Latest updates:
– The LDSD test vehicle has landed in the Pacific Ocean off Hawaii.
– The LDSD test vehicle has been released by its balloon and its rocket has ignited, boosting the saucer-shaped craft above the stratosphere (and into the mesosphere).
– A balloon carrying a test vehicle for NASA’s Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) has lifted off.
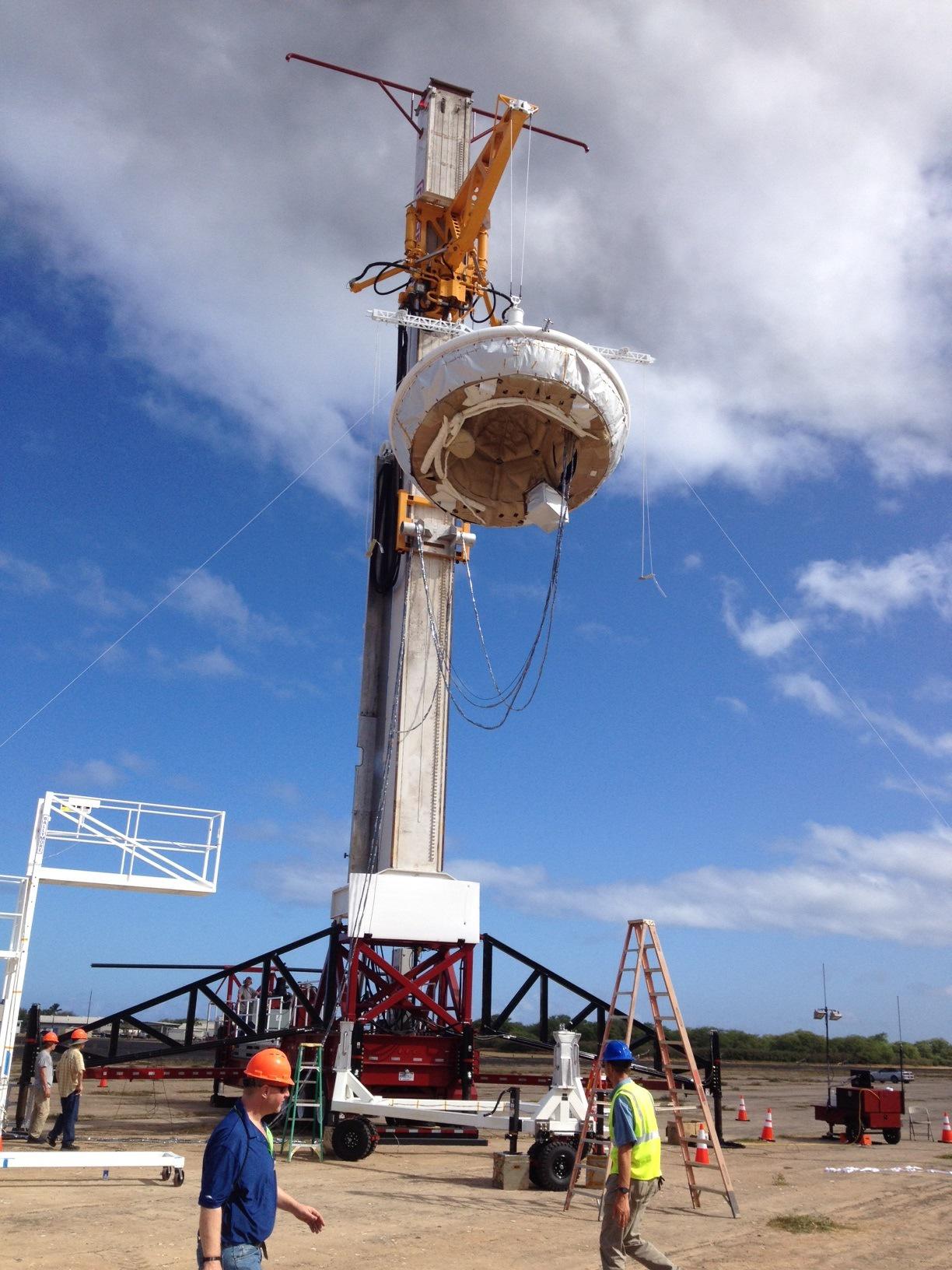

A balloon carrying a test vehicle for NASA’s Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) is scheduled to lift off Saturday, June 28, from its pad at the U.S. Navy’s Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii, during a launch window that opens at 8:15 a.m. Hawaii Standard Time (11:15 a.m. PDT/2:15 p.m. EDT). The vehicle, which resembles a flying saucer, is designed to test landing technologies for future Mars missions.
This first of three LDSD flights will determine the flying qualities of the test vehicle. As a bonus, the flight plan also includes deployment of two new technologies — an inflatable device and mammoth parachute. However, those landing technologies are not officially scheduled to be tested until next summer, in two additional LDSD flights.
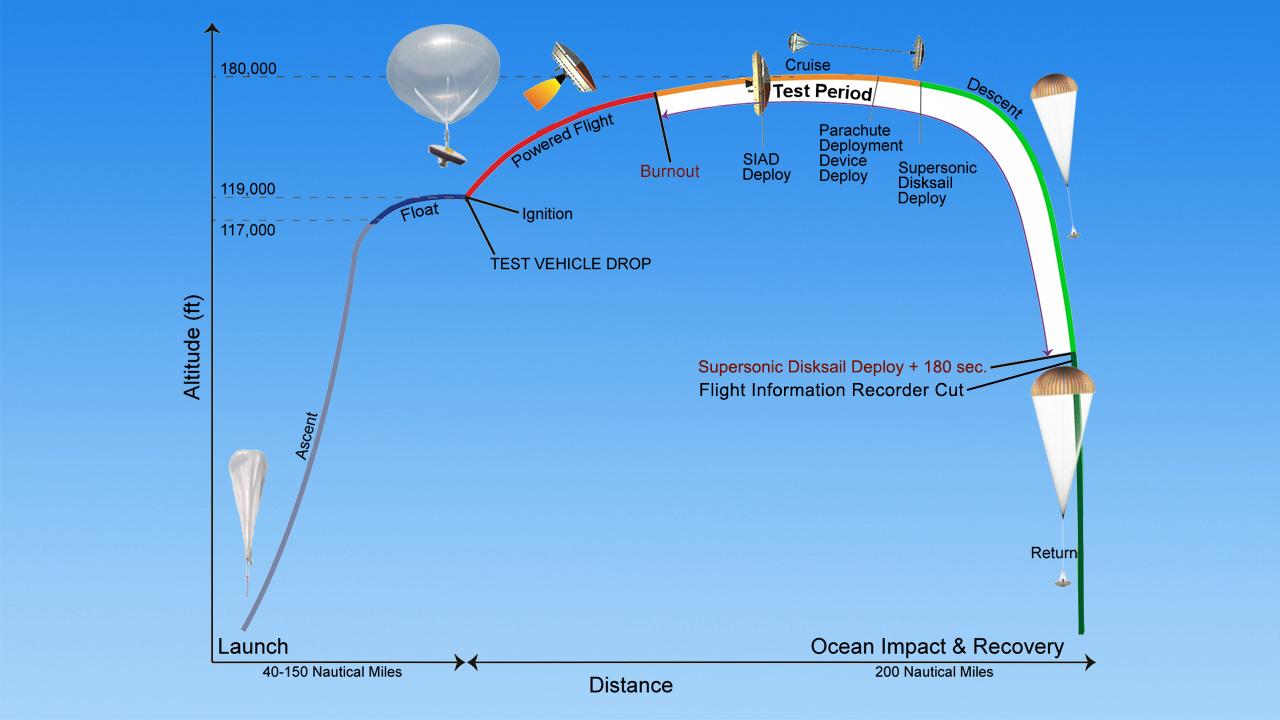
After liftoff, the balloon carrying the LDSD test vehicle will slowly float upward, taking several hours to reach an altitude of 120,000 feet (36,600 meters). At that point, the balloon will release the vehicle and its rocket will kick in, boosting the craft to an altitude of 180,000 feet (54,900 meters).
When the test vehicle reaches 180,000 feet and is traveling at about Mach 3.8, it will deploy the first of the new technologies, a doughnut-shaped tube called the Supersonic Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (SIAD). The SIAD decelerates the test vehicle to approximately Mach 2.5. The test vehicle will then deploy a mammoth parachute (the Supersonic Disk Sail Parachute), which will carry it safely to a controlled water impact about 40 minutes after being dropped from the balloon.
The website will be updated as event milestones occur, at the top of the page.
More information on LDSD is online at:
NASA’s LDSD program is part of the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, which is innovating, developing, testing and flying hardware for use in NASA’s future missions.
DC Agle
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-9011
agle@jpl.nasa.gov
David Steitz
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-236-5829
david.steitz@nasa.gov
Stefan Alford
Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii
808-335-4740
stefan.alford@navy.mil
2014-208