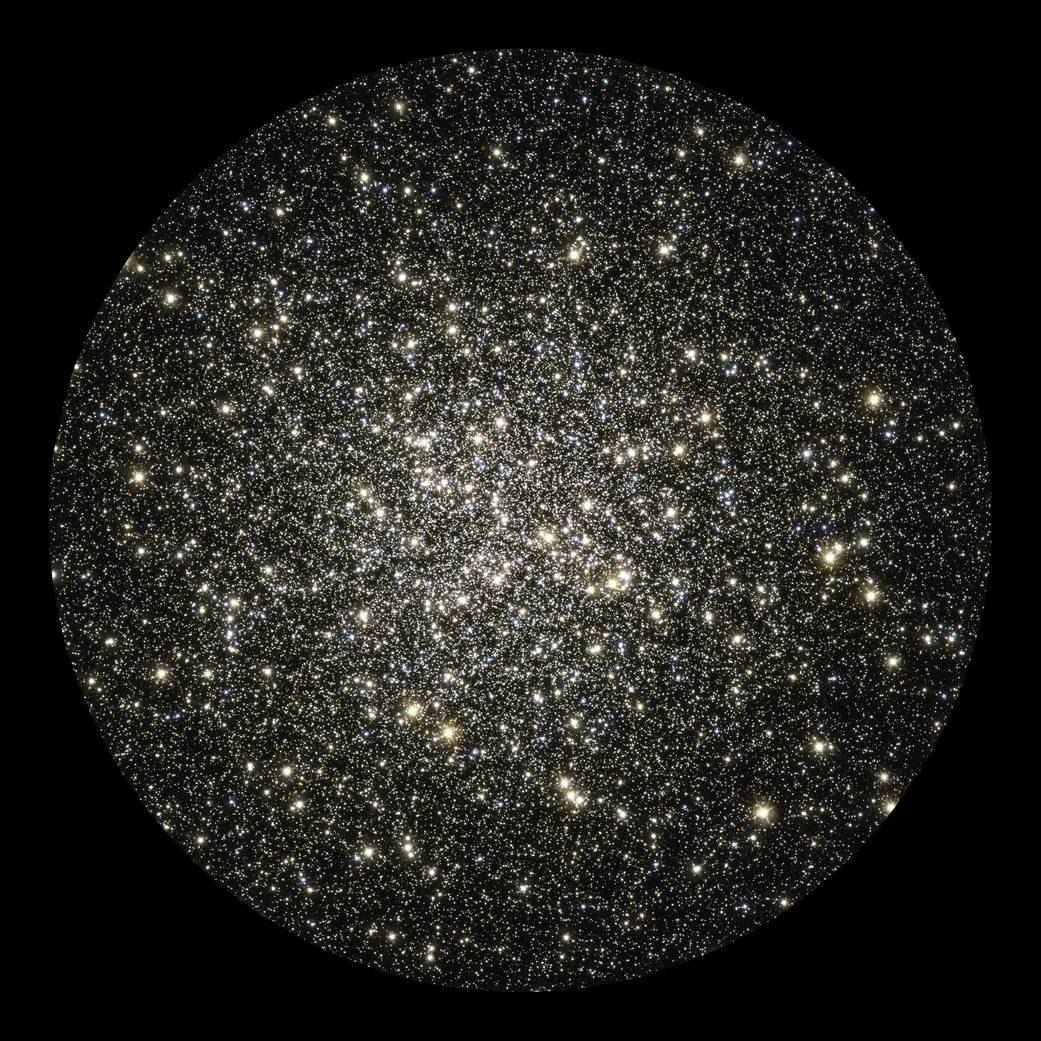
Like swirling, shiny flakes sparkling in a snow globe, this image captures an instantaneous glimpse of many hundreds of thousands of stars moving about in the globular cluster M13, one of the brightest and best-known globular clusters in the northern sky. This glittering metropolis of stars is easily found in the winter sky in the constellation Hercules and can even be glimpsed with the unaided eye under dark skies.
M13 is home to over 100,000 stars and located at a distance of 25,000 light-years. These stars are packed so closely together in a ball, approximately 150 light-years across, that they will spend their entire lives whirling around in the cluster.
Near the core of this cluster, the density of stars is about a hundred times greater than the density in the neighborhood of our sun. These stars are so crowded that they can, at times, slam into each other and even form a new star, called a “blue straggler.” The brightest reddish stars in the cluster are ancient red giants. These aging stars have expanded to many times their original diameters and cooled. The blue-white stars are the hottest in the cluster.
Globular clusters have some of the oldest stars in the universe, which likely formed before our Milky Way, so they are older than nearly all other stars in our galaxy. Studying globular clusters, therefore, tells us about the history of our galaxy.
This image is a composite of archival Hubble data taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 and the Advanced Camera for Surveys. Observations from four separate science proposals taken in November 1999, April 2000, August 2005, and April 2006 were used. The image includes broadband filters that isolate light from the blue, visible, and infrared portions of the spectrum.Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Acknowledgment: C. Bailyn (Yale University), W. Lewin (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), A. Sarajedini (University of Florida), and W. van Altena (Yale University)
2 min read