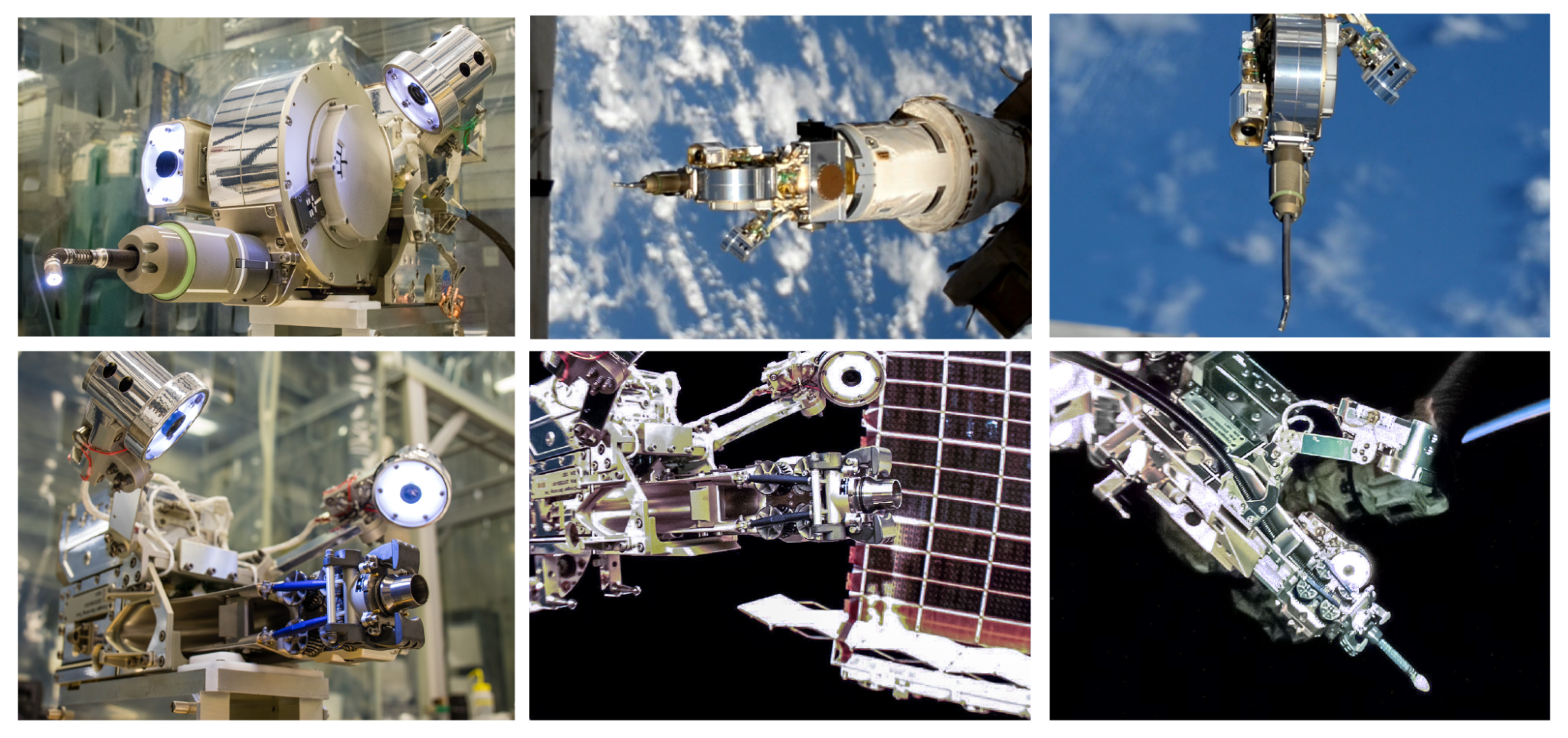
NASA’s Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) has successfully completed its second set of robotic tool operations on the International Space Station, demonstrating key techniques for transferring cryogenic fluids, used as coolants, propellants, or for life support systems in orbit. These technologies have applications for extending spacecraft life and facilitating exploration to the Moon and Mars.
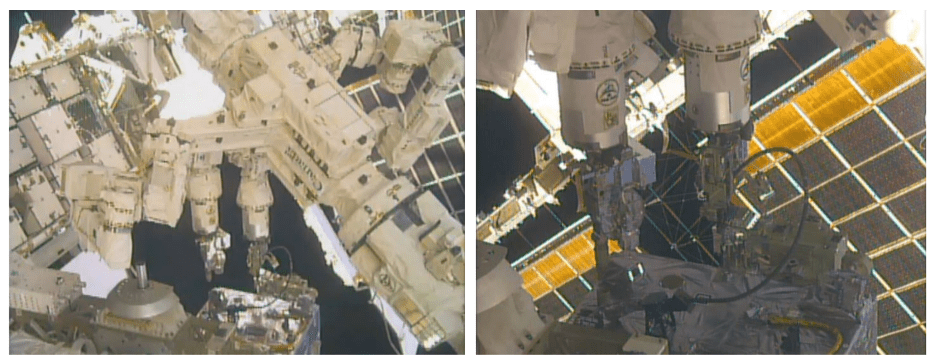
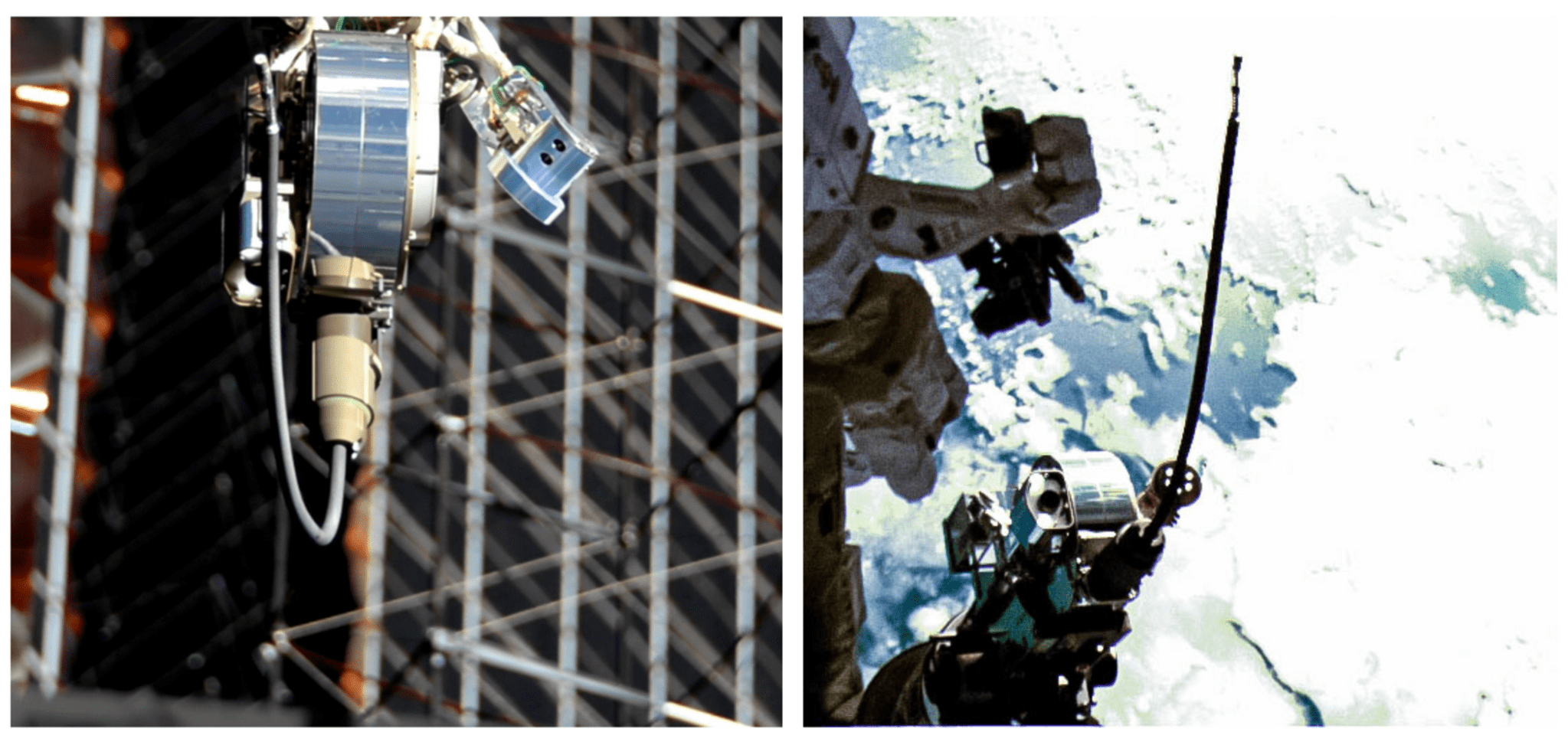
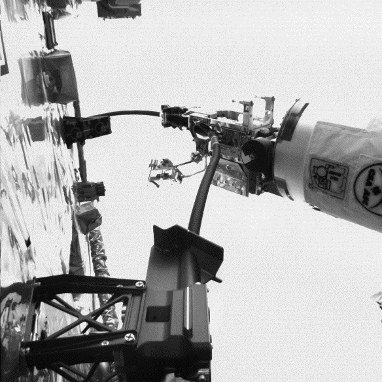
From October 19-22, RRM3 – with the help of the station’s Dextre robot – connected an 11-foot long hose to a designated cryogen port while simultaneously using an inspection tool to verify the hose connection. This marks the first time that Dextre has had tools in both arms completing RRM3 operations. RRM3 supplied the hose and robotic tools of a future servicer spacecraft, as well as a piping system representing that of a satellite in need of fueling.
During the demonstration, Dextre simultaneously operated two RRM3 tools: the Cryogen Servicing Tool (CST) and the Visual Inspection Poseable Invertebrate Robot 2 (VIPIR2) tool. One of Dextre’s arms held the CST, which was needed to grab and guide the hose into the port. The second arm extended the snake-like VIPIR2 camera into the piping system to ensure the hose was inserted correctly.
The mission launched in December 2018 and conducted its first set of robotic operations in August 2019, during which it demonstrated its Multi-Function Tool 2 and a robotic-friendly hose adapter system. This RRM3 demonstration added experience and information to NASA’s knowledge base on transferring cryogenic fuel in space.
Prior to an April 2019 venting operation, RRM3 stored liquid methane for four months, the longest in-space storage of a cryogen without any loss of fluid. This record had been difficult to achieve previously because cryogens vaporize in a process called boil-off when not maintained at a low enough temperature.
RRM3 was developed and operated by NASA’s Exploration and In-space Services (NExIS) projects division (formerly known as the Satellite Servicing Projects Division) at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The demonstration was funded by the Space Technology Mission Directorate’s Technology Demonstration Missions program, which is located at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
By Vanessa Lloyd and Isabelle Yan
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.