America stands on the cusp of a new era in aviation that’s dramatically cleaner, quieter, and even faster.
The details of NASA’s plan to get from here to there are spelled out in President Obama’s recently released federal budget request for the fiscal year beginning Oct. 1, 2016. If approved, next year will be the first in a bold 10-year plan by NASA Aeronautics to achieve huge goals in reducing fuel use, emissions, and noise by the way aircraft are designed, and the way they operate in the air and on the ground.
One exciting piece of this 10-year plan is New Aviation Horizons – an ambitious undertaking by NASA to design, build and fly a variety of flight demonstration vehicles, or “X-planes.” It’s a shout-out to NASA’s century-old heritage in using experimental aircraft to test advanced technologies and revolutionary designs, and to reduce the time it takes for the tech to be adopted by industry and moved into the marketplace.
Thanks to recent extraordinary results coming out of six years of technology demonstrations done with other government agencies, industry and academia, NASA Aeronautics feels confident to enter X-plane territory.
The demos included advancements in lightweight composite materials that are needed to create revolutionary aircraft structures, an advanced fan design to improve propulsion and reduce noise in jet engines, designs to reduce noise from wing flaps and landing gear, and shape-changing wing flaps, and even coatings to prevent bug residue buildup on wings. Researchers predict the tech could save the airline industry $255 billion accrued during the first 25 years after being put into service.
“We’re at the right place, at the right time, with the right technologies,” said Jaiwon Shin, associate administrator for NASA’s Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate. “The full potential of these technologies can’t be realized in the tube-and-wing shape of today’s aircraft,” he explained. “We need the X-planes to prove, in an undeniable way, how that tech can make aviation more Earth friendly, reduce delays and maintain safety for the flying public, and support an industry that’s critical to our nation’s economic vitality.”
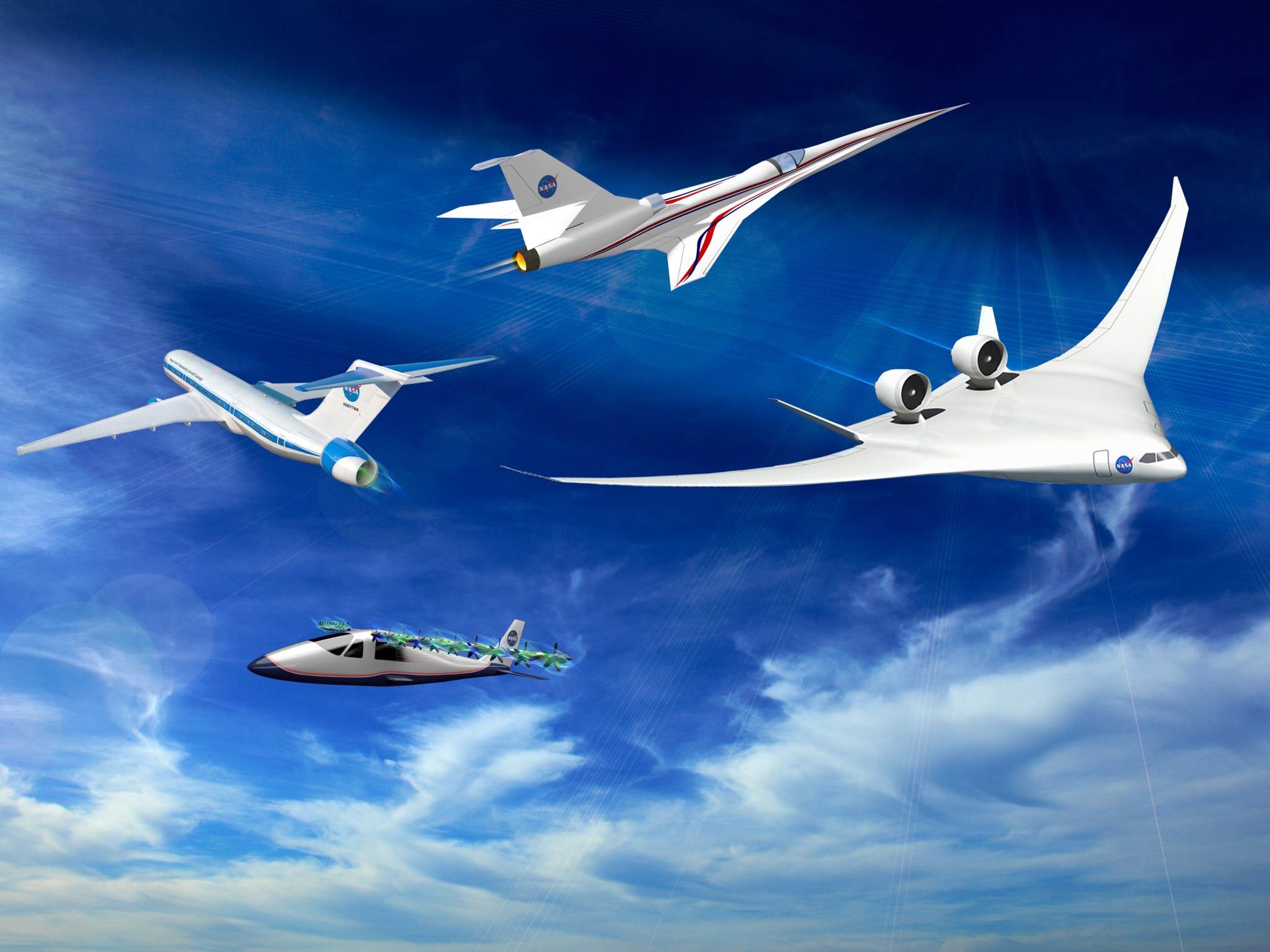
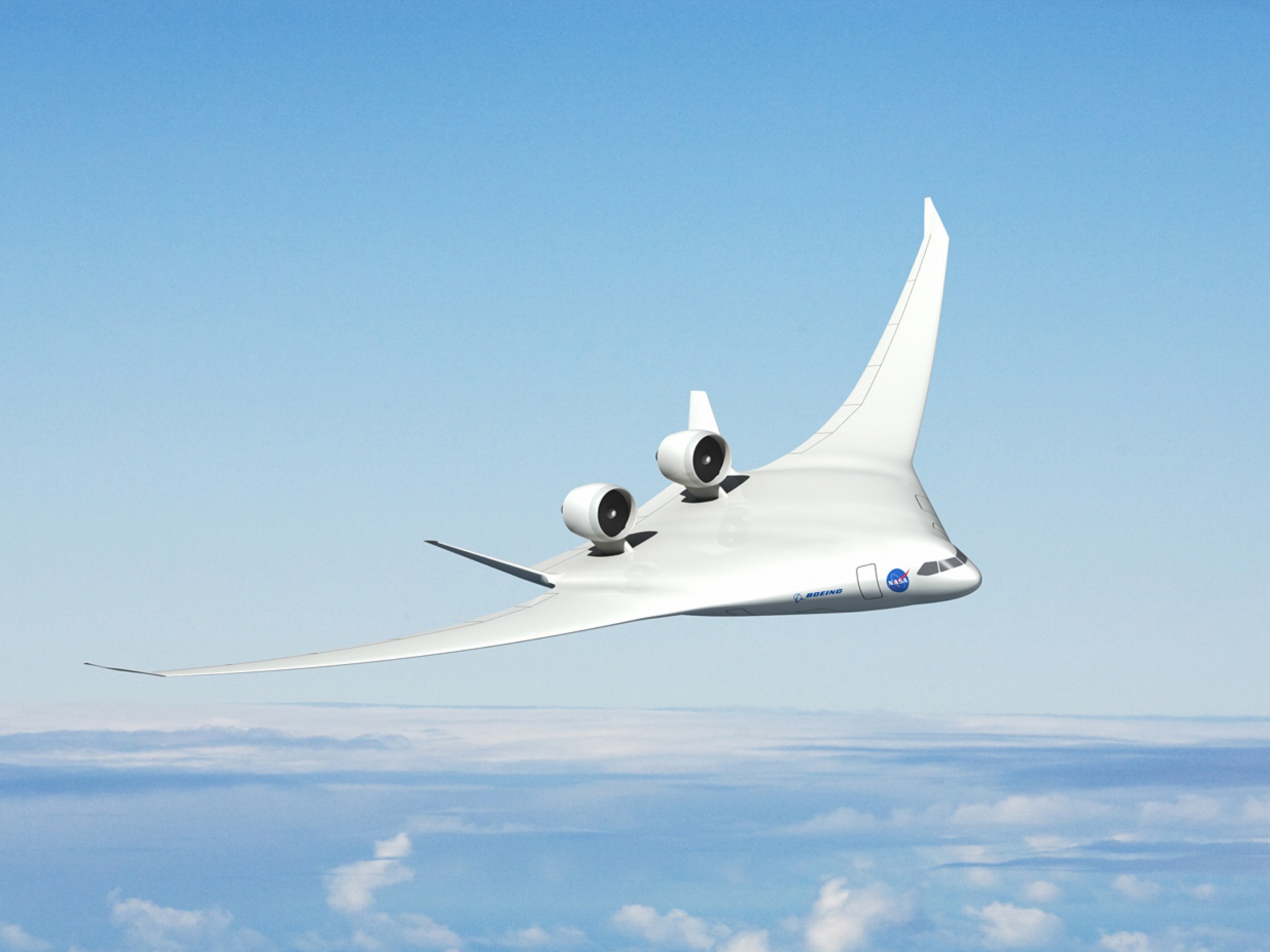
One of the first X-planes is expected to be a hybrid wing body shape, where the familiar tube-and-wing instead becomes a wing that blends into the body. It flies the same speeds as commercial transport aircraft.
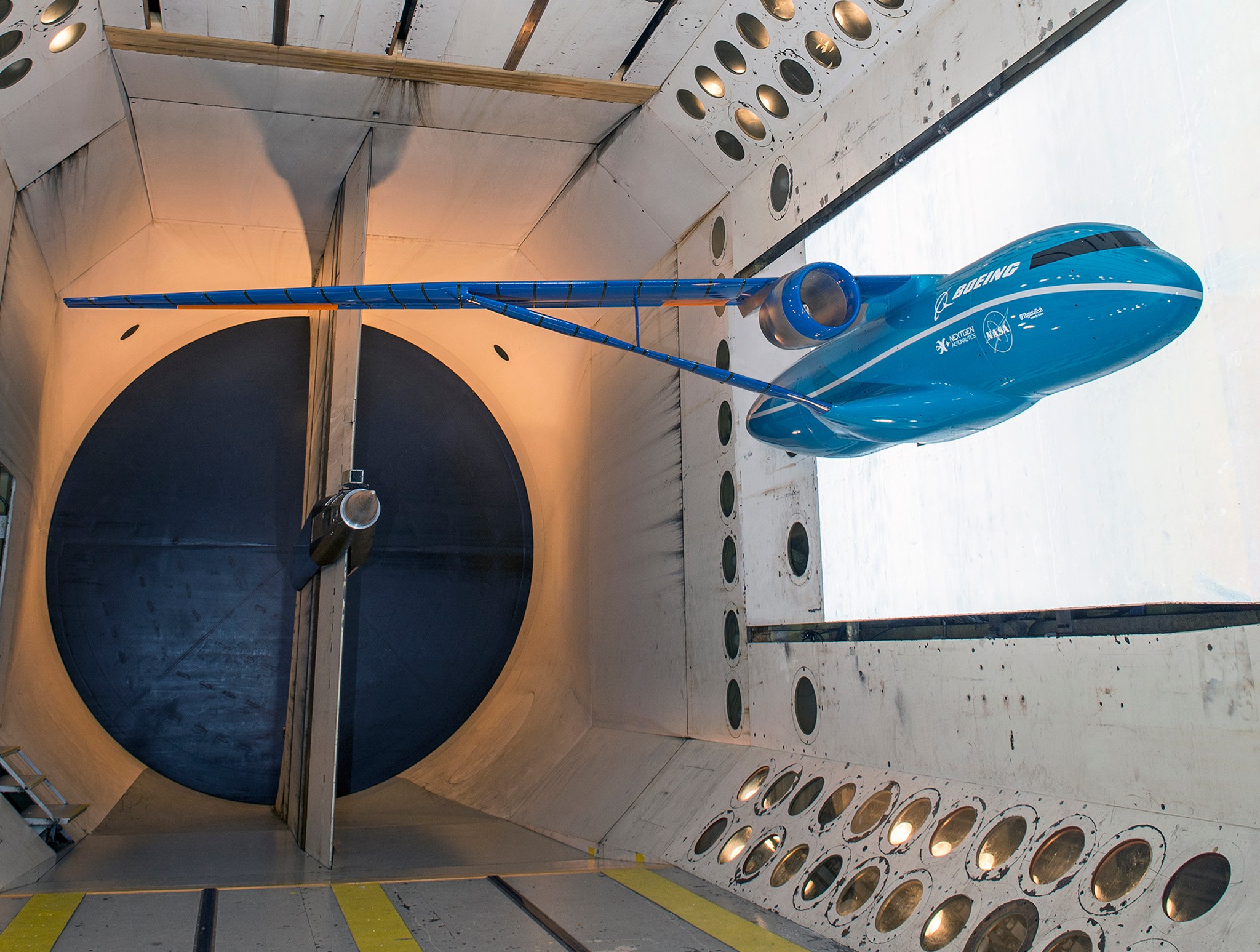
Engines are on top of a fuselage that is itself revolutionary because of the shape and what’s required to build it to withstand the stresses of flight. For the past decade, NASA and partners have studied the performance and benefits of the hybrid wing body configuration using computers, wind tunnels and even subscale unpiloted flight tests. A lot of data is already in hand to inform an X-plane that will test the highest number of advanced technologies.
Other X-planes will demonstrate specific technologies related to ultra-efficient subsonic aircraft designs in flight – possibilities include very long but narrow wings, forms of electric propulsion, a double-wide fuselage, or engines embedded into the vehicle.
And in a world “first,” another X-plane will be a business-jet-sized supersonic vehicle that burns low carbon bio-fuels and generates such quiet sonic booms that people on the ground will barely hear them.
The New Aviation Horizons X-planes will typically be about half-scale of a production aircraft, although some may be smaller or larger, and are likely to be piloted. Design-and-build will take several years, with vehicles going to flight starting around 2020 depending on funding.
The 10-year plan also includes major field tests in collaboration with airlines, airports and the Federal Aviation Administration to continue improving air traffic flow in the air and on the ground at airports. Improving the flow leads to reduced fuel use and emissions, and less noise during takeoff, approach and landing. And NASA will continue researching and testing technologies that could be used to safely integrate unmanned aircraft systems, or drones, into the airspace.
“This is an exciting time for the entire NASA Aeronautics team and for those who benefit from aviation, which, frankly, is everyone,” Shin said. “With this 10-year plan to accelerate the transformation of aviation, the United States can maintain its status as the world’s leader in aviation for many years to come.”
NASA Aeronautics research takes place primarily at the Ames Research Center and Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, the Glenn Research Center in Ohio and the Langley Research Center in Virginia.