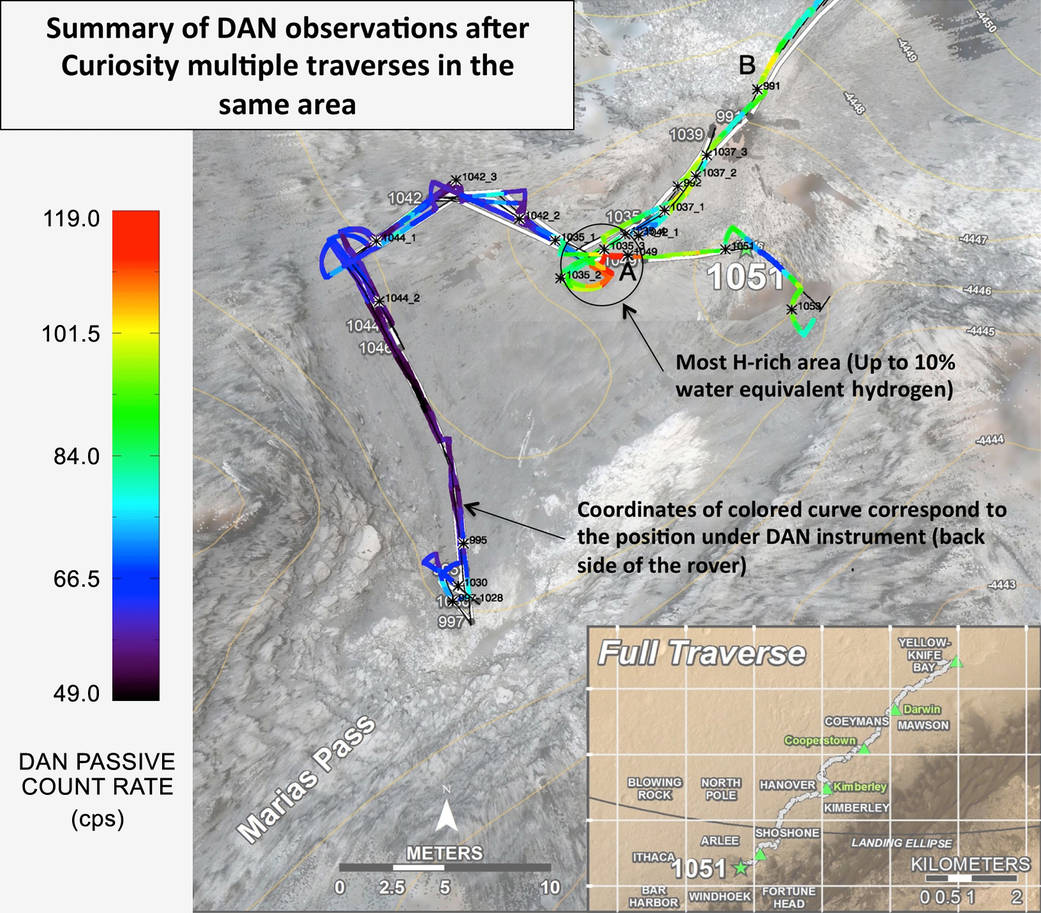
Curiosity’s Russian-made instrument for checking hydration levels in the ground beneath the rover detected an unusually high amount at a site near “Marias Pass,” prompting repeated passes over the area to map the hydrogen amounts.
The instrument is named Dynamic Albedo of Neutrons, or DAN. It detects hydrogen by the effect of hydrogen atoms on neutrons entering the ground either from cosmic rays and Curiosity’s power source (DAN’s passive mode) or from the instrument’s neutron pulse generator (DAN’s active mode). DAN recognizes which neutrons have bounced off hydrogen from their rerduced energy level.
This map, covering an area about 130 feet (40 meters) across, shows results from DAN’s multiple traverses over the area, with color coding for levels of hydrogen detected. The red coding indicates amounts of hydrogen three to four times as high as the amounts detected anywhere previously along Curiosity’s traverse of about 6.9 miles (11.1 kilometers) since landing in August 2012. The inset map at lower right shows the full traverse through Sol 1051 (July 21, 2015), with names assigned to rectangles within Gale Crater for geological mapping purposes. The vertical bar at left indicates the color coding according to counts per second in DAN’s passive mode.
The hydrogen detected by DAN is interpreted as water molecules or hydroxyl ions bound within minerals or water absorbed onto minerals in the rocks and soil, to a depth of about 3 feet (1 meter) beneath the rover. The amount of hydrogen is often expressed as “water equivalent hydrogen” based on two hydrogen atoms per molecule of water.
In the same area where DAN detected an unusually high amount of hydration, Curiosity’s Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) instrument detected an unusually high amount of silica in several rock targets. The DAN and ChemCam findings led to the rover’s science team choosing a rock target called “Buckskin” for collection of a drilled sample to be analyzed by the rover’s internal laboratory instruments.
Russia’s Space Research Institute developed DAN in close cooperation with the N.L. Dukhov All-Russia Research Institute of Automatics, Moscow, and the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna. The neutron generator development was supervised by the late technical designer German A. Smirnov of the All-Russia Institute of Automatics. Moscow.
More information about Curiosity is online at https://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Russian Space Research Institute