Tracking and Data Relay Satellites
The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system is NASA's network of specialized communications satellites in geosynchronous orbit that provide communications services to many NASA spacecraft. These satellites relay signals between spacecraft, including the International Space Station, and ground control stations on Earth.
What's Next
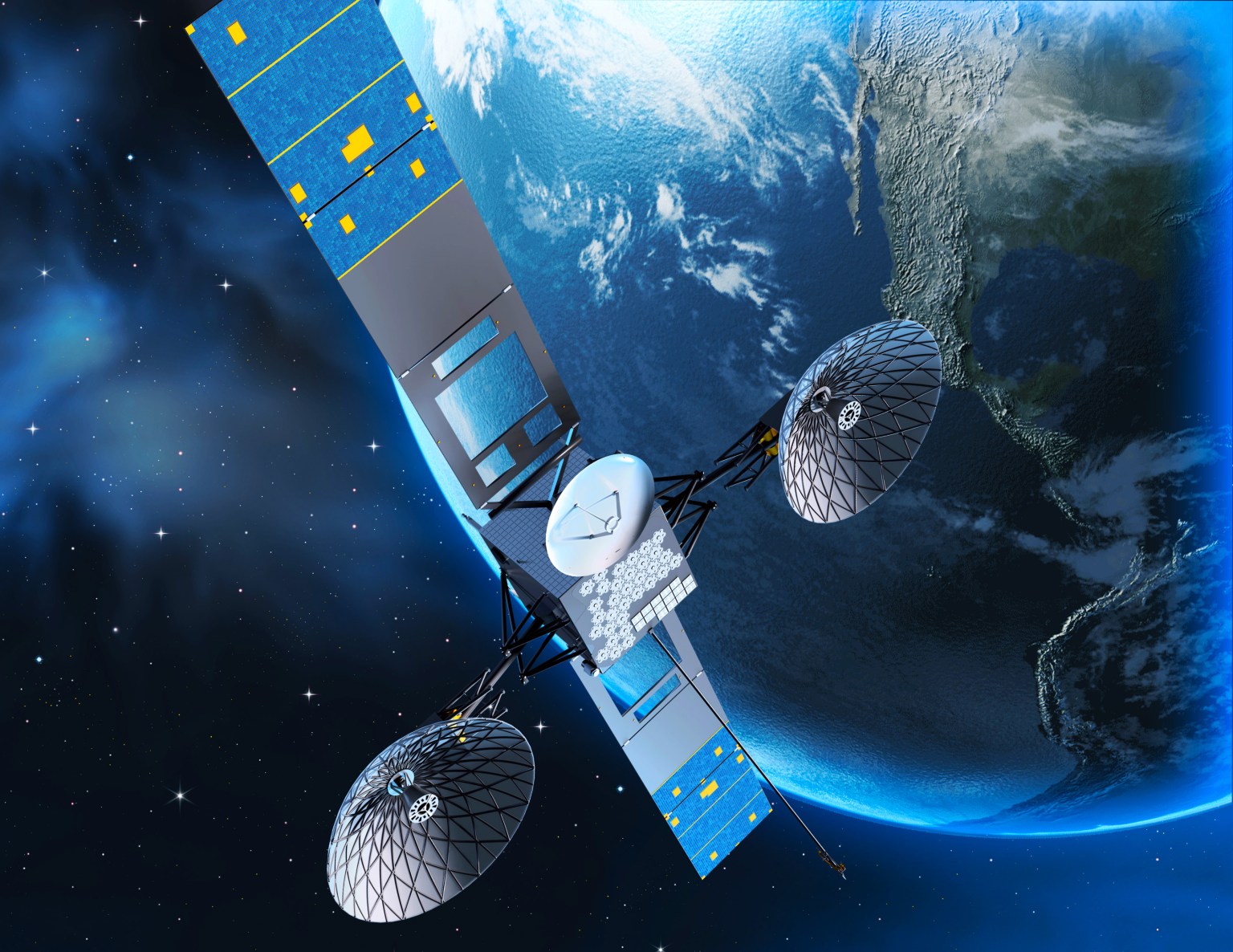

Satellites
Tracking and Data Relay Satellites
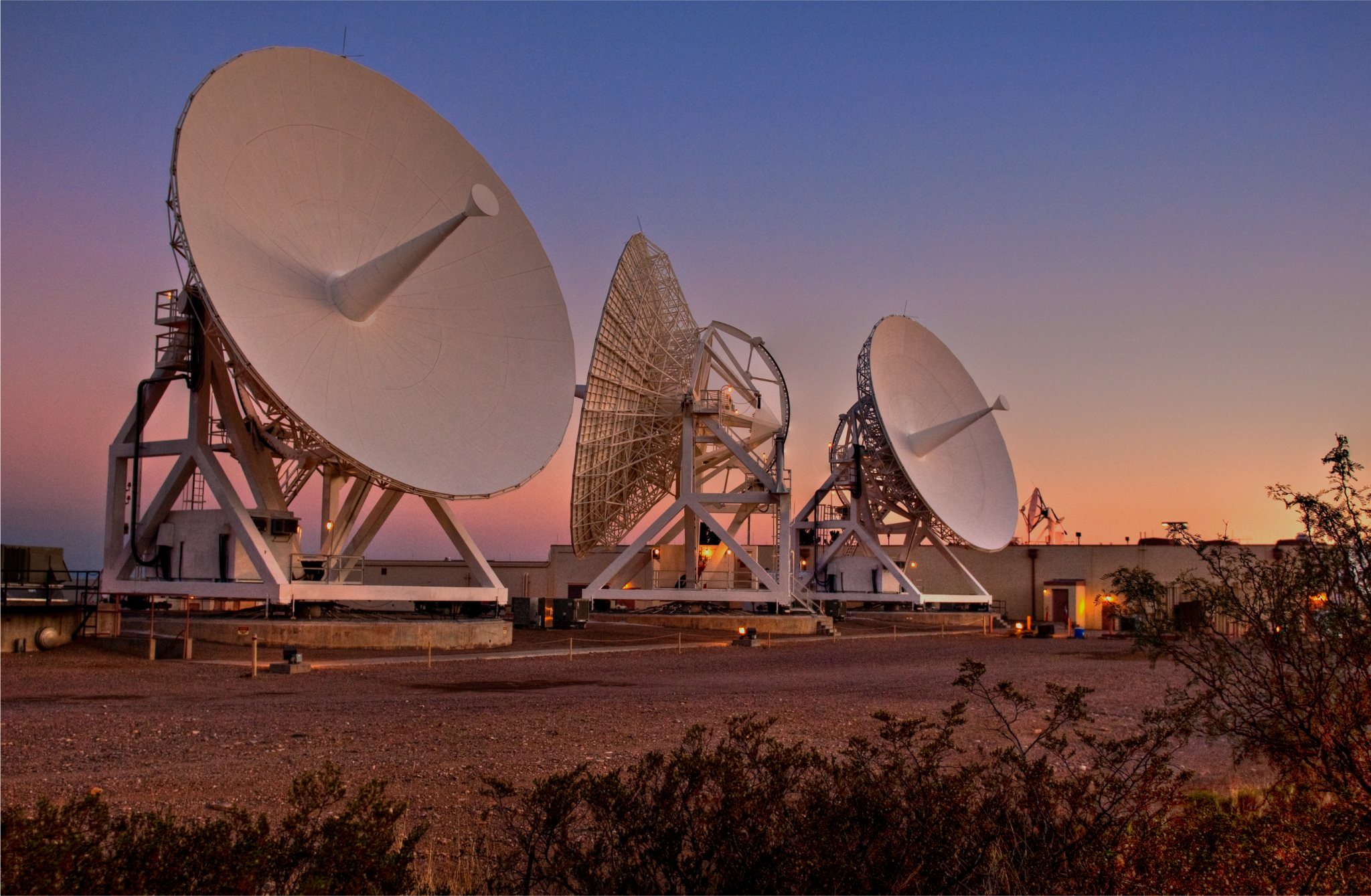
TDRS comprises the space segment of the government-owned portion of the Near Space Network. TDRS can provide near-constant communication relay links between its ground facilities (located in White Sands, New Mexico and Guam) and orbiting satellites below geosynchronous orbit.
Learn More about Tracking and Data Relay Satellites
TDRS Resources
Featured News
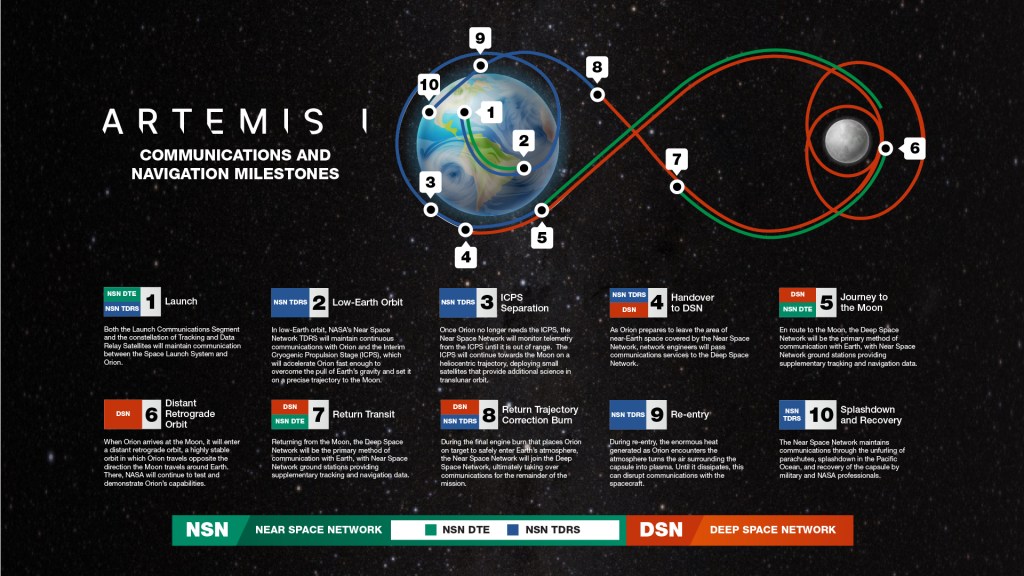
Communicating with Missions
Reliable space communication systems are critical to every NASA mission. Spacecraft commands, never-before-seen images, and scientific data are sent and received daily by NASA's giant antennas on Earth.
Learn More about Communicating with Missions