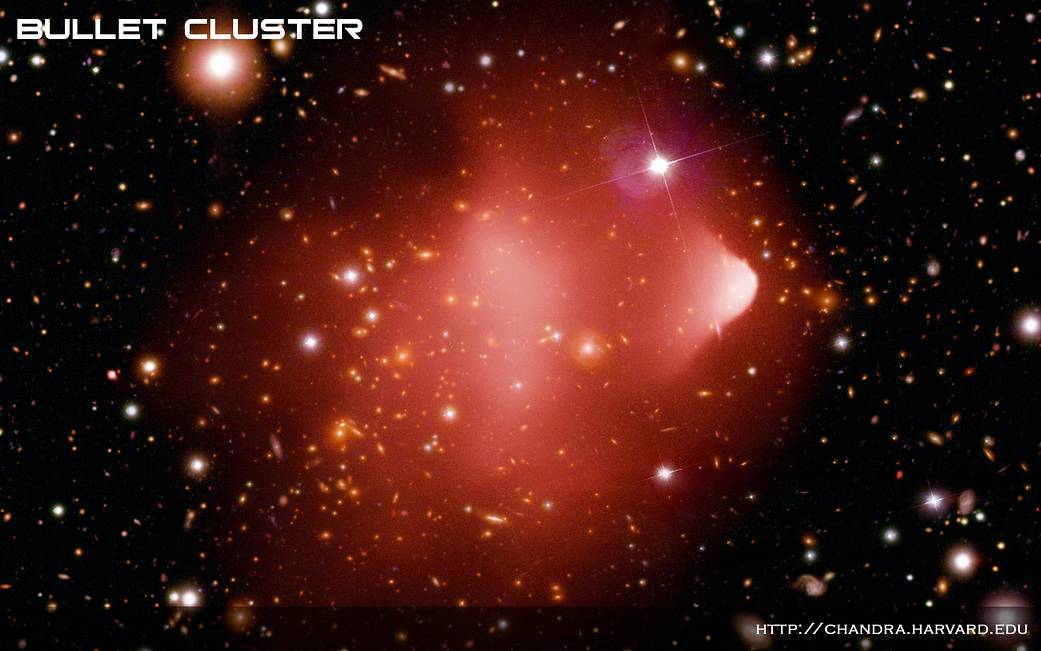
Officially known as 1E 0657-56, the Bullet Cluster was formed after the violent collision of two large clusters of galaxies. Located about 3.8 billion light years from Earth, this image combines an image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory with optical data from the Hubble Space Telescope and Magellan telescope in Chile. The cluster has become an extremely popular object for astrophysical research, including studies of the properties of dark matter and the dynamics of million-degree gas.
In this latest research effort, the Bullet Cluster was used to search for the presence of antimatter leftover from the very early universe. Antimatter is made up of elementary particles that have the same masses as their corresponding matter counterparts – protons, neutrons and electrons – but the opposite charges and magnetic properties.Image Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/M.Markevitch et al. Optical: NASA/STScI; Magellan/U.Arizona/D.Clowe et al.