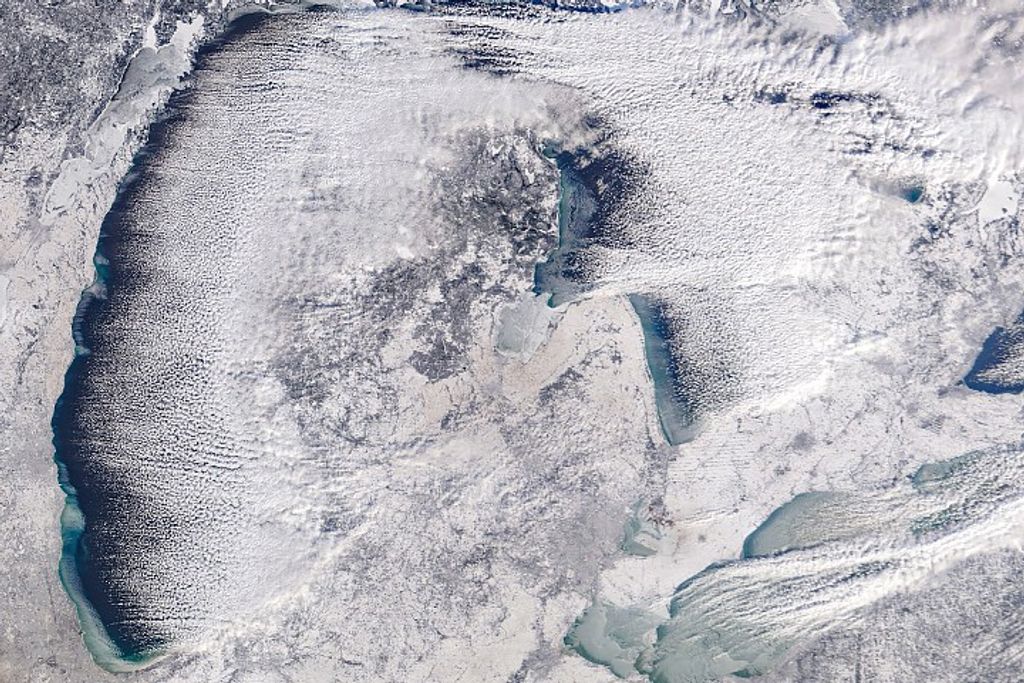
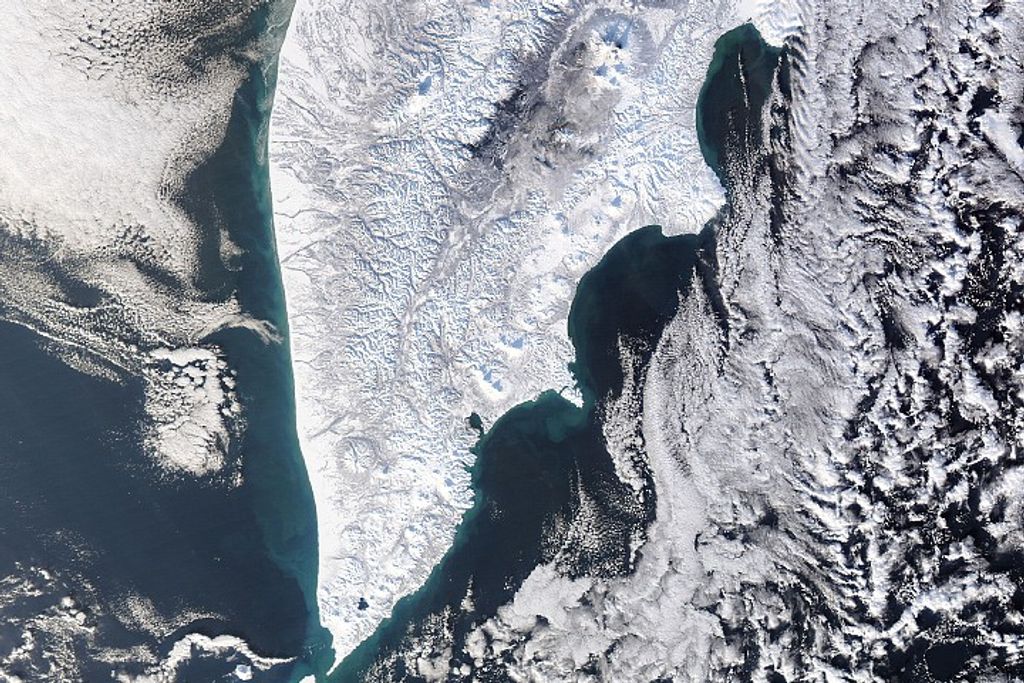
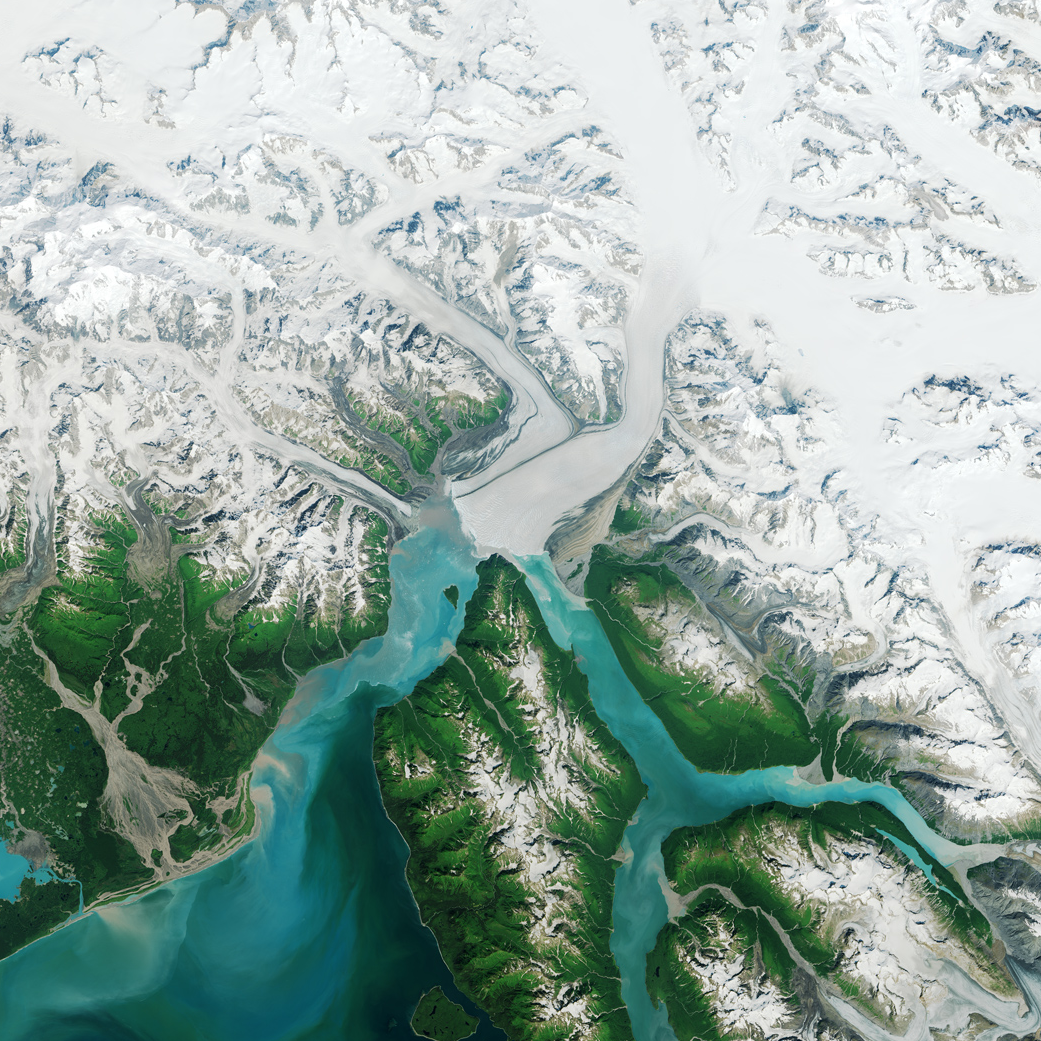
Since measurements began in 1895, Alaska’s Hubbard Glacier has been thickening and steadily advancing into Disenchantment Bay. The advance runs counter to so many thinning and retreating glaciers nearby in Alaska and around the world.
This image, acquired by the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8, shows Hubbard Glacier on July 22, 2014.
According to Leigh Stearns, a glaciologist at the University of Kansas, Hubbard’s advance is due to its large accumulation area; the glacier’s catchment basin extends far into the Saint Elias Mountains. Snow that falls in the basin either melts or flows down to the terminus, causing Hubbard to steadily grow. In addition, Hubbard is building up a large moraine, shoveling sediment, rock, and other debris from Earth’s surface onto the glacier’s leading edge. The moraine at the front gives the glacier stability and allows it to advance more easily because the ice does not need to be as thick to stay grounded. (If it is thin, it can start floating and will not necessarily advance.)
Twice in the past hundred years—in 1986 and again in 2002—the moraine has made contact with Gilbert Point and blocked the entrance to Russell Fjord. With nowhere to drain, runoff caused the water level in the fjord to rise rapidly.
More information and annotated images.
Image Credit: NASA/Earth Observatory