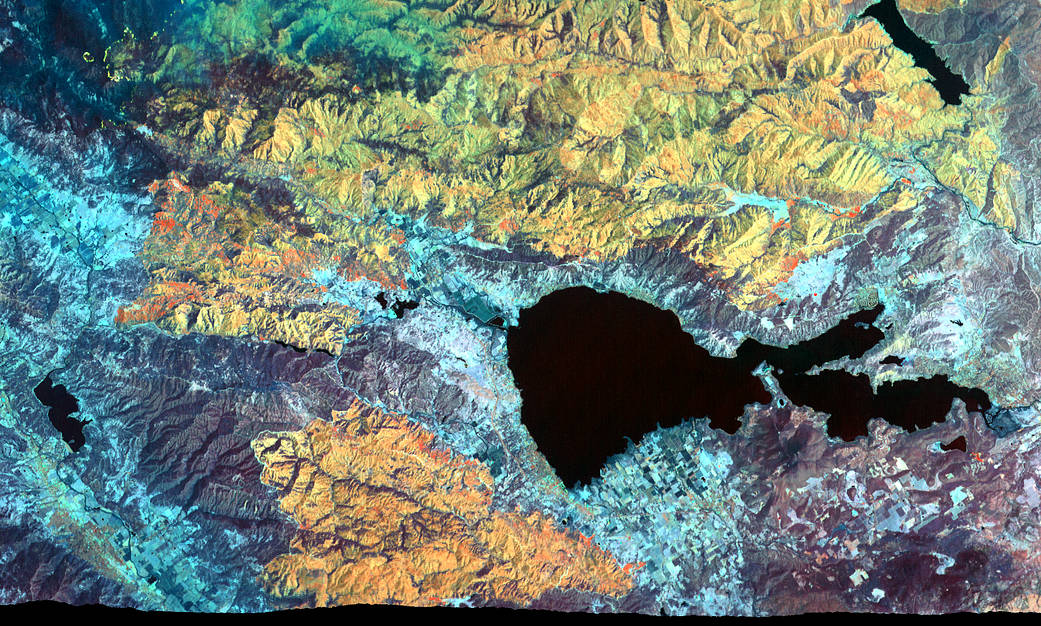
The Mendocino Complex Fire is now the largest wildfire in California history with well over 350,000 acres burned. This false-color image was captured on August 9, 2018 by an instrument installed aboard a NASA research aircraft that flew over both fires making up the complex in the area around Clear Lake (the central, black feature) in northern California. Active fire zones are seen in yellow, with warm, burned areas in orange. Unburned vegetation appears in blue and green. The flames of small, active fires can be seen at the leading edges of the fire perimeter.
Operated by NASA’s Ames Research Center, in California’s Silicon Valley, the instrument used to collect this data on the vast and still-burning wildfire is known as MASTER, short for MODIS-ASTER airborne simulator. Collecting data during flights aboard a high-altitude aircraft, it provides a simulation of two instruments currently gathering Earth science data from aboard the Terra and Aqua satellites. MASTER supports the teams operating those instruments — MODIS and ASTER — in the areas of algorithm development for data processing, sensor calibration and validation.
For the Aug. 9 flight, MASTER flew aboard NASA’s ER-2 high-altitude aircraft, based at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. The data collected was processed at Ames and delivered to the US Forest Service to assist with emergency wildfire response.
MASTER is maintained and operated under contract by the Universities Space Research Association at the Airborne Sensor Facility at Ames. This work is sponsored by the NASA Science Mission Directorate Earth Observing Program and Airborne Science Program.
Image credit: NASA/USRA