrument (EVI-4) Mission to map the mineral composition of arid dust source regions via imaging spectroscopy in the visible and short-wave infrared range.
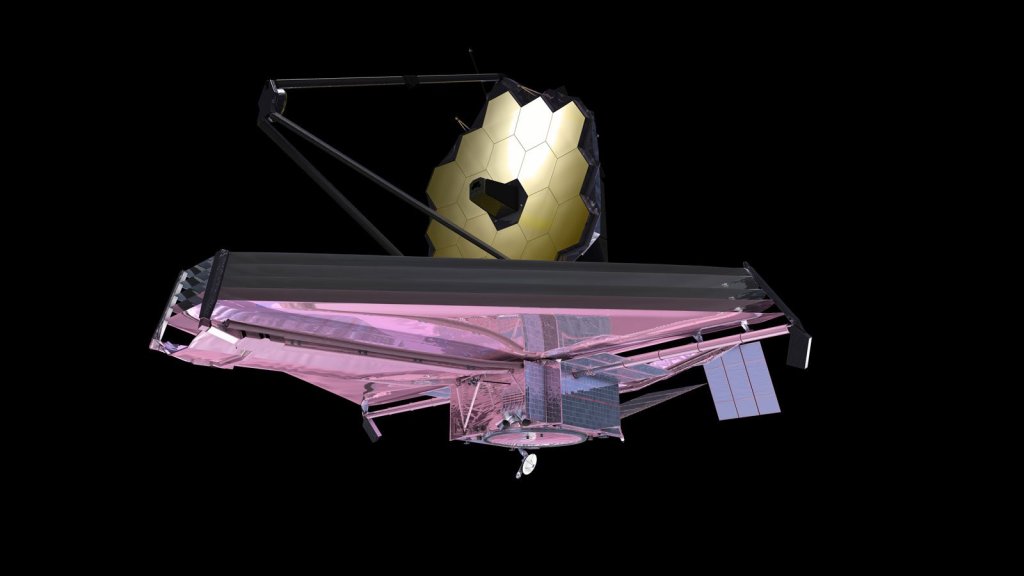
Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI)
One of four instruments on the James Webb Space Telescope, the Mid-Infrared Instrument, or MIRI, studies planets, stars, and galaxies in infrared light.
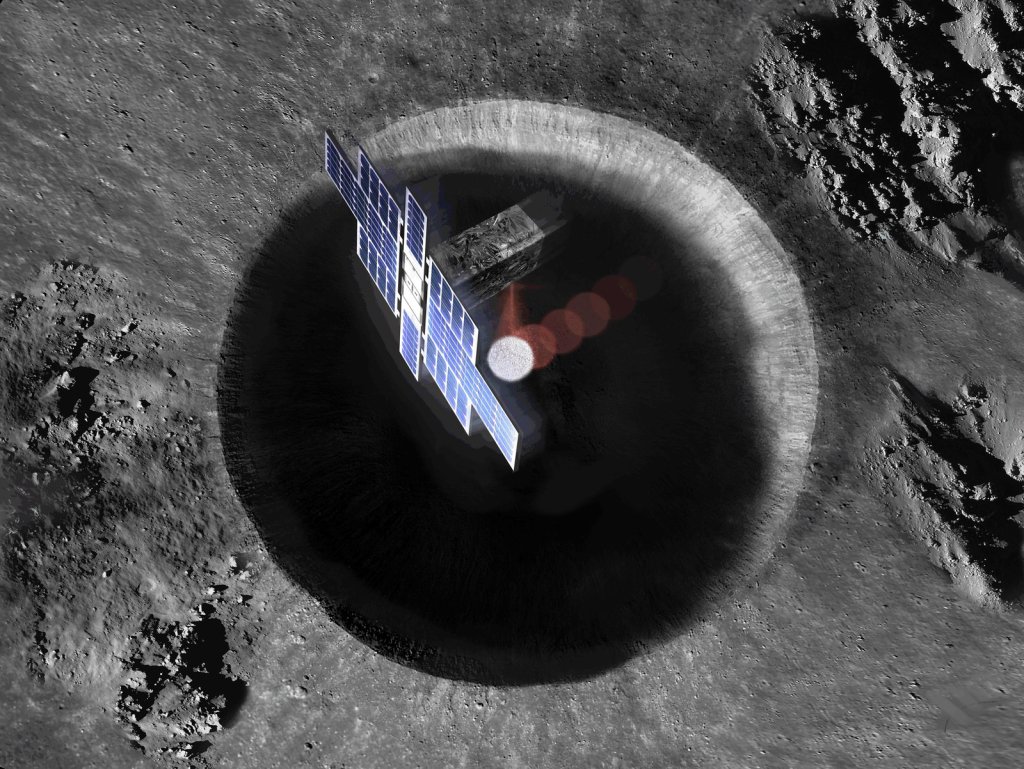
Lunar Flashlight
Roughly the size of a briefcase, Lunar Flashlight is a very small satellite being developed and managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that will use near-infrared lasers and an onboard spectrometer to map ice in permanently shadowed regions near the Moon's south pole.
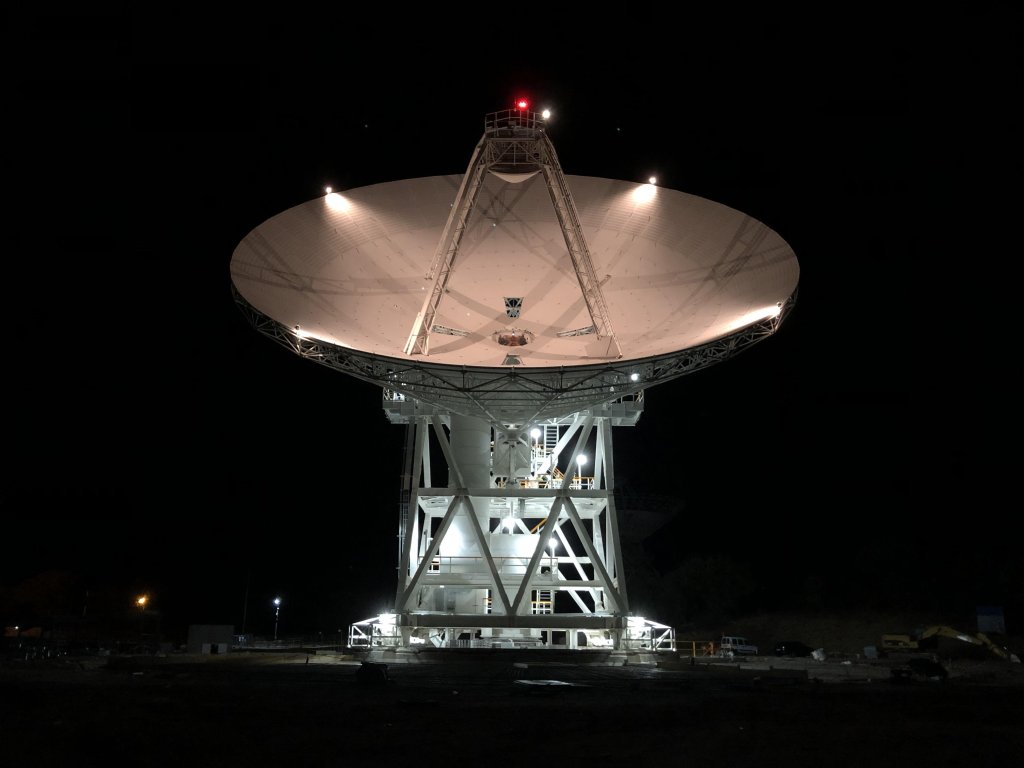

Deep Space Network
The Deep Space Network is NASA’s international network of facilities used to communicate with faraway spacecraft exploring our solar system.
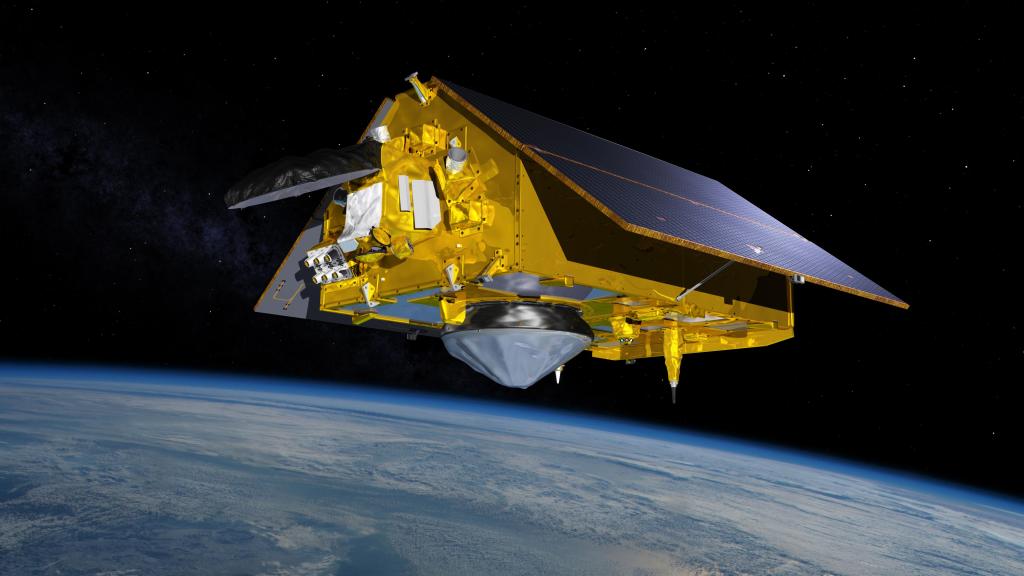

Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich Satellite
Designed to measure the height of the ocean – a key component to understanding how Earth's climate is changing – Sentinel-6/Jason CS consists of two identical satellites that will be launched five years apart.
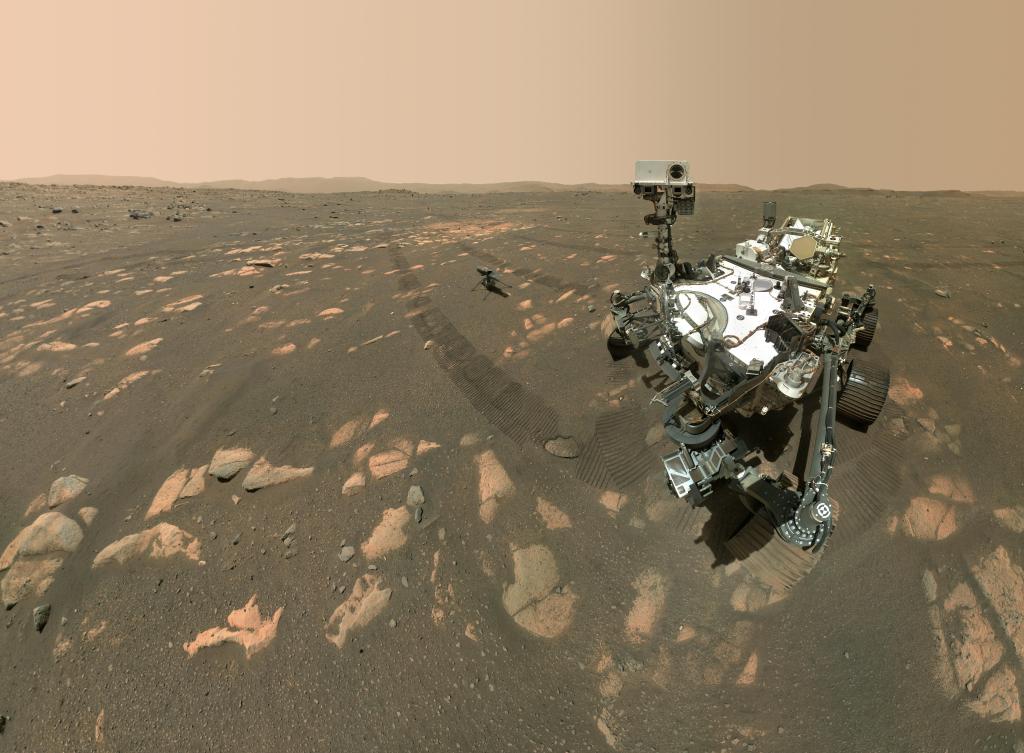

Perseverance Rover
The Mars 2020 mission with its Perseverance rover is the first step of a roundtrip journey to return Mars samples to Earth for further study.
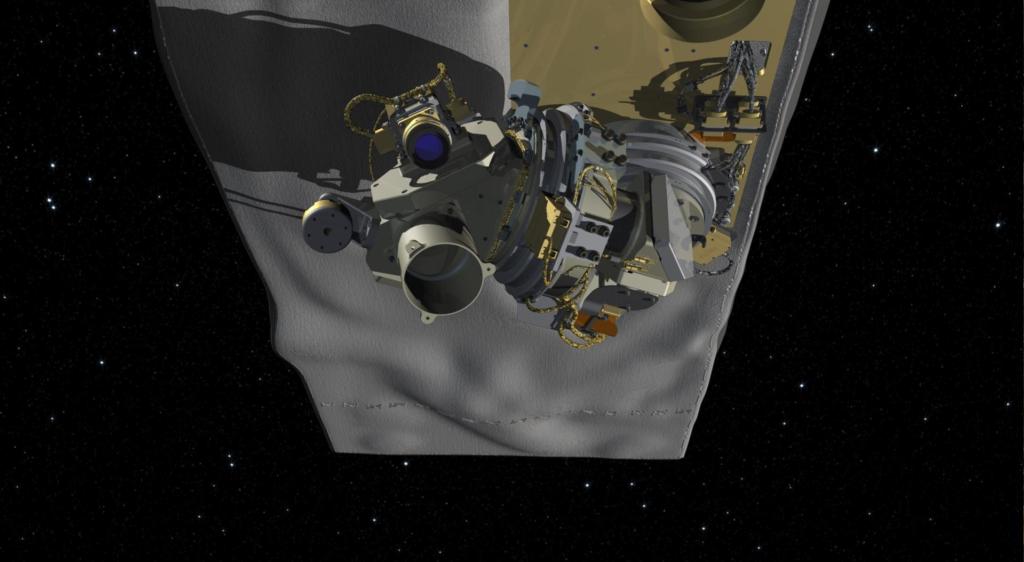

Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, is a space instrument designed to investigate important questions about the distribution of carbon dioxide on Earth as it relates to growing urban populations and changing patterns of fossil fuel combustion.
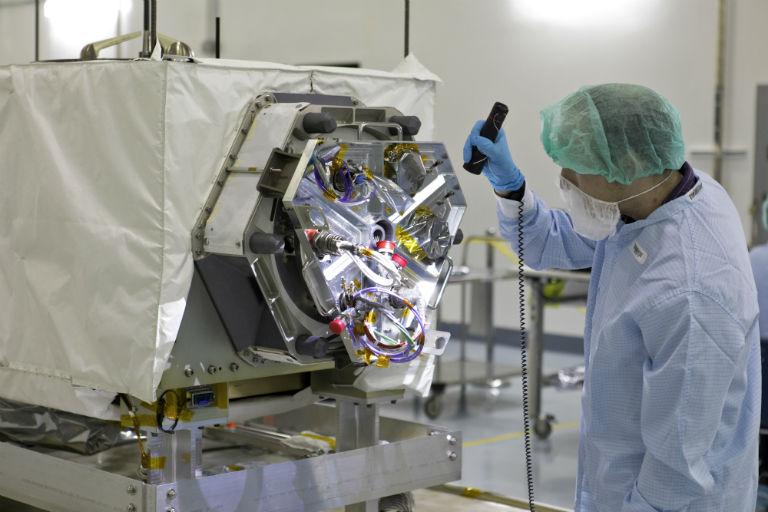

ECOSTRESS
The ECOsystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS), will monitor one of the most basic processes in living plants: the loss of water through the tiny pores in leaves.
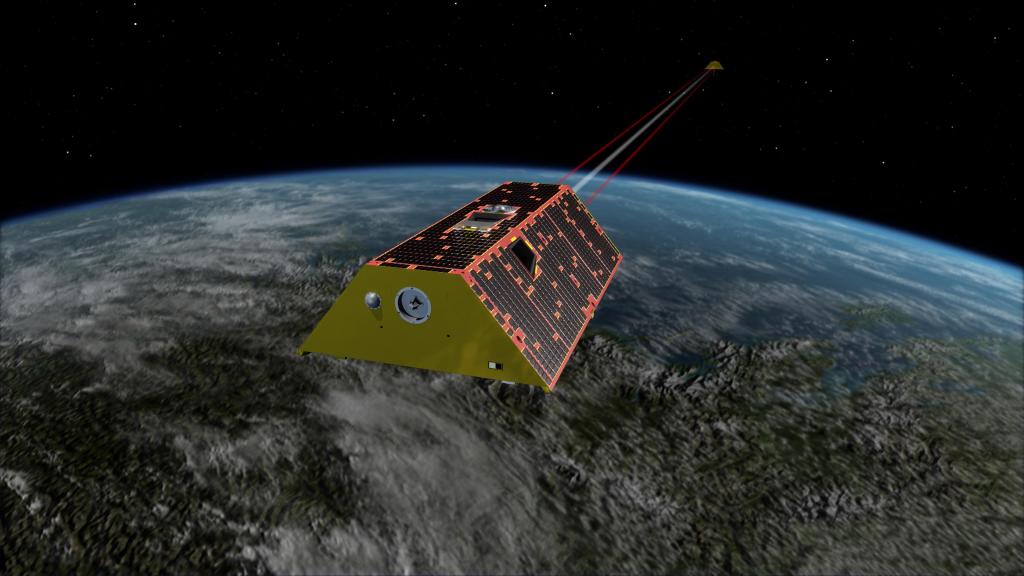

GRACE-FO
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-on (GRACE-FO) measures changes in Earth’s gravity field in order to track water movement and surface mass changes across the planet.
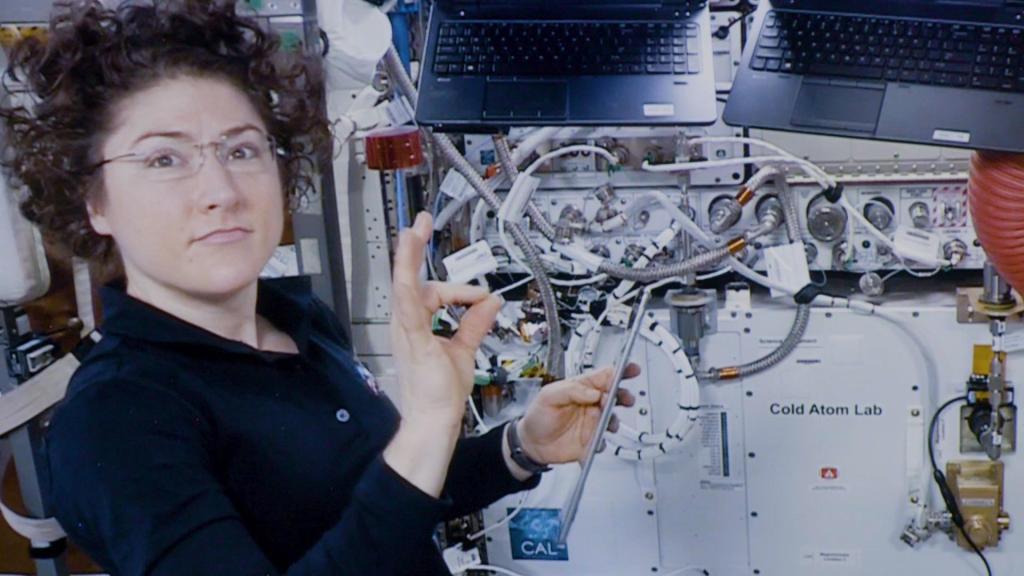
Cold Atom Laboratory
A facility aboard the International Space Station, the Cold Atom Laboratory, will makes use of the space station's microgravity environment to study quantum phenomena in ways that aren’t possible on Earth.
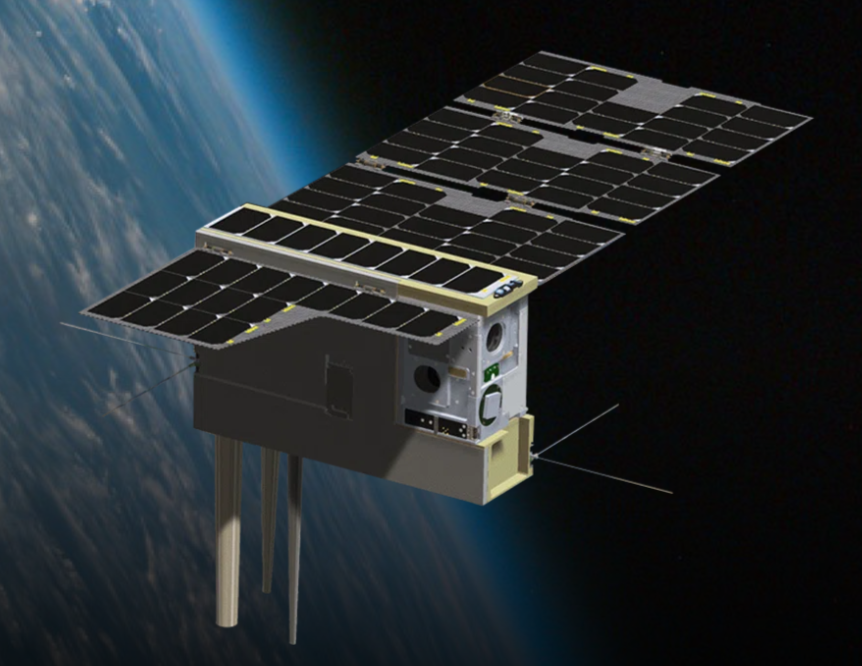

CubeRRT
The main objective of the CubeRRT mission is to demonstrate the RFI mitigation technology on a flight-ready hardware in space, increasing the technology readiness level (TRL) from 6 to 7.
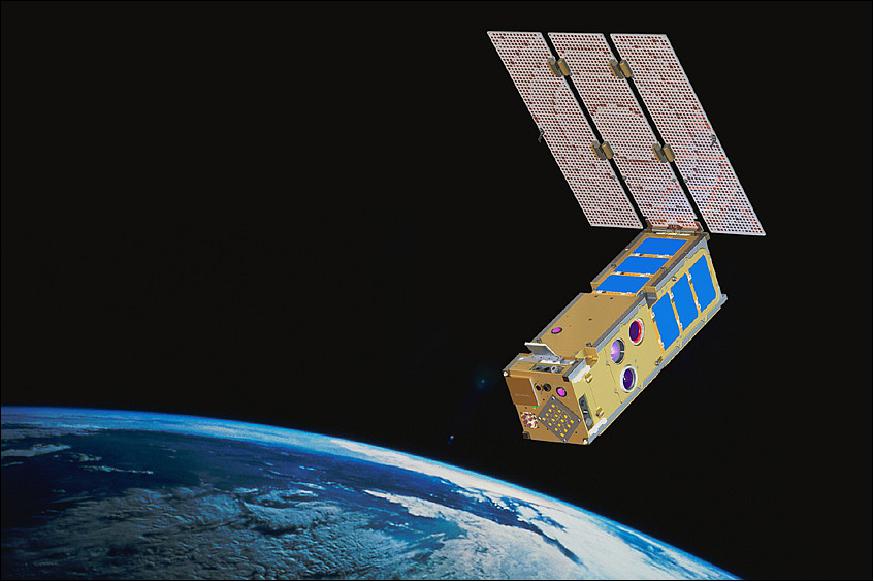

ISARA
The ISARA mission will demonstrate a high bandwidth Ka-band CubeSat communications capability that is ready for immediate infusion into commercial, government and military systems.
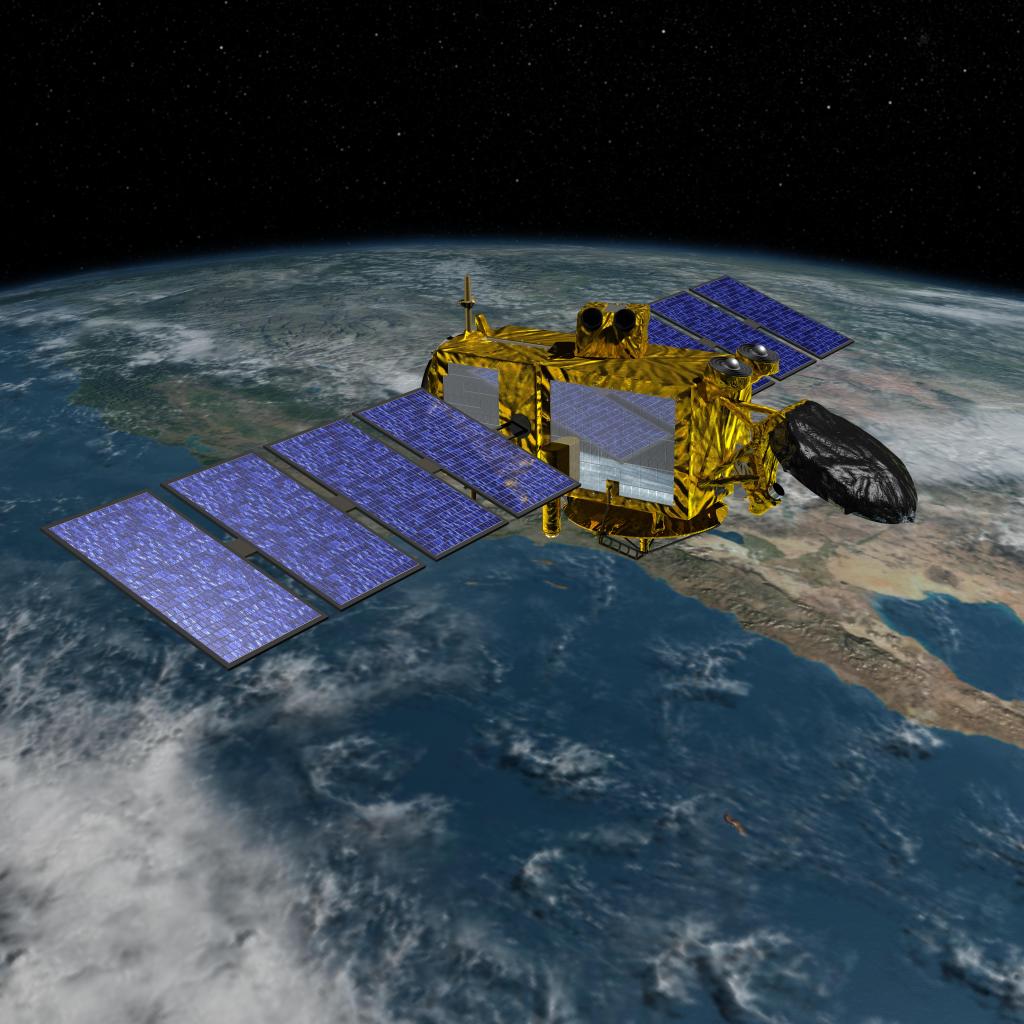

Jason-3
Extending the timeline of ocean surface topography measurements begun by the Topex/Poseidon and Jason-1 and-2 satellites, Jason-3 will make highly detailed measurements of sea-level on Earth to gain insight into ocean circulation and climate change.
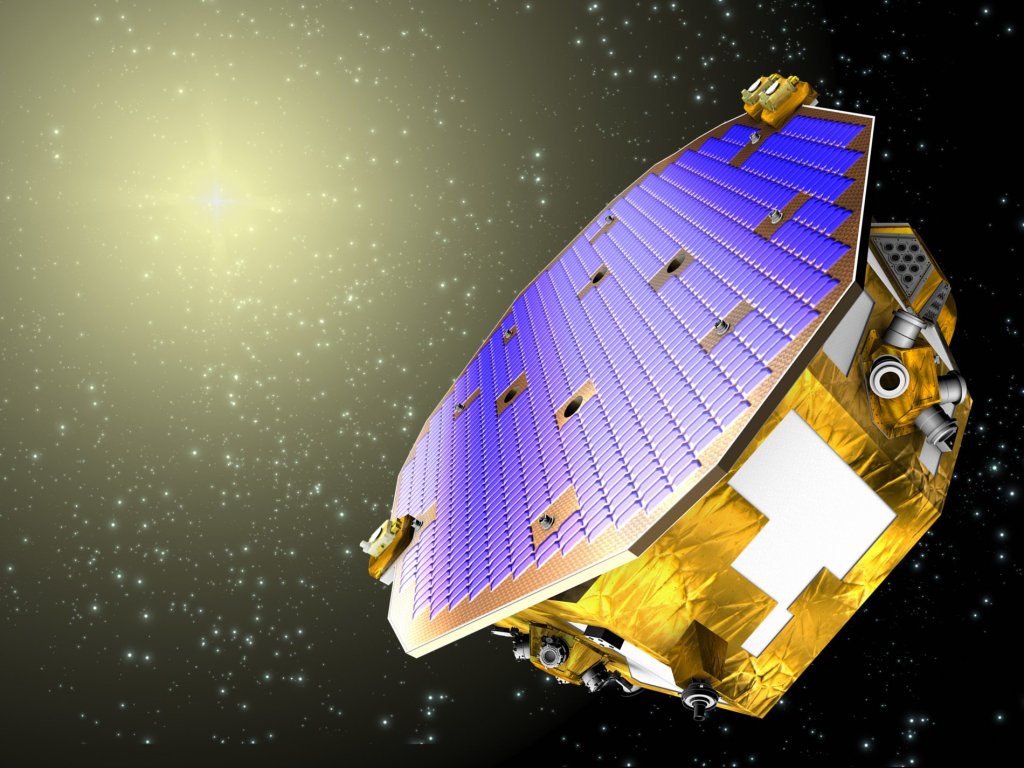

Disturbance Reduction System
The Disturbance Reduction System, or DRS, designed as part of the Space Technology 7 project, is an experimental system for measuring gravitational waves in space, which are thought to contain important data about the history of the universe.
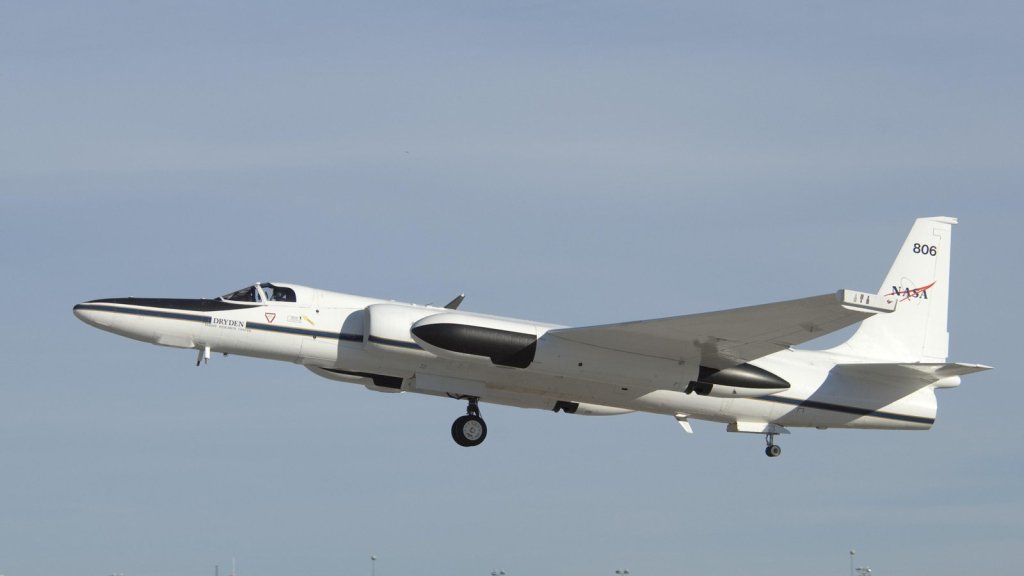

AVIRIS-NG
AVIRIS-NG has been developed to provide continued access to high signal-to-noise ratio imaging spectroscopy measurements in the solar reflected spectral range.
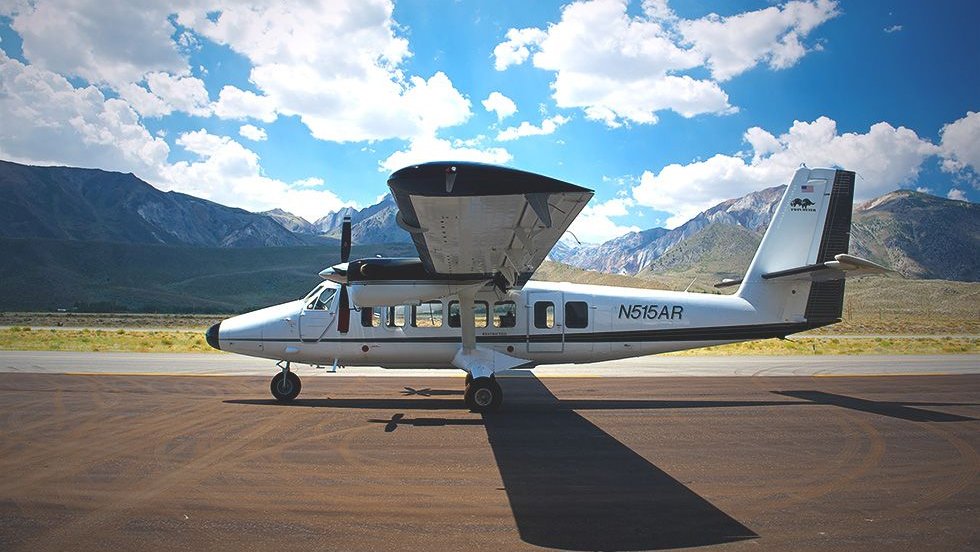

PRISM
A compact, lightweight, airborne Portable Remote Imaging SpectroMeter was developed to study natural and human-induced events, from tsunamis, to toxic blooms, and oil spills.
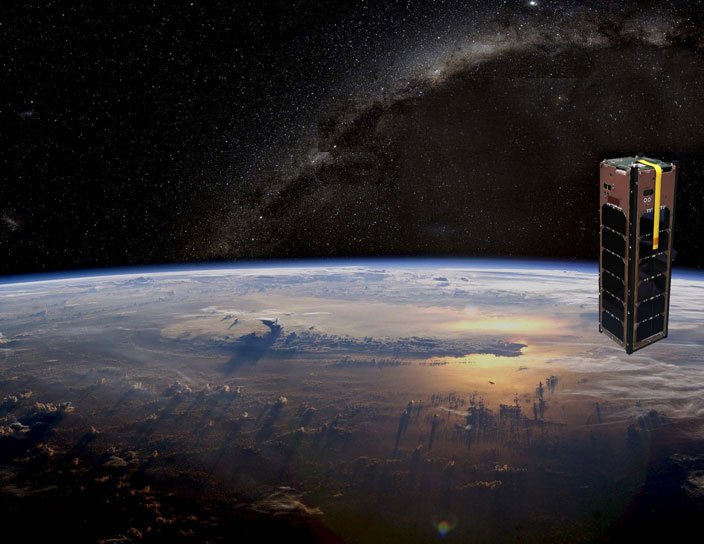

GRIFEX
The GEO-CAPE ROIC In-Flight Performance Experiment (GRIFEX) is a 3U CubeSat that will perform engineering assessment of a JPL-developed all digital in-pixel high frame rate Read-Out Integrated Circuit (ROIC).
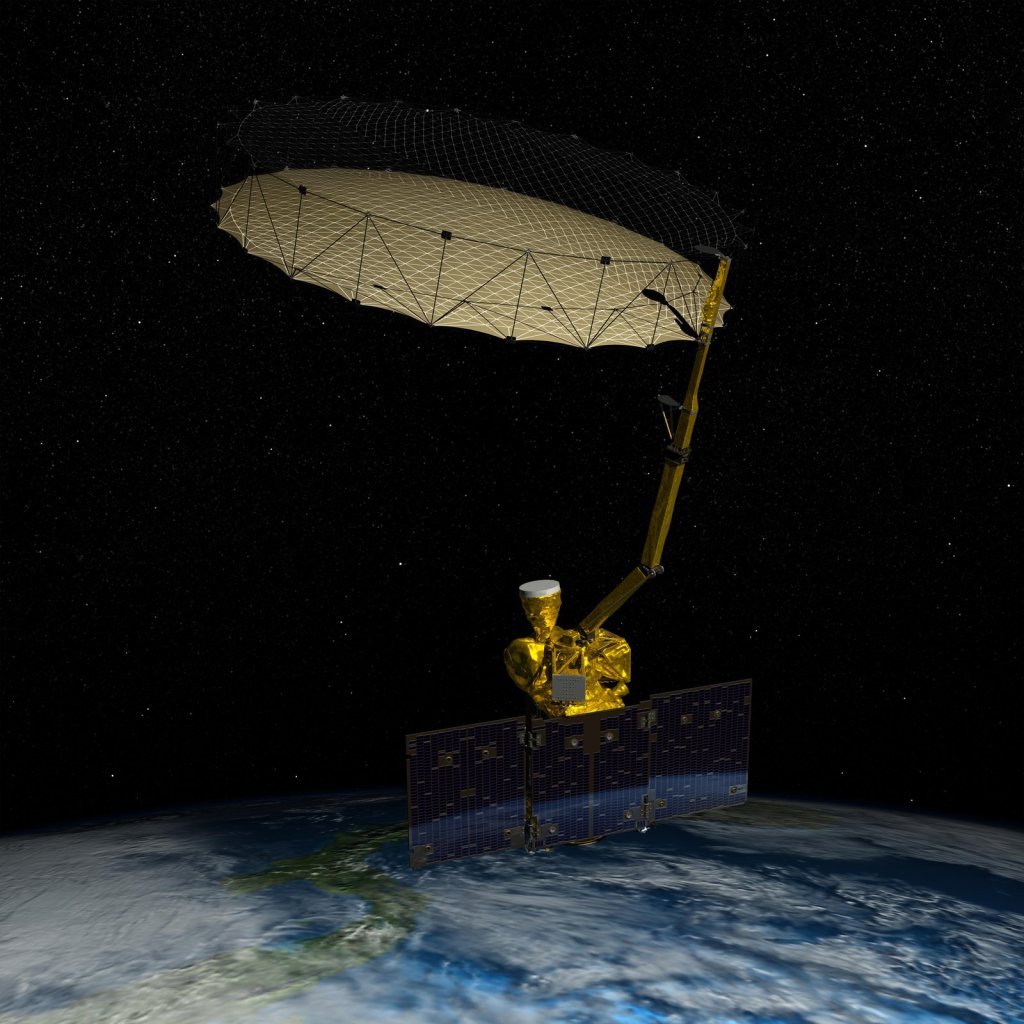
SMAP
Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, is an Earth satellite mission designed to measure and map Earth's soil moisture and freeze/thaw state to better understand terrestrial water, carbon and energy cycles.
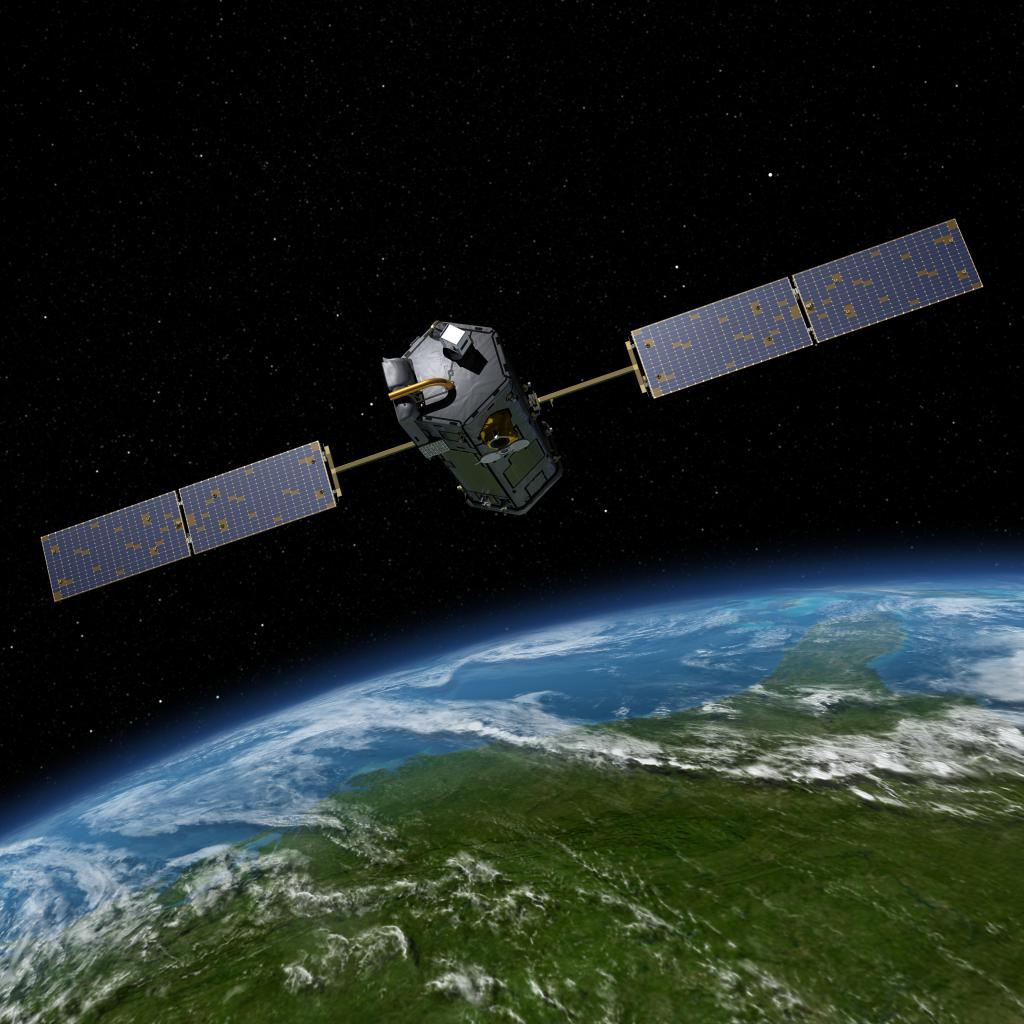

Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2, or OCO-2, is an Earth satellite mission designed to study the sources and sinks of carbon dioxide globally and provide scientists with a better idea of how carbon is contributing to climate change.

Airborne Snow Observatory
The Airborne Snow Observatory is an Earth-based mission designed to collect data on the snow melt flowing out of major water basins in the western United States.
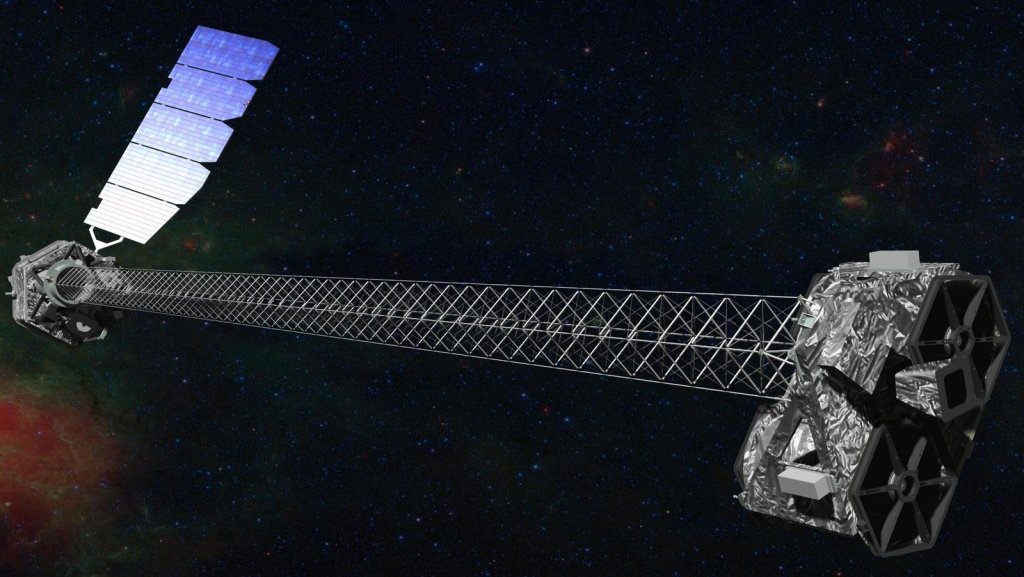
NuSTAR
The Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, mission studies the universe in high energy X-rays to better understand the dynamics of black holes, exploding stars and the most extreme active galaxies.
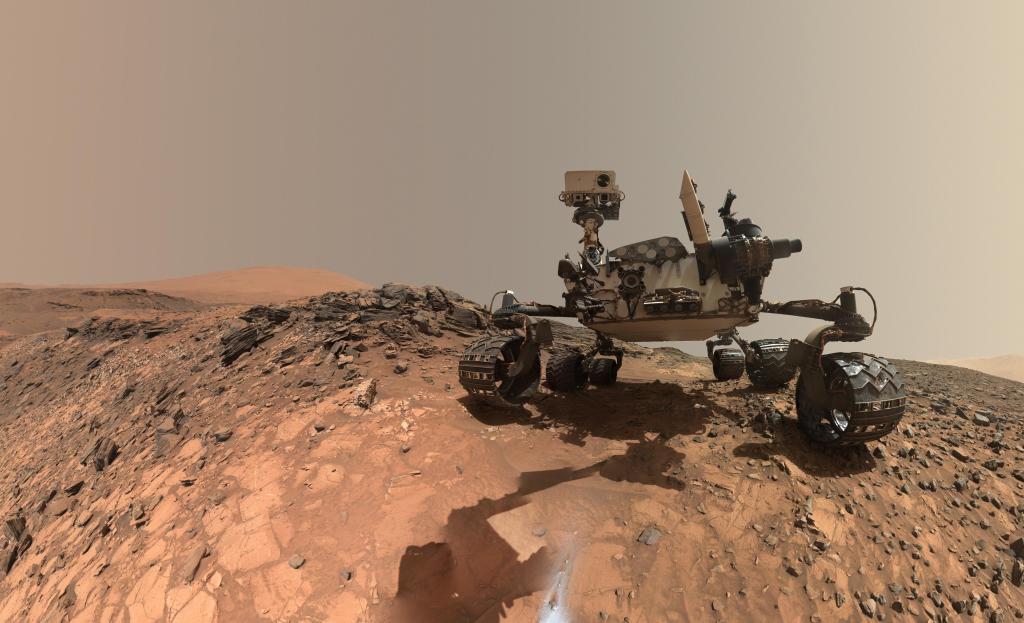

Curiosity Rover
The Mars Science Laboratory mission's Curiosity rover landed in Mars' Gale Crater the evening of August 5, 2012, PDT. Curiosity's mission is to determine whether the Red Planet ever was habitable to microbial life.
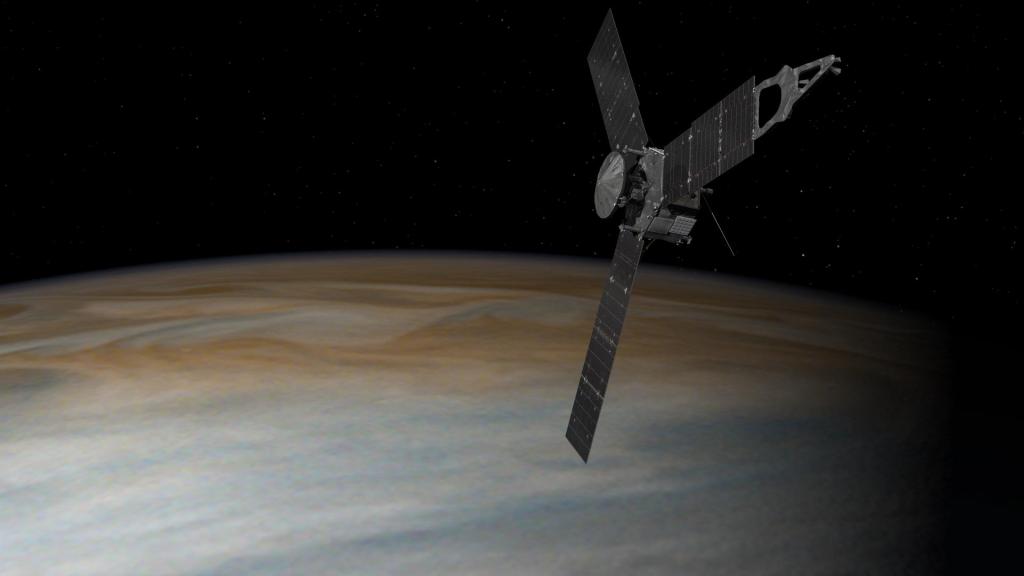

Juno
The Juno spacecraft, which entered orbit around Jupiter on July 4, 2016, is the first explorer to peer below the planet's dense clouds to answer questions about the gas giant itself and the origins of our solar system.
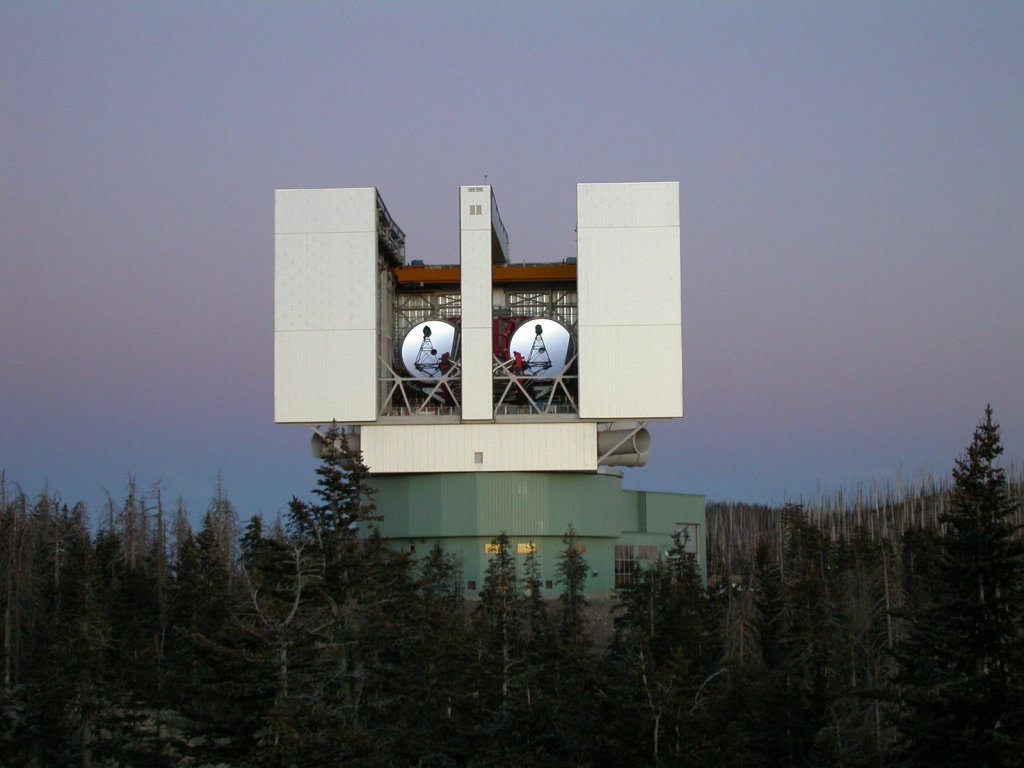

Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer
The Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer, or LBTI, is a ground-based instrument connecting two 8-meter class telescopes on Mount Graham in Arizona to form the largest single-mount telescope in the world.
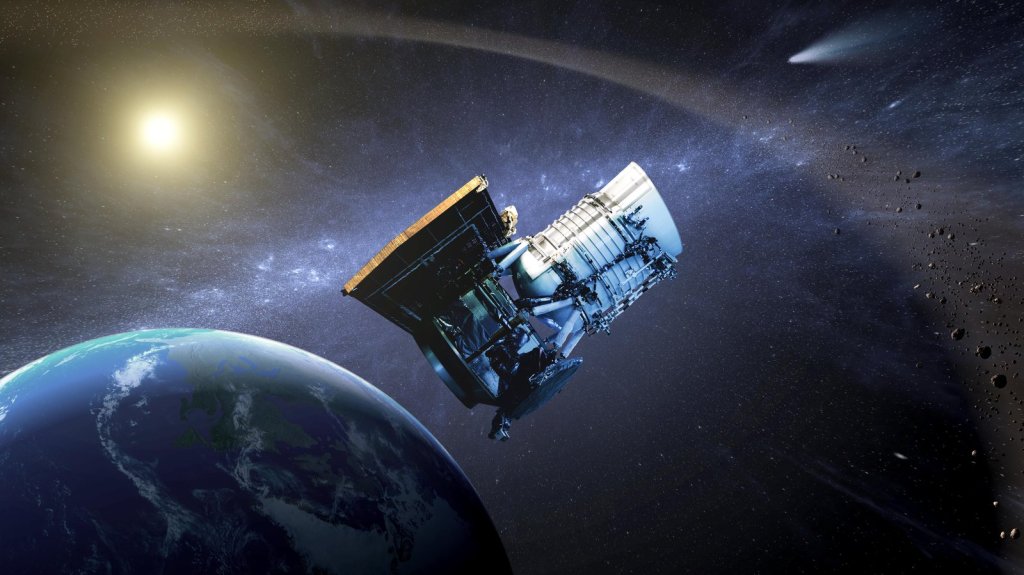

NEOWISE
The NEOWISE mission uses a space telescope to hunt for asteroids and comets, including those that could pose a threat to Earth.
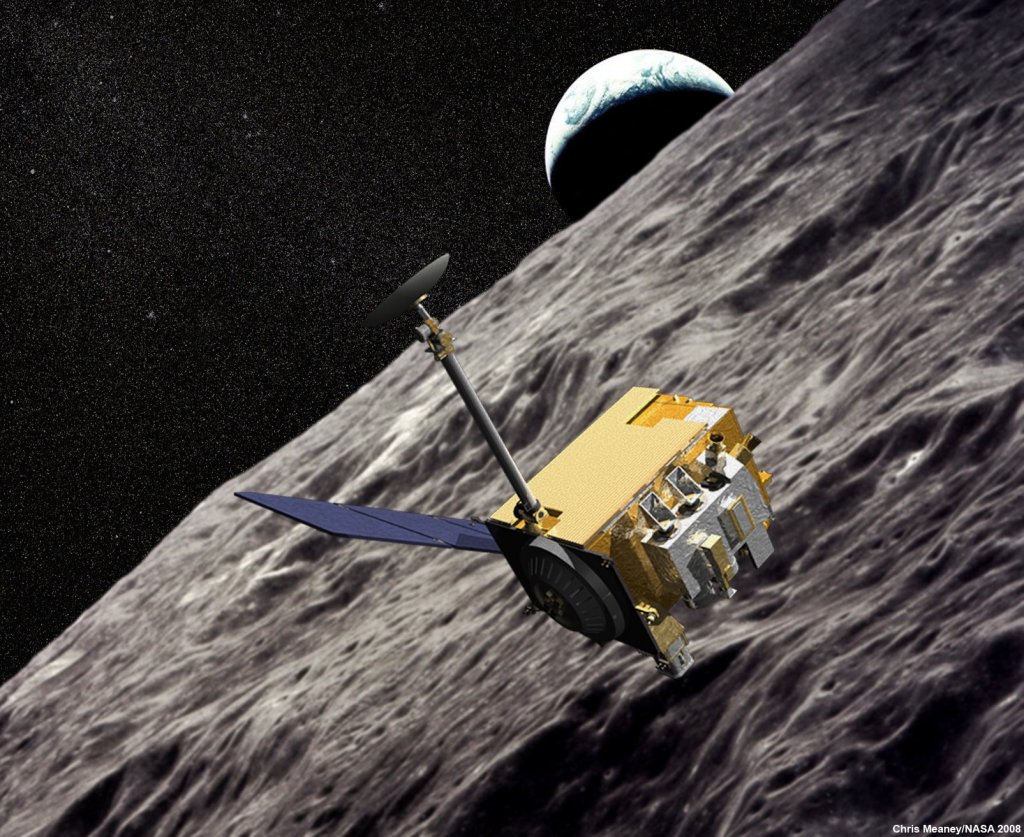

Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment
An instrument flying aboard NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Experiment is designed to measure surface temperatures on the moon, providing key information for future lunar surface operations and exploration.
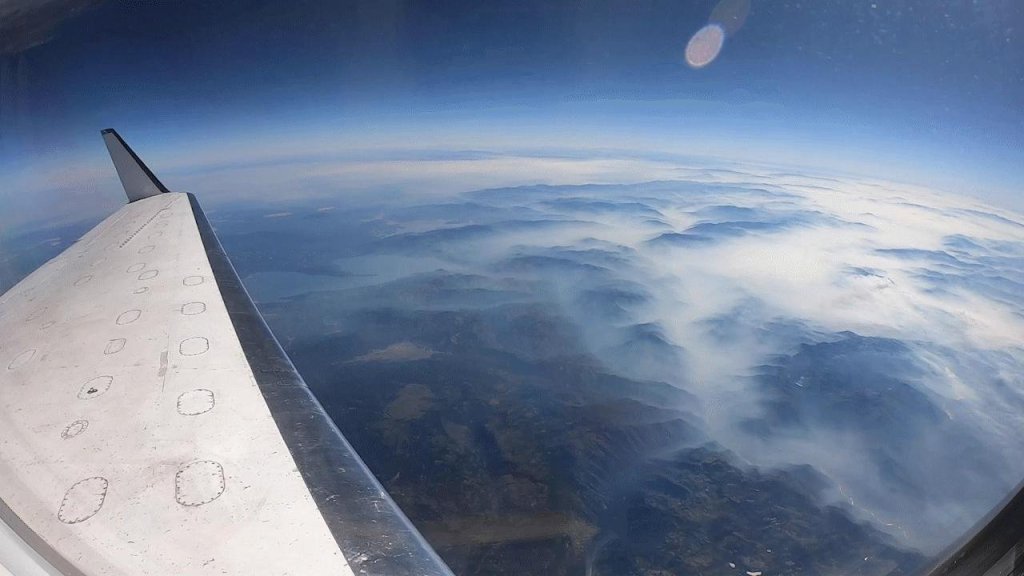

Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar
The Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar, or UAVSAR, is an imaging radar instrument that collects key measurements of Earth deformation.
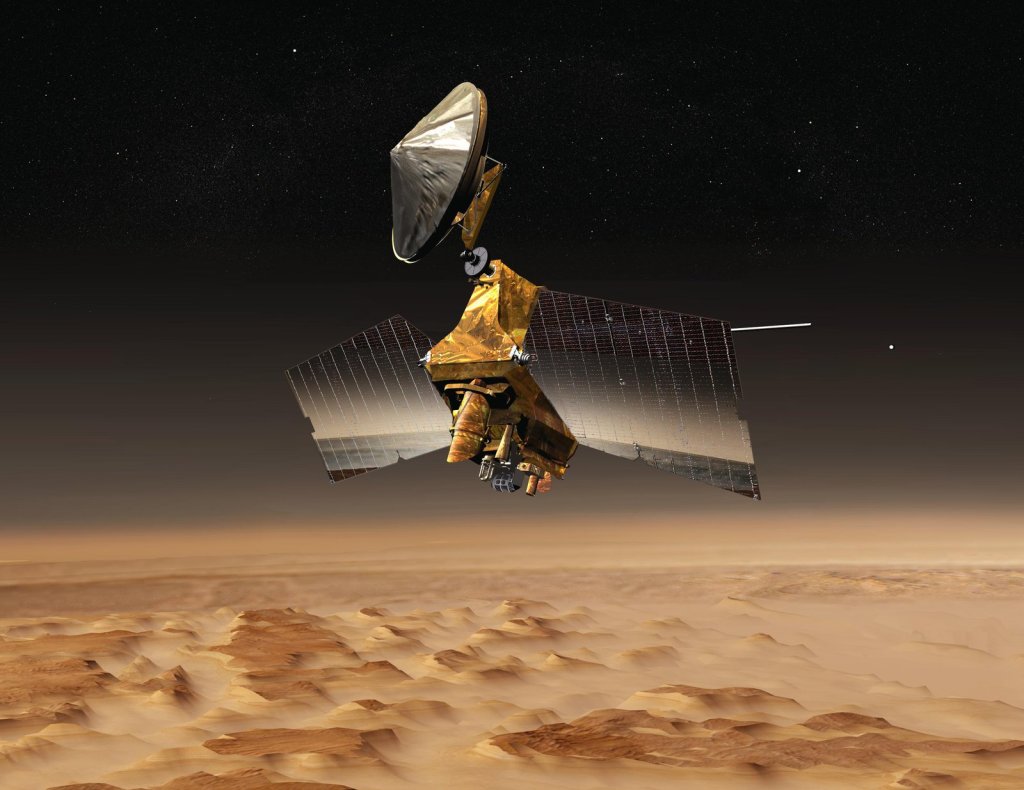

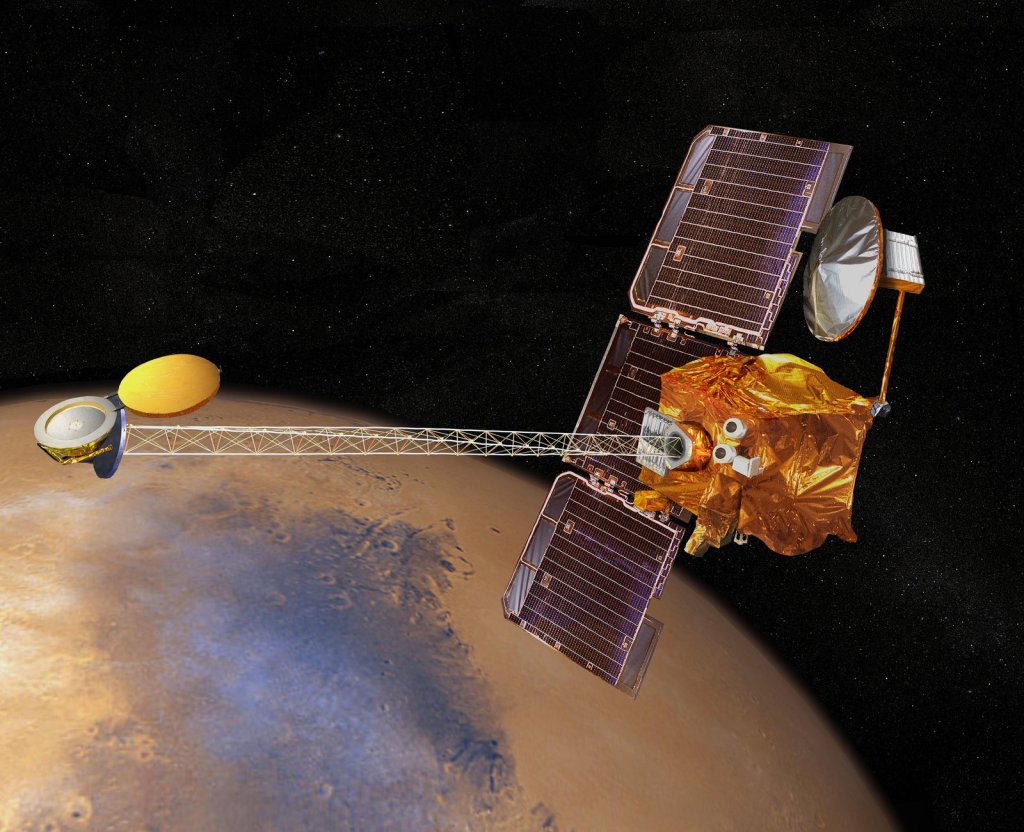
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, or MRO, has studied the Red Planet's atmosphere and terrain from orbit since 2006 and also serves as a key data relay station for other Mars missions.
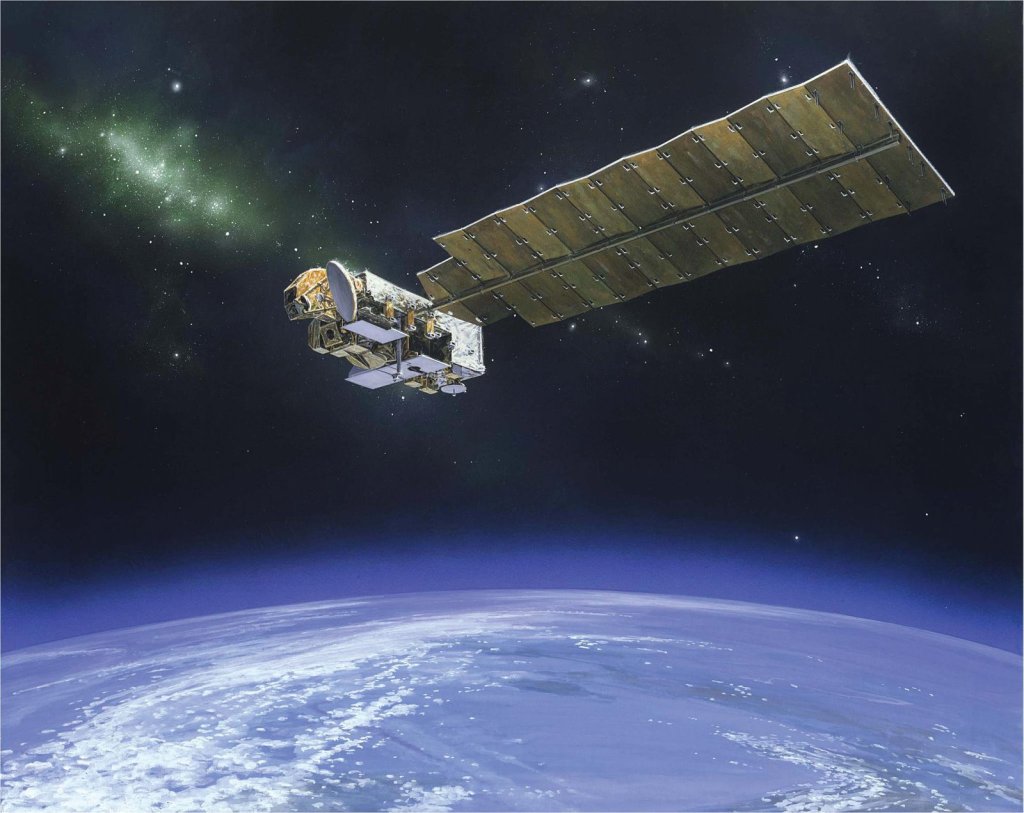

Microwave Limb Sounder
Making up one piece of the most advanced and accurate atmospheric chemistry laboratory ever deployed in space, the Microwave Limb Sounder, or MLS, instrument flies aboard NASA's Aura Earth satellite with three other instruments.

Atmospheric Infrared Sounder
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, or AIRS, instrument is a key tool for climate studies on greenhouse gases and carbon dioxide distribution, as well as weather forecasts.

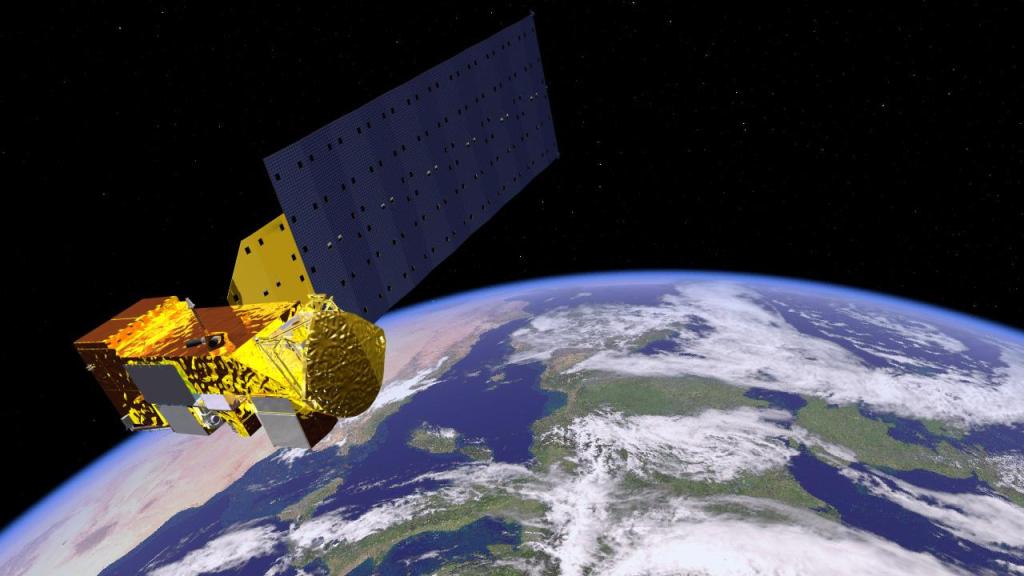
Mars Odyssey
With more than 20 years in orbit and counting, the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft has spent more time in orbit around the Red Planet, collecting data on Mars' climate and geology, than any other spacecraft in history.
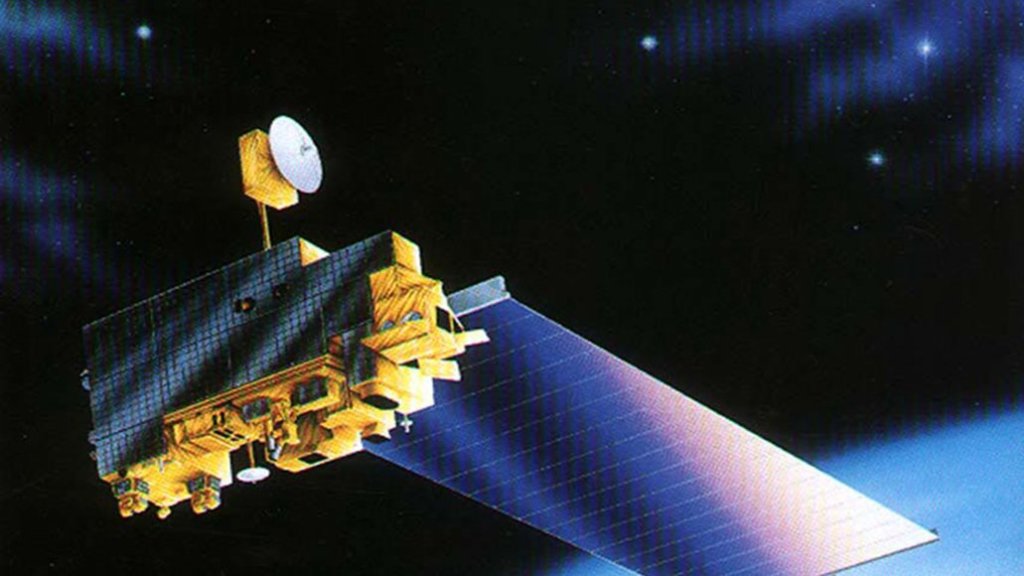

ASTER
Designed to capture high-resolution images of Earth, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer, or ASTER, instrument is one of five instruments aboard NASA's Terra satellite.
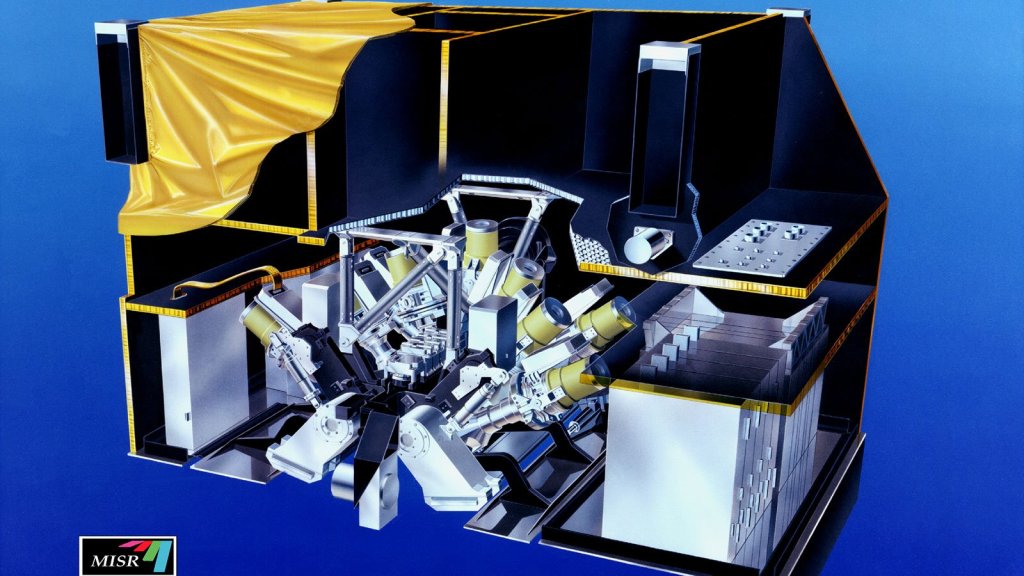

MISR
The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer, or MISR, instrument is one of five instruments aboard NASA's Terra satellite, which is collecting important data on the causes and effects of global climate change.
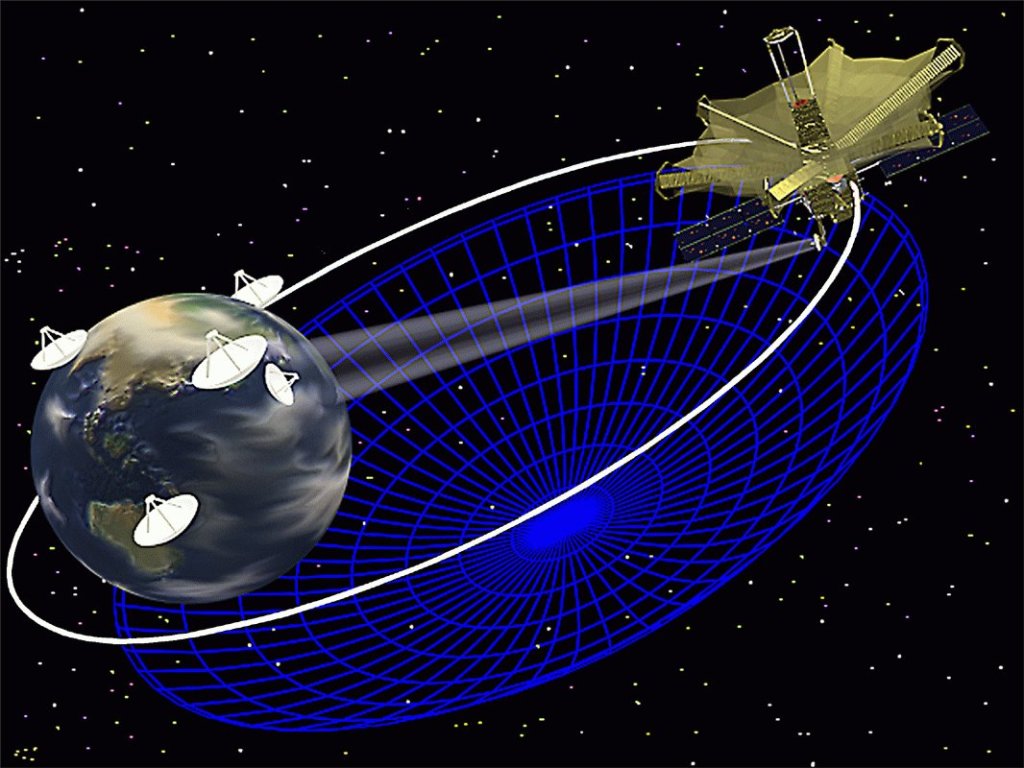
Space Very Long Baseline Interferometry
The Space Very Long Baseline Interferometry is a network of space- and Earth-based radio antennas that combine to create the equivalent of a telescope with a diameter more than two-and-a-half times the diameter of Earth.

Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer
AVIRIS is the first full spectral range imaging spectrometer and dedicated to Earth Remote Measurement.
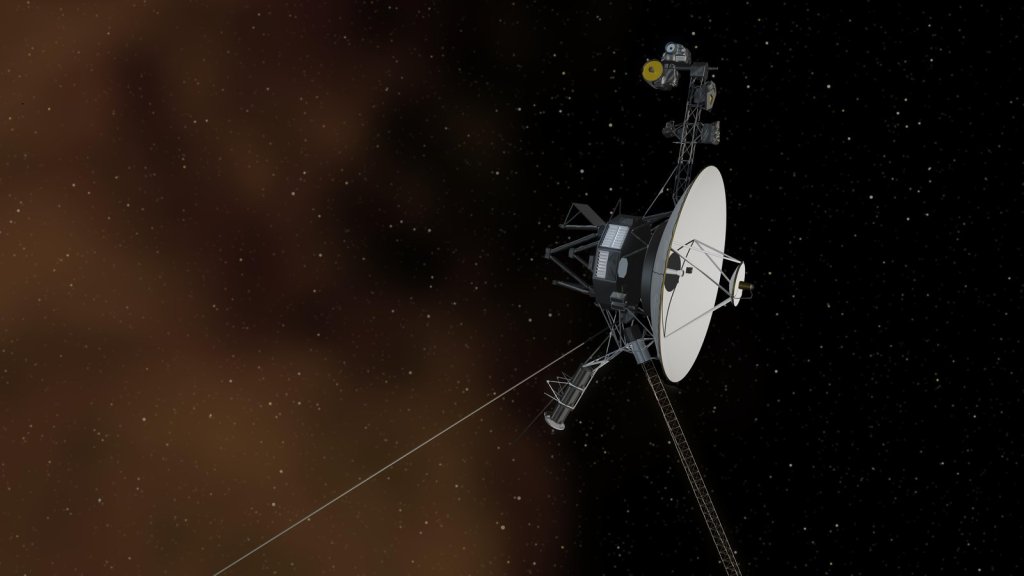

Voyager 1
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence.
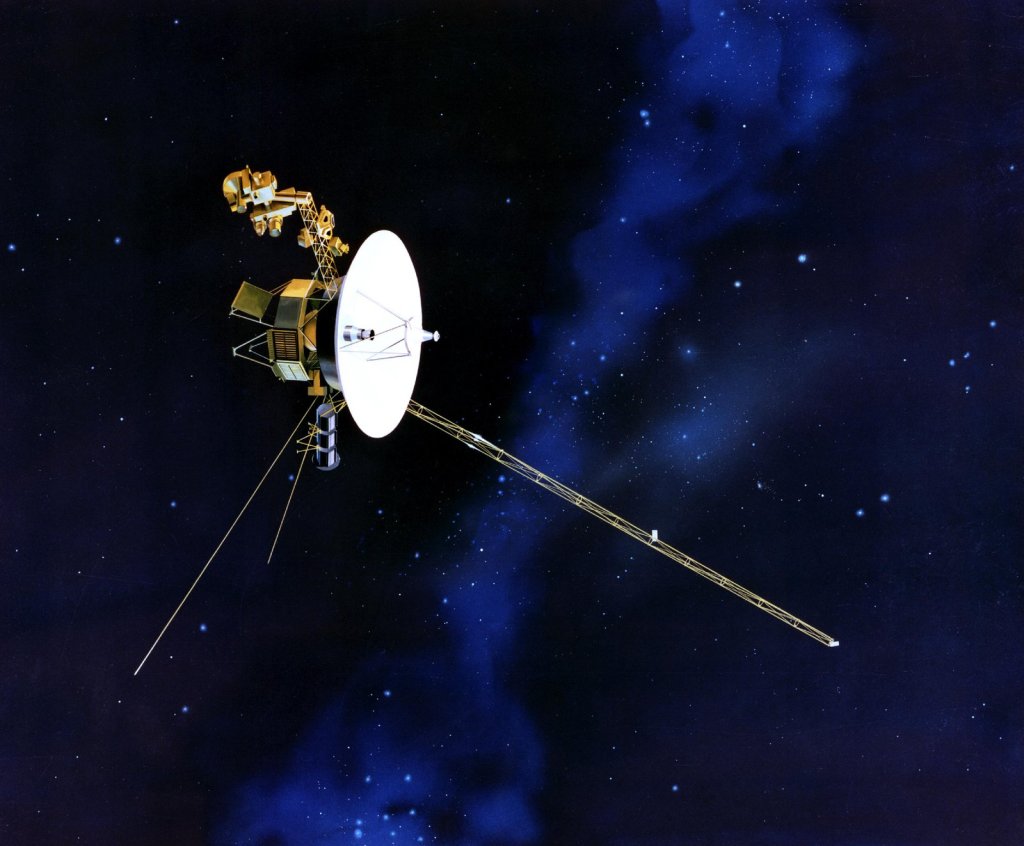

Voyager 2
The Voyager 2 spacecraft, which has been in operation since 1977 and is the only spacecraft to have ever visited Uranus and Neptune, has made its way to interstellar space, where its twin spacecraft, Voyager 1, has resided since August 2012.