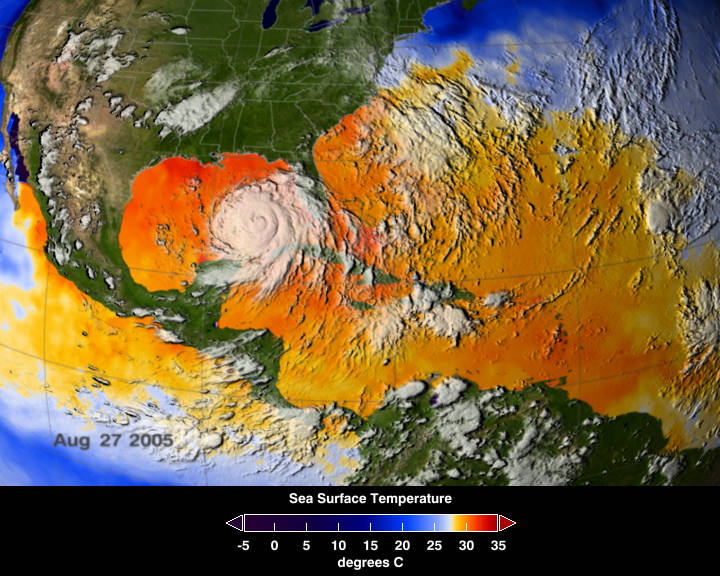
Warm ocean waters fuel hurricanes, and there was plenty of warm water for Katrina to build up strength once she crossed over Florida and moved into the Gulf of Mexico. This image depicts a 3-day average of actual sea surface temperatures (SSTs) for the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, from August 25-27, 2005.
Credits: NASA/SVS
Warm ocean waters fuel hurricanes, and there was plenty of warm water for Katrina to build up strength once she crossed over Florida and moved into the Gulf of Mexico. This image depicts a 3-day average of actual sea surface temperatures (SSTs) for the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, from August 25-27, 2005. Every area in yellow, orange or red represents 82 degrees Fahrenheit or above. A hurricane needs SSTs at 82 degrees or warmer to strengthen. The data came from the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR-E) instrument on NASA’s Aqua satellite. The GOES satellite provided the cloud data for this image.
View animation showing sea surface temperatures from June 9-August 9, 2005




























