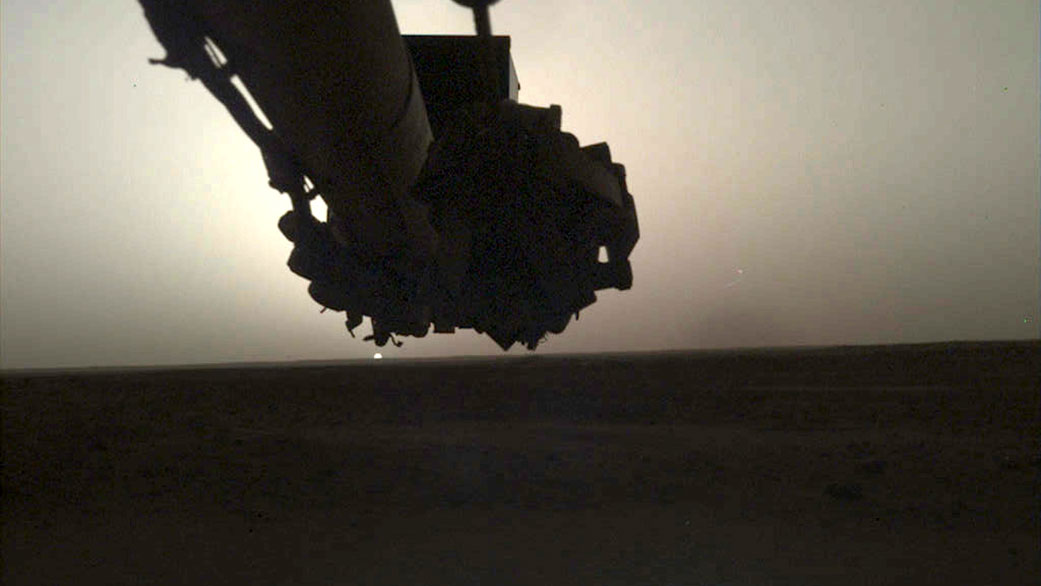
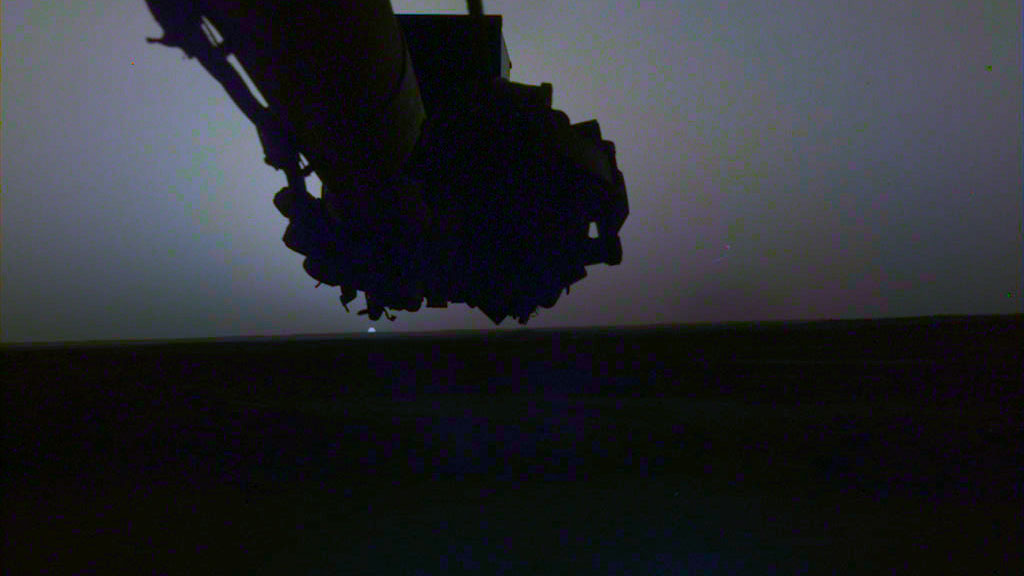
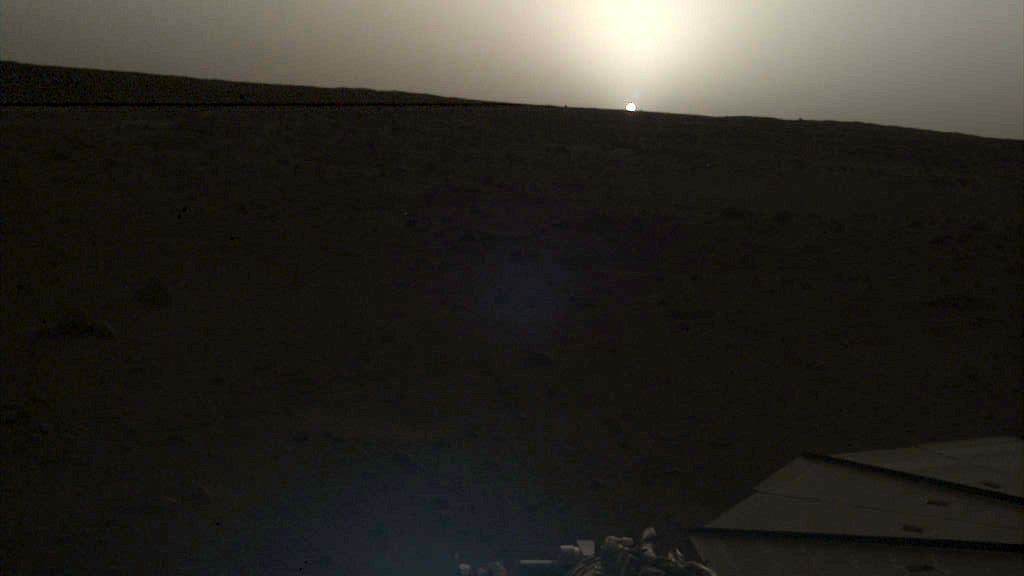
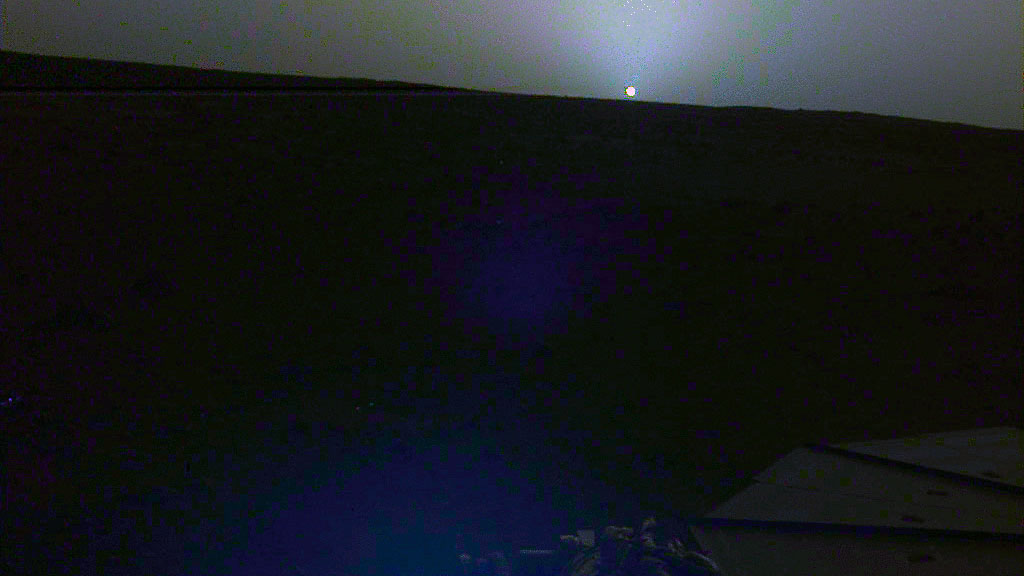
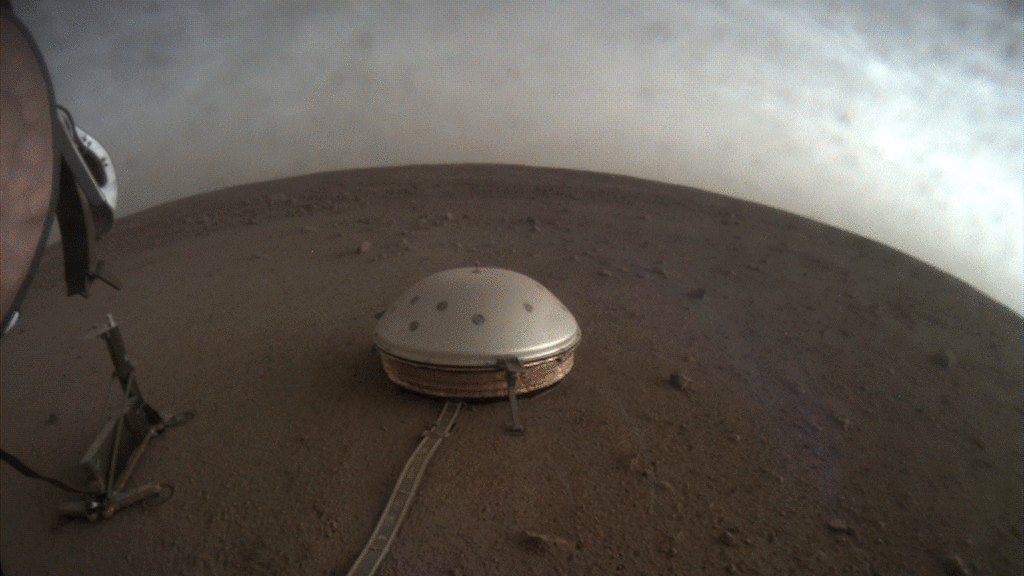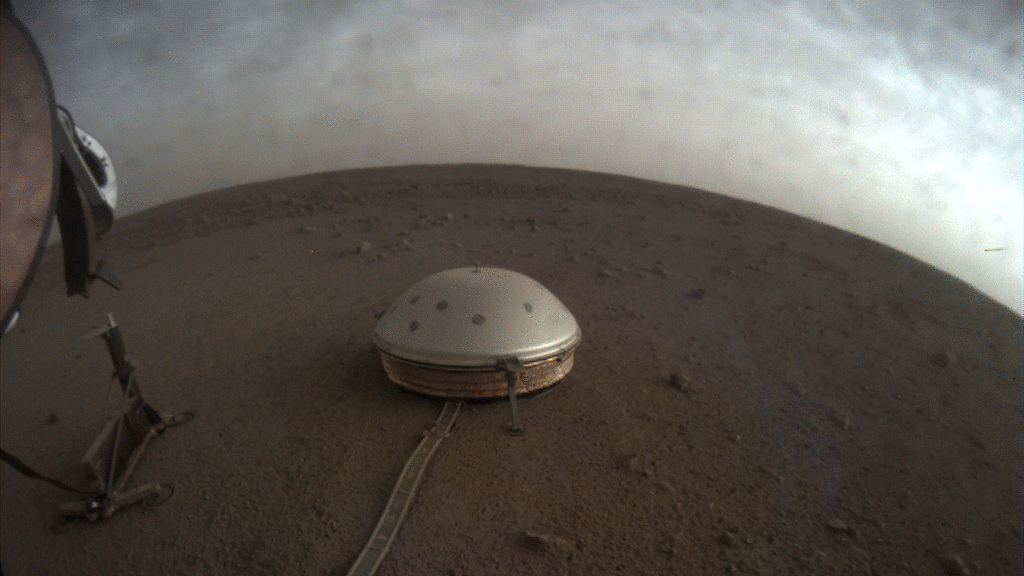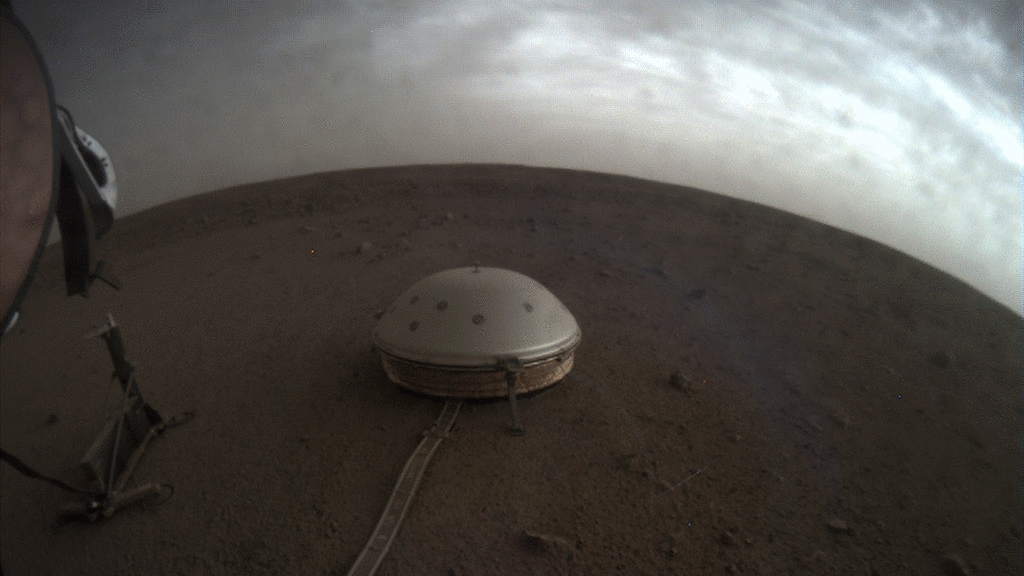
NASA’s InSight lander captured a series of sunrise and sunset images.
A camera on the spacecraft’s robotic arm snapped the photos on April 24 and 25, the 145th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. In local Mars time, the shots were taken starting around 5:30 a.m. and then again starting around 6:30 p.m. As a bonus, a camera under the lander’s deck also caught clouds drifting across the Martian sky at sunset.
These images are available as both “raw” and color-corrected versions. It’s easier to see some details in the raw versions, but the latter more accurately show the images as the human eye would see them. Much farther from Mars than it is from Earth, the Sun appears only about two-thirds the size that it does when viewed from Earth.
This is actually the second time InSight has captured these daily events: The camera took practice shots on March 2 and 10. “It’s been a tradition for Mars missions to capture sunrises and sunsets,” said Justin Maki, InSight science team co-investigator and imaging lead at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. “With many of our primary imaging tasks complete, we decided to capture the sunrise and sunset as seen from another world.”
The first mission to send back such images was the Viking 1 lander, which captured a sunset on Aug. 21, 1976; Viking 2 captured a sunrise on June 14, 1978. Since then, both sunrises and sunsets have been recorded by the Spirit, Opportunity and Curiosity rovers, among other missions.
About InSight
JPL manages InSight for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate. InSight is part of NASA’s Discovery Program, managed by the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver built the InSight spacecraft, including its cruise stage and lander, and supports spacecraft operations for the mission.
A number of European partners, including France’s Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR), are supporting the InSight mission. CNES provided the Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) instrument to NASA, with the principal investigator at IPGP (Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris). Significant contributions for SEIS came from IPGP; the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS) in Germany; the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH Zurich) in Switzerland; Imperial College London and Oxford University in the United Kingdom; and JPL. DLR provided the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3) instrument, with significant contributions from the Space Research Center (CBK) of the Polish Academy of Sciences and Astronika in Poland. Spain’s Centro de Astrobiología (CAB) supplied the temperature and wind sensors.
For more about InSight, visit:
https://mars.nasa.gov/insight/
Andrew Good
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-2433
andrew.c.good@jpl.nasa.gov
2019-080