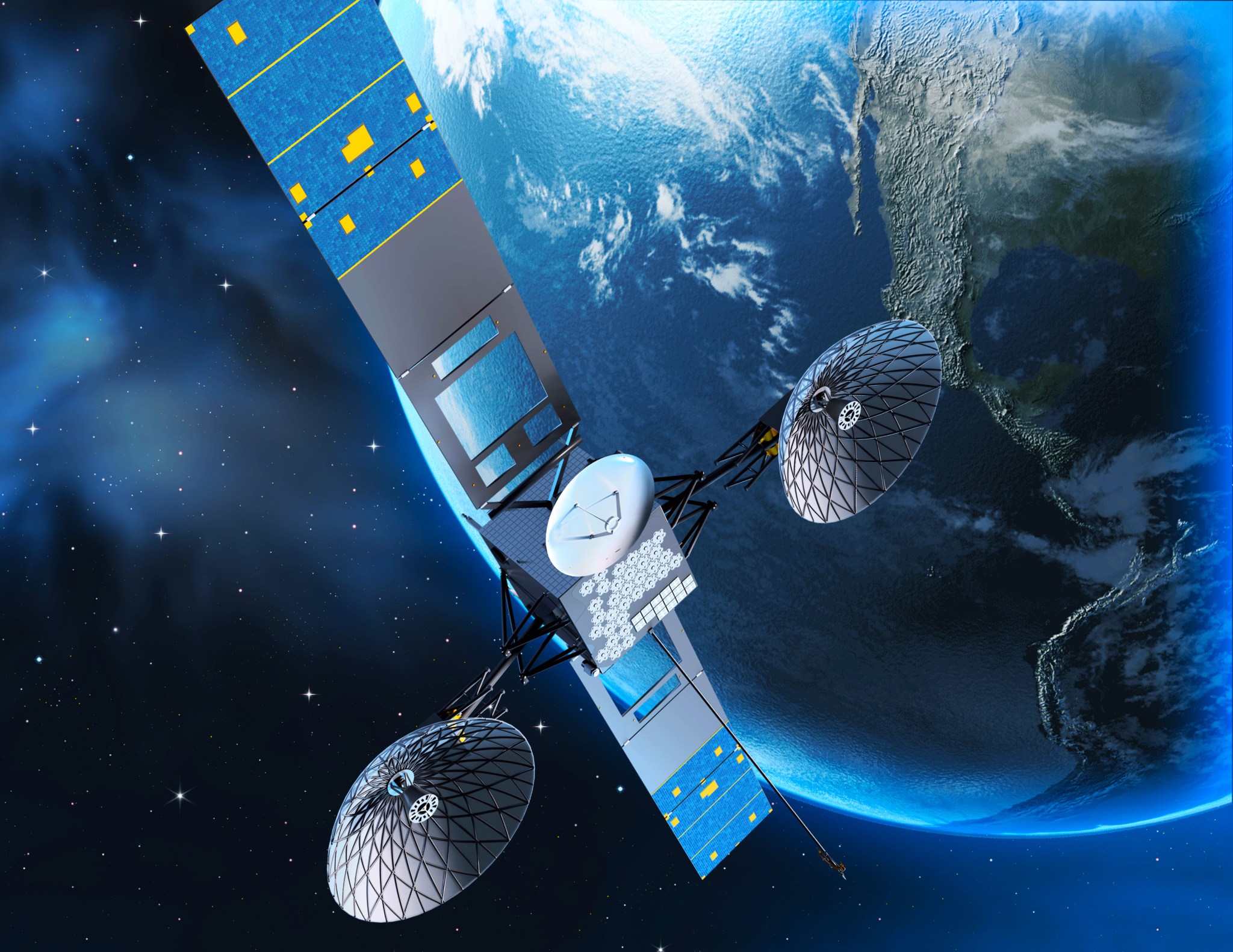
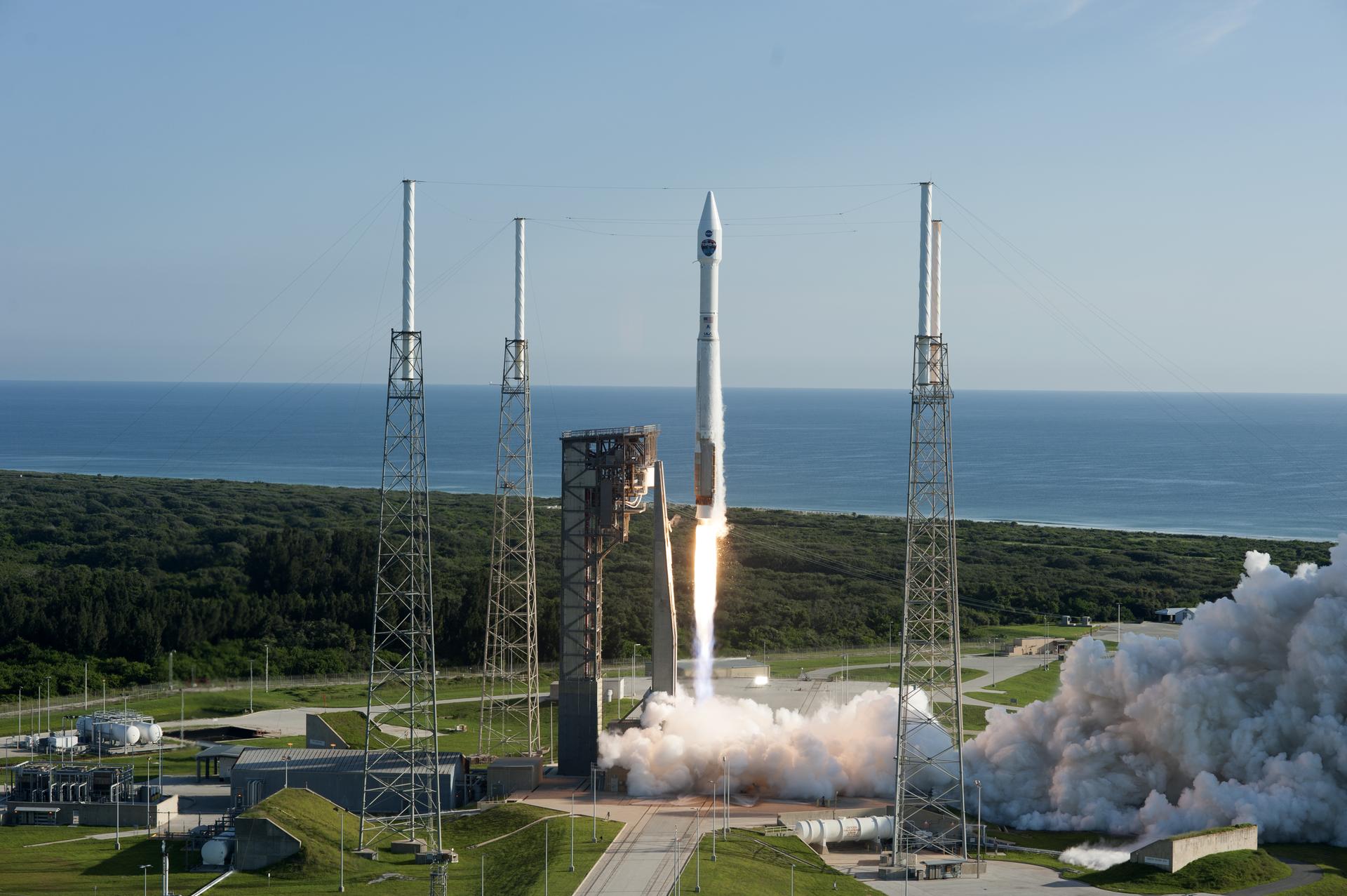
NASA has begun operating the last satellite of its kind in the network that provides communications and tracking services to more than 40 NASA missions, including critical, real-time communication with the International Space Station. Following its August launch and a five-month period of in-orbit testing, the third-generation Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS), referred to as TDRS-M until this important milestone, was renamed TDRS-13, becoming the tenth operational satellite in the geosynchronous, space-based fleet.
“With TDRS-13’s successful acceptance into the network, the fleet is fully replenished and set to continue carrying out its important mission through the mid-2020s,” said Badri Younes, NASA’s deputy associate administrator for Space Communications and Navigation at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Now, we have begun focusing on the next generation of near-Earth communications relay capabilities.”
The 10 TDRS spacecraft comprise the space-based portion of the Space Network, relaying signals from low-Earth-orbiting missions with nearly 100 percent coverage.
“The acceptance of this final third-generation TDRS into the Space Network is the result of many years of dedication and hard work by the TDRS team,” said Dave Littmann, the TDRS project manager at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “As a result, critical space communication and tracking services that enable NASA human spaceflight and scientific discovery will continue well into the next decade.”
TDRS-13 launched on Aug. 18, 2017, aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Built by Boeing in El Segundo, California, TDRS-13 and its nearly identical third-generation sister spacecraft are performing well. TDRS-K and -L launched in 2013 and 2014, respectively.
NASA established the TDRS project in 1973, and the first satellite launched 10 years later, providing NASA an exponential increase in data rates and contact time communicating with the space shuttle and other orbiting spacecraft, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. Since then, NASA has continued to expand the TDRS constellation and advance the spacecraft capabilities.
“NASA looks forward to the future, developing even better ways to meet missions’ communications needs,” said Younes. “We will leverage NASA’s success in optical communications and other innovative technologies, as well as significantly increase our partnership with industry, as we envision a shift to increased reliance on commercial networks for most, if not all, of our communications needs in the near-Earth environment.”
Goddard is home to the TDRS project, which is responsible for the development and launch of these communication satellites. Boeing, headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, is the private contractor for the third-generation TDRS spacecraft. TDRS is the space element of NASA’s Space Network, providing the critical communication and navigation lifeline for NASA missions. NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) program, part of the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters in Washington, is responsible for NASA’s Space Network.
For more information about NASA’s TDRS satellites, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/tdrs
For more information about SCaN, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/SCaN
By Ashley Hume
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.