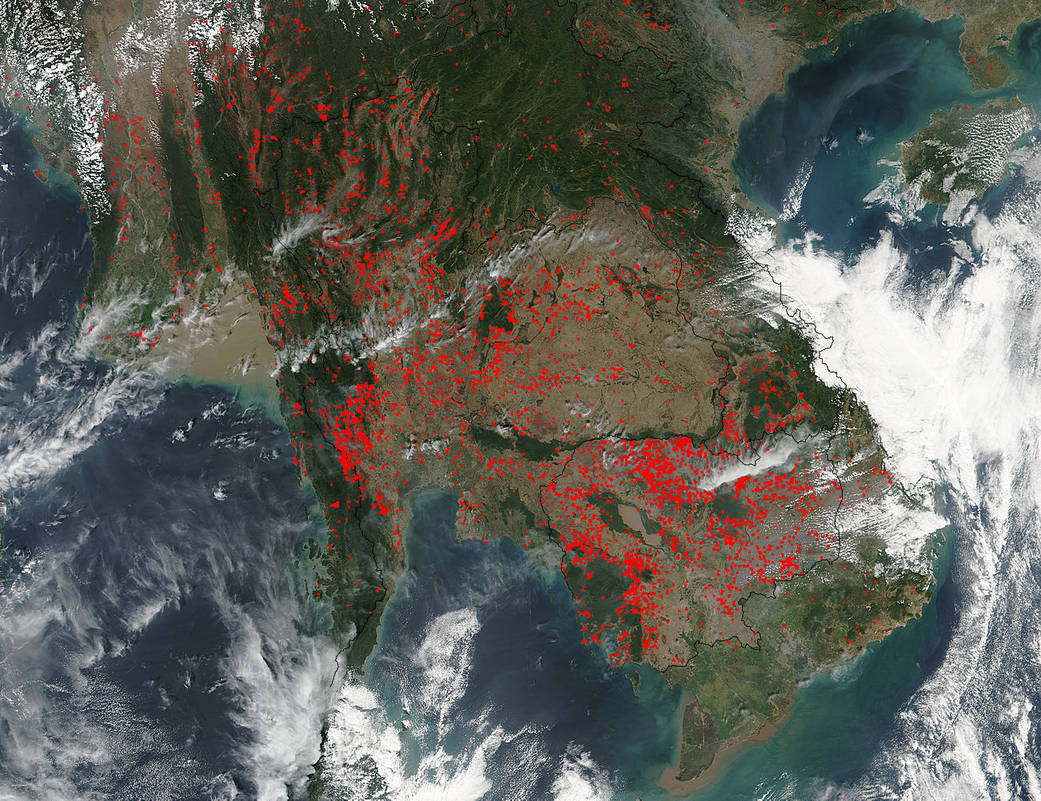
NASA’s Suomi NPP satellite collected this natural-color image using the VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) instrument on February 08, 2016 which detected hundreds of fires burning in various regions of Indochina. The location, widespread nature, and number of fires suggest that these fires were deliberately set to manage land. Farmers often use fire to return nutrients to the soil and to clear the ground of unwanted plants.
While fire helps enhance crops and grasses for pasture, the fires also produce smoke that degrades air quality. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the VIIRS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire. The smoke released by any type of fire (forest, brush, crop, structure, tires, waste or wood burning) is a mixture of particles and chemicals produced by incomplete burning of carbon-containing materials. All smoke contains carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and particulate matter or soot.
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz LANCE/EOSDIS MODIS Rapid Response Team, GSFC. Caption by Lynn Jenner