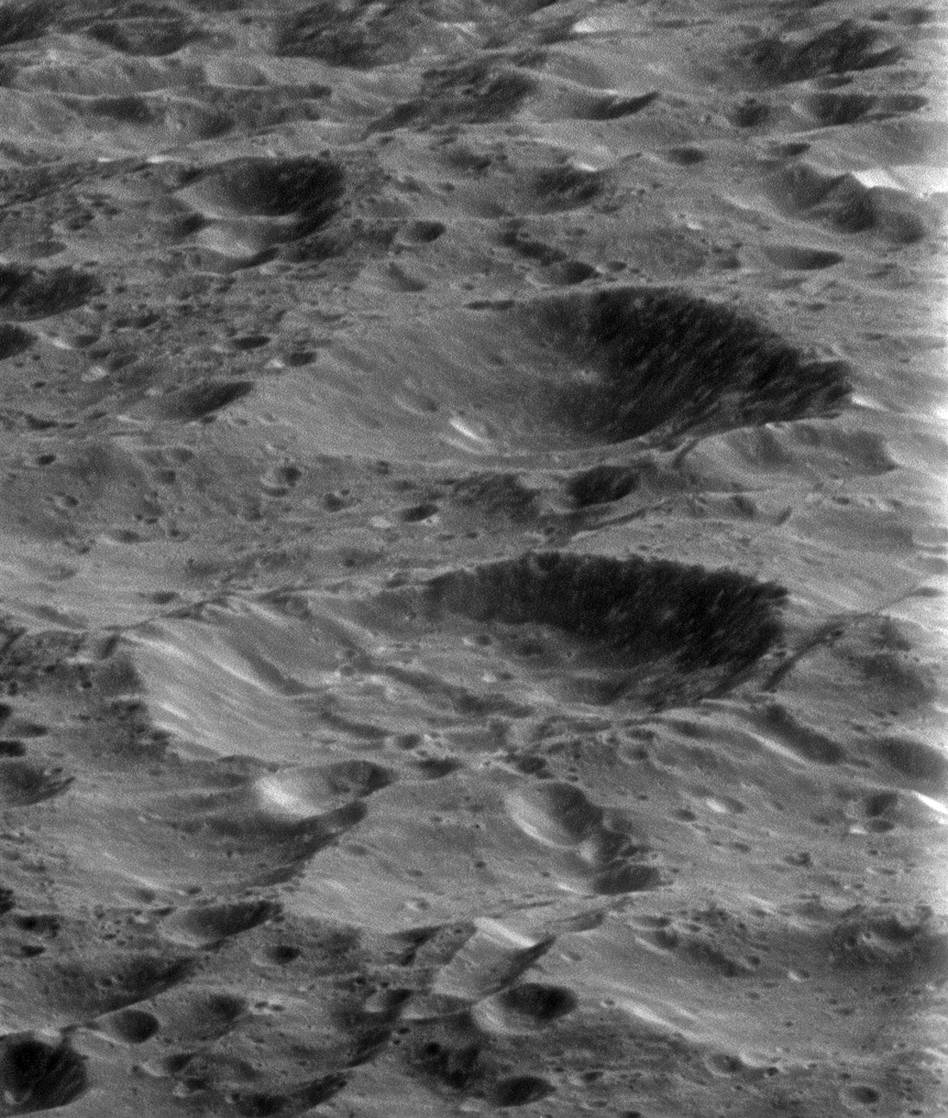
On its fourth and final targeted flyby of Rhea, the Cassini spacecraft provided this stunning view of the ancient and heavily cratered surface. Billions of years of impacts have sculpted Rhea’s surface into the form we see today.
With a diameter of 949 miles (1,528 kilometers) Rhea is Saturn’s second-largest moon.
This view is centered on terrain at 33 degrees north latitude, 358 degrees west longitude. The image was taken in visible light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on March 9, 2013.
The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 2,280 miles (3,670 kilometers) from Rhea and at a Sun-Rhea-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 92 degrees. Image scale is 72 feet (22 meters) per pixel.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov . The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org .
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute
2 min read