NASA Glenn Research Center
Historic Facilities
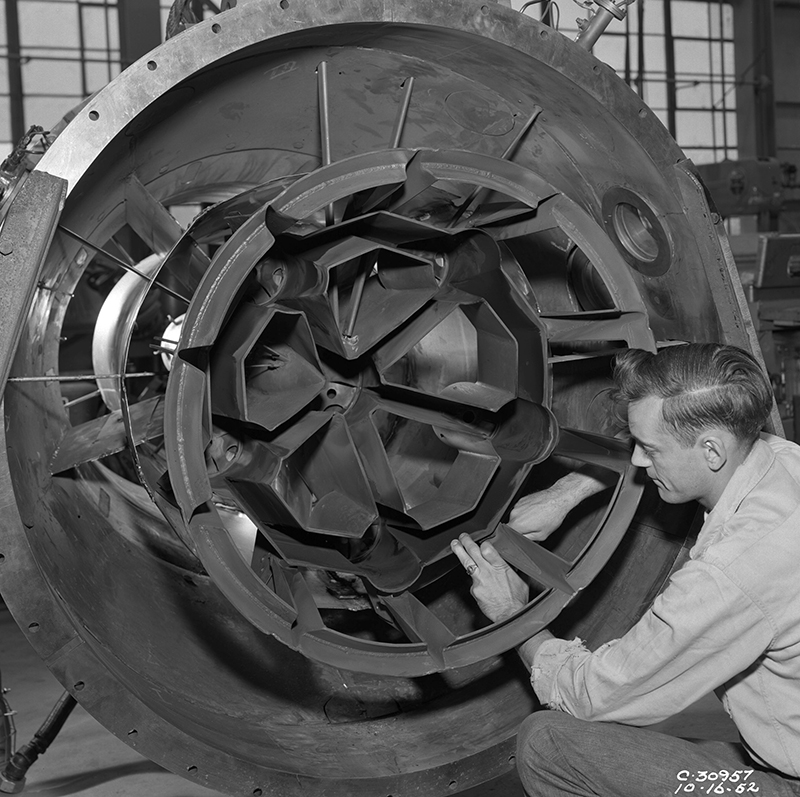
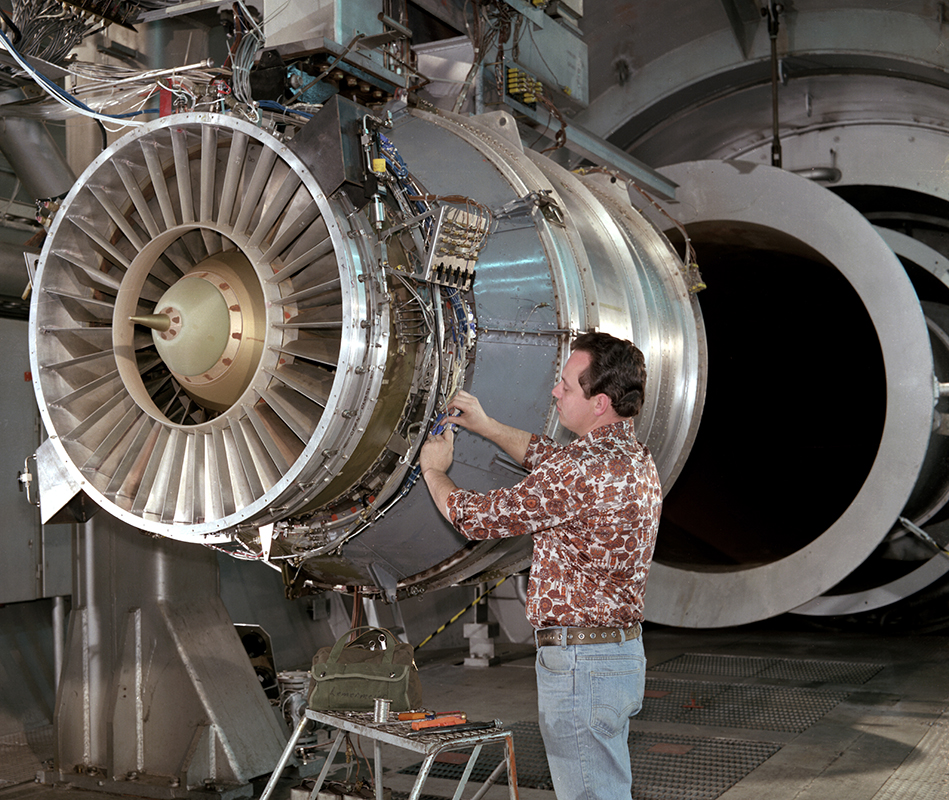
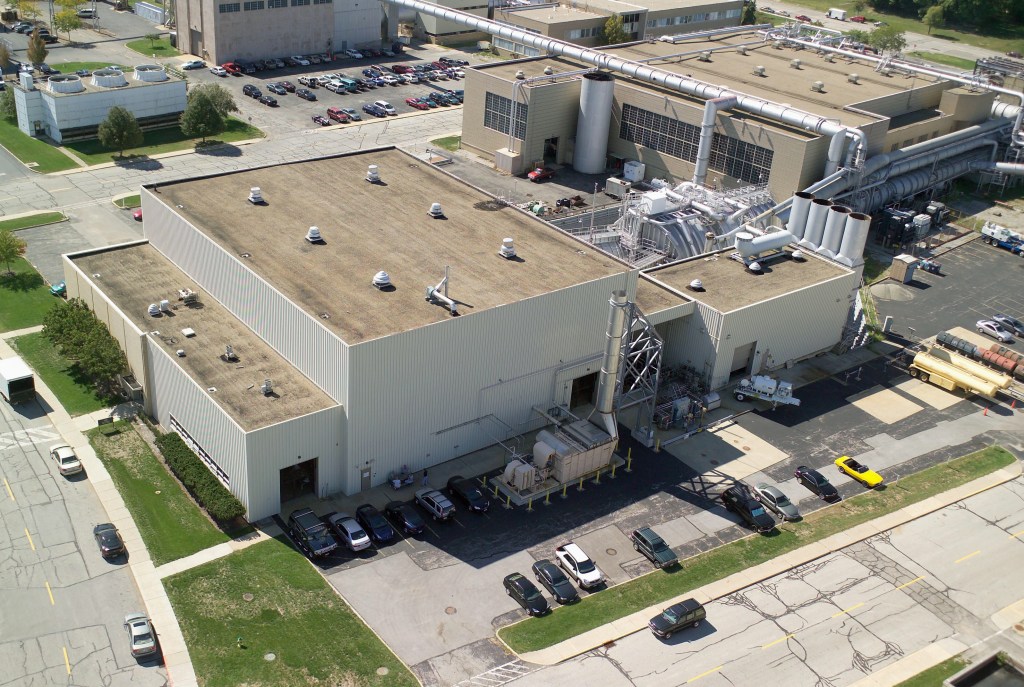
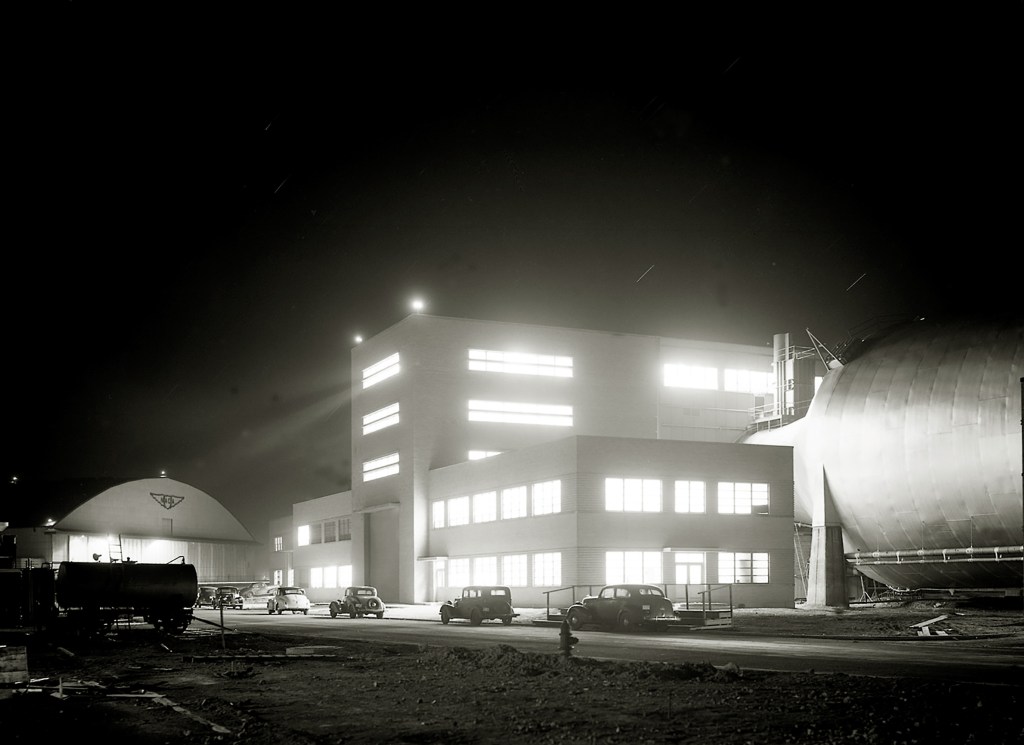
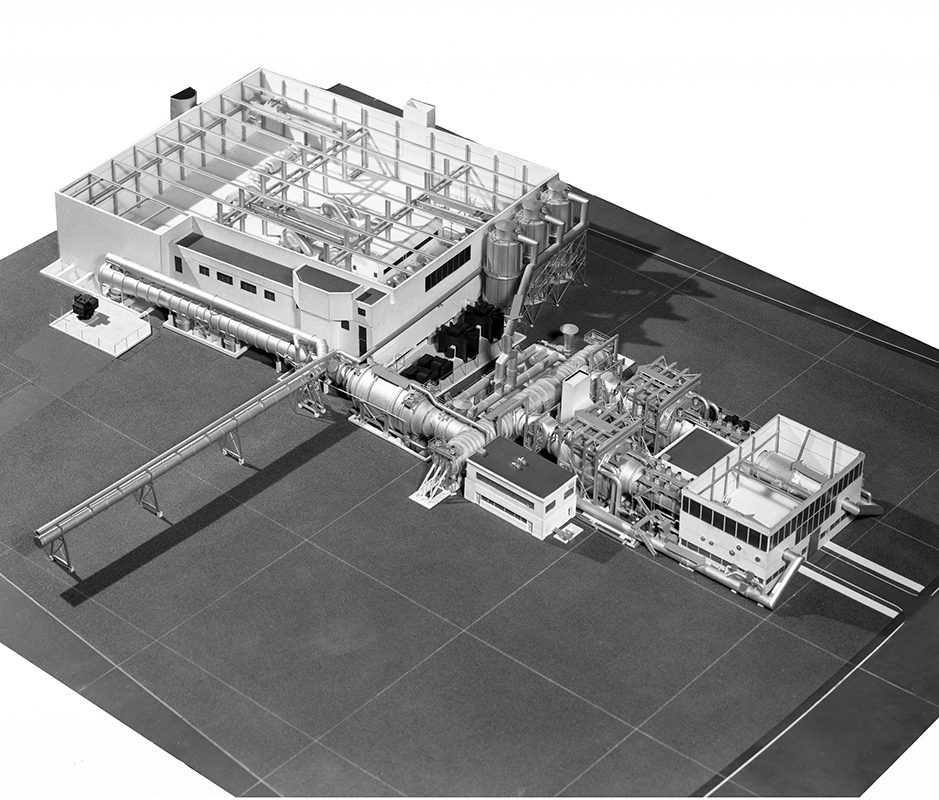
Propulsion Systems Laboratory (PSL) No. 1 and 2
Events Timeline (1938 – 2009)
1938
- The NACA studies the need for additional laboratories
1939
- German Heinkel He-178 performs first flight using a jet engine
- The NACA approves establishment of an Aircraft Engine Research Lab (AERL)
1941
- Construction of the AERL begins
- General Electric begins work on first U.S. jet engine
- U.S. enters World War II
1944
- The Altitude Wind Tunnel becomes the first U.S. propulsion tunnel
- AERL begins testing early U.S. jet engines
1945
- World War II ends
- AERL undergoes reorganization to focus on turbojets and high-speed flight
- Design of Four Burner Area altitude chambers begins
1946
- Air Force approves the development of a surface-to-surface intercontinental missile
1947
- Four Burner Area altitude chambers begin operation
- NACA Lewis Research Facilities Panel discusses new altitude facility
- AERL name is changed to the Flight Propulsion Research Laboratory
1948
- Lab renamed the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory
- Congress allocates $10 million for PSL construction
- Eugene Wasielewski appointed PSL Project Engineer
- 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel begins operation
1949
- Sam Emerson Co. hired to construct PSL Operations Building
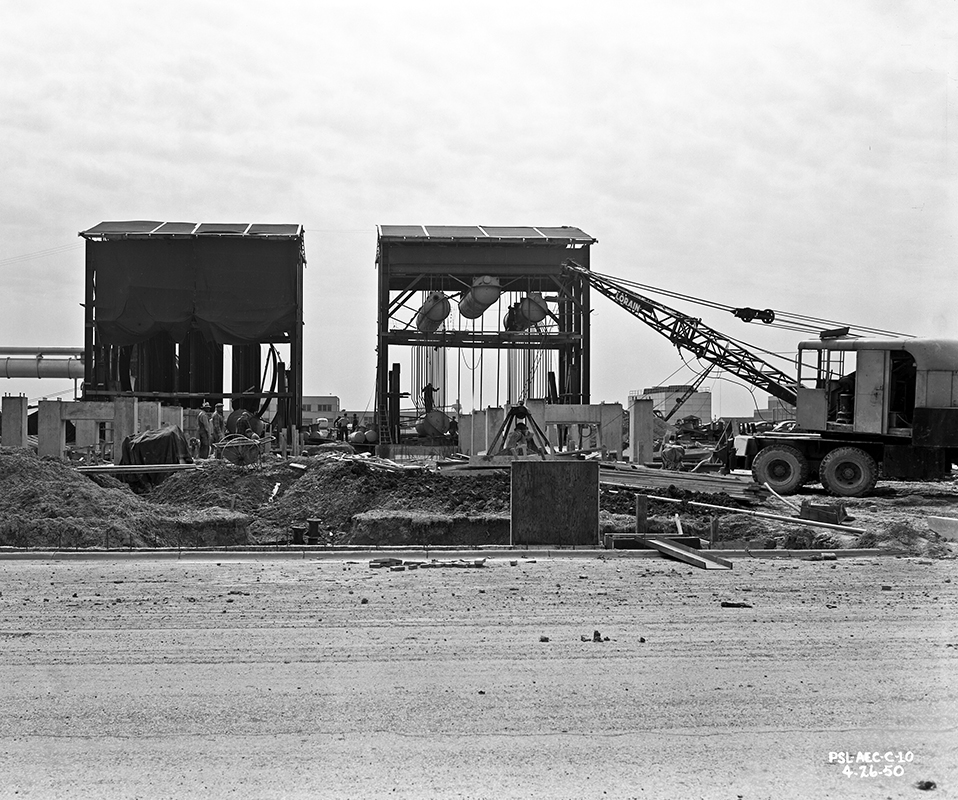
- Excavation of PSL site and construction of cooling tower begin
- Treadwell Construction contracted to build PSL altitude chambers
- Abe Silverstein becomes NACA Lewis director of research
1951
- Burns and Roe completes PSL design work
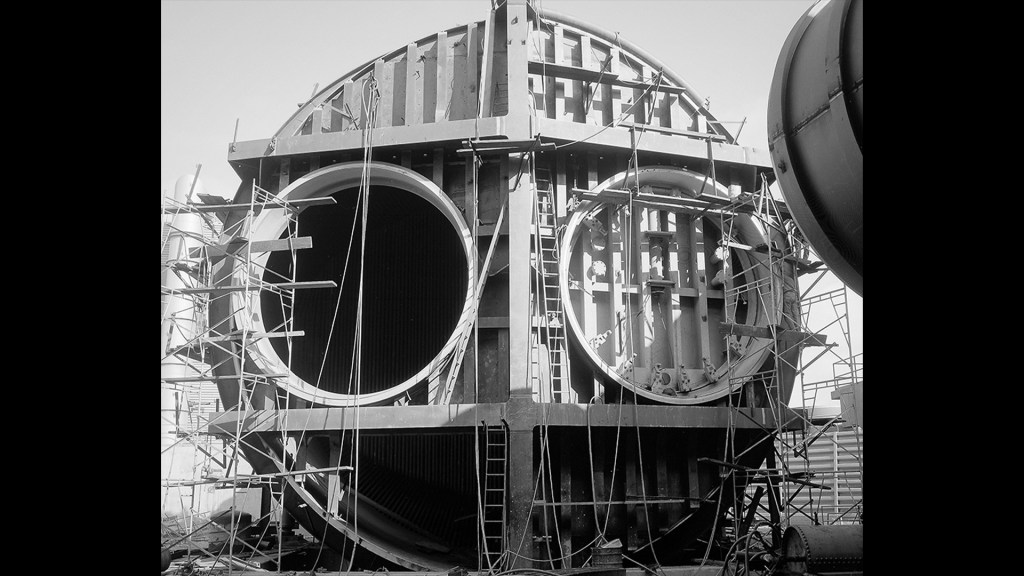
- Delivery of altitude chambers to PSL site
1952
- Compressors and exhausters installed in Equipment Building
- Construction of PSL No. 1 and 2 completed in September
- Westinghouse ramjet is first item tested at PSL
1954
- 1954 NACA Inspection features PSL
1955
- New exhauster and compressors installed
- Air dryer tank and Reactivation Bldg. constructed
- First flight test of General Electric J79
1956
- Instrument Room added to Shop and Access Building
- Desiccant Air Dryer added
1957
- Navaho Missile Program cancelled
- Sputnik I launched
- Lewis hosts NACA Inspection and Flight Propulsion Conference
- General Dynamics begins design of the Centaur
1958
- Pebble Bed Heater added to PSL
- NACA Lewis incorporated into the new NASA space agency
- Boeing 707 becomes first major U.S. jet airliner to enter service
- Pratt & Whitney begins development of RL-10 engine
1961
- Yuri Gagarin becomes first human in space
- President Kennedy calls for manned lunar landing
- Lewis begins expanding staff and facilities
1962
- First Centaur (F–1) launch fails
- Centaur Program transferred to NASA Lewis
- Bomarc missile sites installed
1963
- Chemical Rocket Division created to conduct PSL testing
1964
- First flight of P&W TF-30 turbofan engine
1966
- Creation of Airbreathing Engine Division
- Lewis budget and staffing peak
- Library relocated to PSL Operations Building
1967
- Surveyor spacecraft makes first landing on Moon
- PSL switches focus to aeronautics research
- Design work underway for PSL expansion
1968
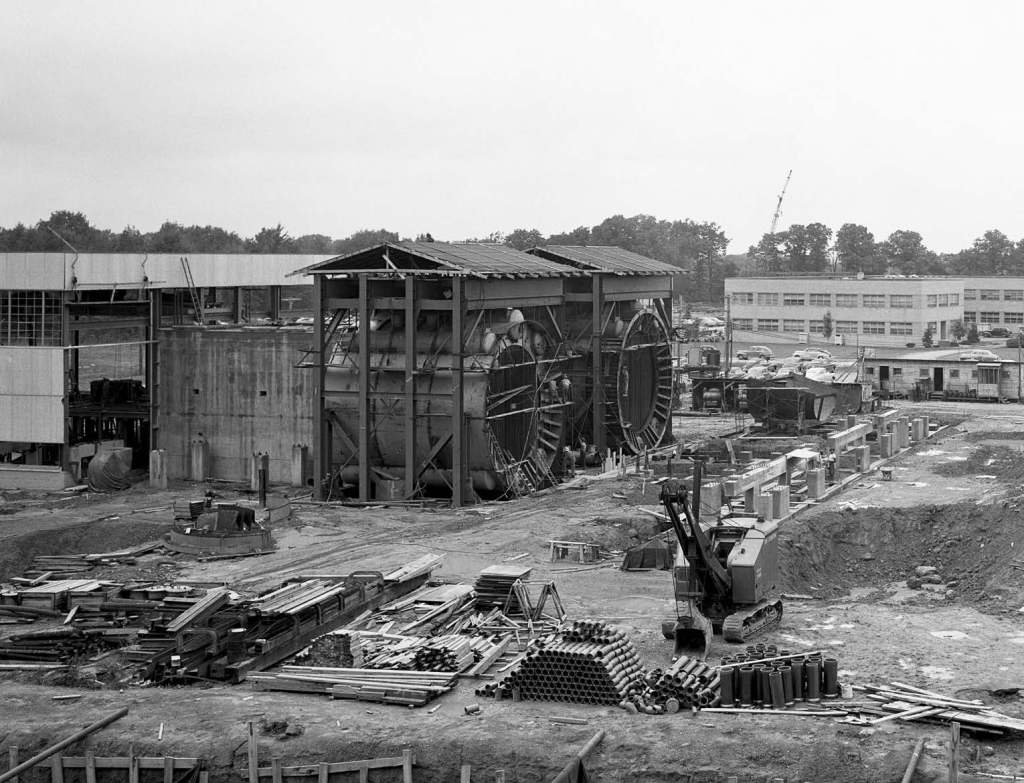
- Construction underway for PSL No. 3 and 4
1969
- Majority of construction on PSL No. 3 and 4 complete
- Flamespreader installed on PSL Chamber No. 2
- Apollo 11 makes first lunar landing
1971
- No testing in PSL-2 during 1971
- Explosion in PSL Equipment Building
1972
- First test run in PSL No. 3 in November
- Space Shuttle Program approved
1973
- First test run in PSL No. 4 in July
- Recognition ceremony for PSL No. 3 and 4 design and construction
- NASA Lewis closes Plum Brook Station [today, the Neil Armstrong Test Facility]
1976
- PSL No. 1 closed in September until June 1977 for failure investigation
1979
- Final PSL No. 2 test completed in July
- Final PSL No. 1 test completed in September
1981
- First flight test of FADEC engine control system
2004
- NASA Glenn begins demolition planning
2006
- Community Awareness Meeting held April 27
2007
- Historical documentation of PSL begins
2008
- Demolition of PSL No.1 and 2 begins
2009
- Demolition of PSL No. 1 and 2 completed
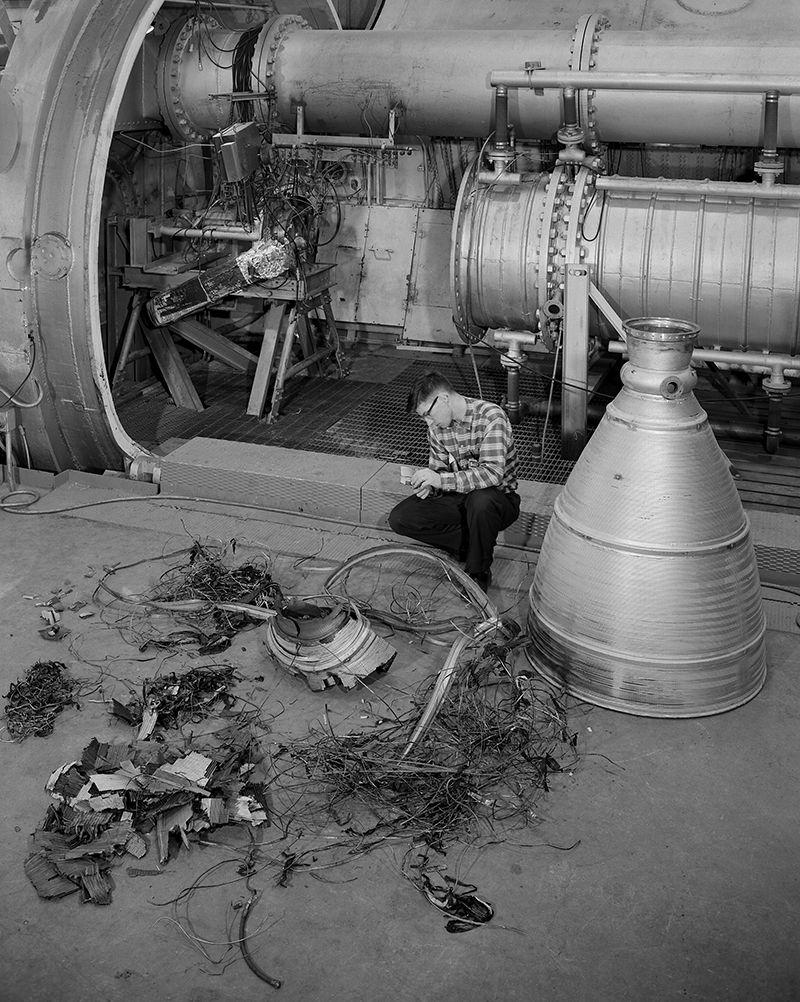
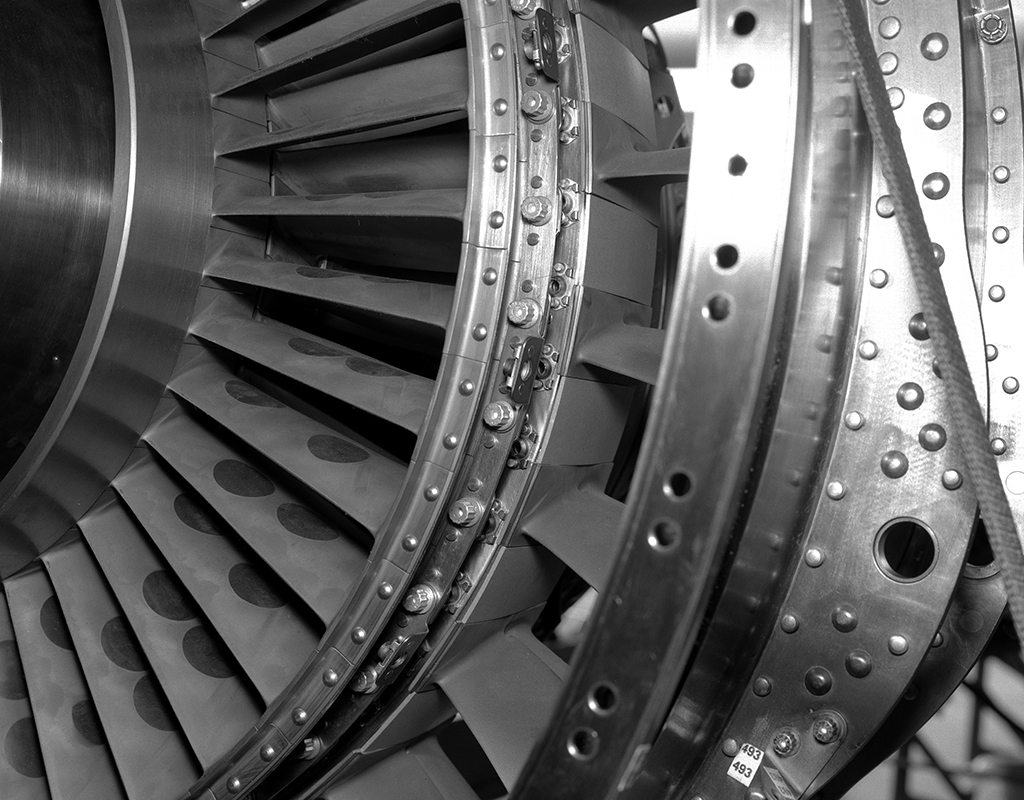
Tests in PSL No. 1 and 2
| Year | PSL No. 1 | PSL No. 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1952 | General Electric J73 turbojet | Wright XJ47 for Navaho |
| 1953 | General Electric J73 turbojet | Wright XJ47 for Navaho |
| 1954 | General Electric J73 turbojet | Wright XJ47 for Navaho |
| 1954 | Marquardt RJ43 for Bomarc | Wright XJ47 for Navaho |
| 1955 | General Electric J79 turbojet | Wright XJ47 for Navaho |
| 1956 | General Electric J70 turbojet | |
| 1957 | Orenda PS-13 Iroquois | |
| 1958 | NASA 2.5k rocket | NASA isenthropic rocket |
| 1959 | NASA regenerative rocket | TRW nozzle project |
| 1960 | NASA 20k rocket | Thrust vector rig |
| 1961 | Pratt & Whitney RL-10 rocket | NASA fluorine rocket |
| 1962 | Pratt & Whitney RL-10 rocket | |
| 1963 | Pratt & Whitney RL-10 rocket | RF engine |
| 1964 | NASA ablative engine | Contour nozzles |
| 1965 | Ablative engine | 260-inch Solid Rocket |
| 1966 | 260-inch Solid Rocket | |
| 1967 | Pratt & Whitney TF30-P1 distortion | General Electric Lift Cruise Engine |
| 1968 | Pratt & Whitney TF30-P1 distortion | General Electric J85-13/Lift Cruise Engine |
| 1969 | Pratt & Whitney TF30-P1 distortion | General Electric J85-13/Lift Cruise Engine |
| 1970 | Pratt & Whitney TF30-P1 distortion | General Electric J85-13 nozzle |
| 1971 | Pratt & Whitney TF30-P1 distortion | |
| 1972 | Garrett TFE 731-2 Compass Cope | General Electric J85-13 distortion |
| 1973 | Garrett ATF-3 Compass Cope | NASA Low Cost Engine |
| 1973 | Pratt & Whitney TF30 P9 controls | |
| 1974 | Pratt & Whitney TF30 P1 afterburner | GE J85-13 nozzle, treatment |
| 1975 | Pratt & Whitney F-100 FX213 flutter | Pratt & Whitney TF30-P9 controls |
| 1976 | Pratt & Whitney F-100 FX213 flutter | GE J85-21 compressor |
| 1977 | Pratt & Whitney F-100 XD11 flutter | General Electric J85-21 compressor |
| 1978 | Pratt & Whitney F-100 controls | General Electric J85-21 nozzle and flutter |
| 1979 | General Electric J-85 Pulse Generator | Pratt & Whitney F401 controls |
Tests in PSL No. 3 and 4
| Year | PSL No. 3 | PSL No. 4 |
|---|---|---|
| 1972 | Quiet Engine Program | |
| 1973 | Quiet Engine Program | Pratt & Whitney J58 emissions |
| 1973 | Quiet Engine Program | Pratt & Whitney J58/JT8D Refan |
| 1975 | Airflow Airjet Duct Test | Pratt & Whitney TF30 augmenter mixer |
| 1976 | Pratt & Whitney TF30 P-3 distortion | Pratt & Whitney F-100 P059 calibration |
| 1977 | Pratt & Whitney TF30 P-3 distortion | Pratt & Whitney F-100 P063 afterburner |
| 1978 | Pratt & Whitney TF-34 inlet vanes | Pratt & Whitney F-100 P072 afterburner |
| 1979 | Pratt & Whitney TF34 inlet vanes | Pratt & Whitney F-100 P072 afterburner |