The Apollo 13 prime crew of Commander James A. Lovell, Command Module Pilot (CMP) Thomas K. Mattingly, and Lunar Module Pilot (LMP) Fred W. Haise, and their backups John W. Young, John L. “Jack” Swigert, and Charles M. Duke, continued to train for their 10-day mission planned to include a landing in the Fra Mauro region of the Moon. Engineers continued to prepare their Saturn V rocket and spacecraft at the launch pad for the April 11, 1970, liftoff and completed the Flight Readiness Test of the vehicle on Feb. 26. All six astronauts spent many hours in flight simulators training for the mission while the Moon walkers practiced landing the Lunar Module and rehearsed their planned Moon walks.
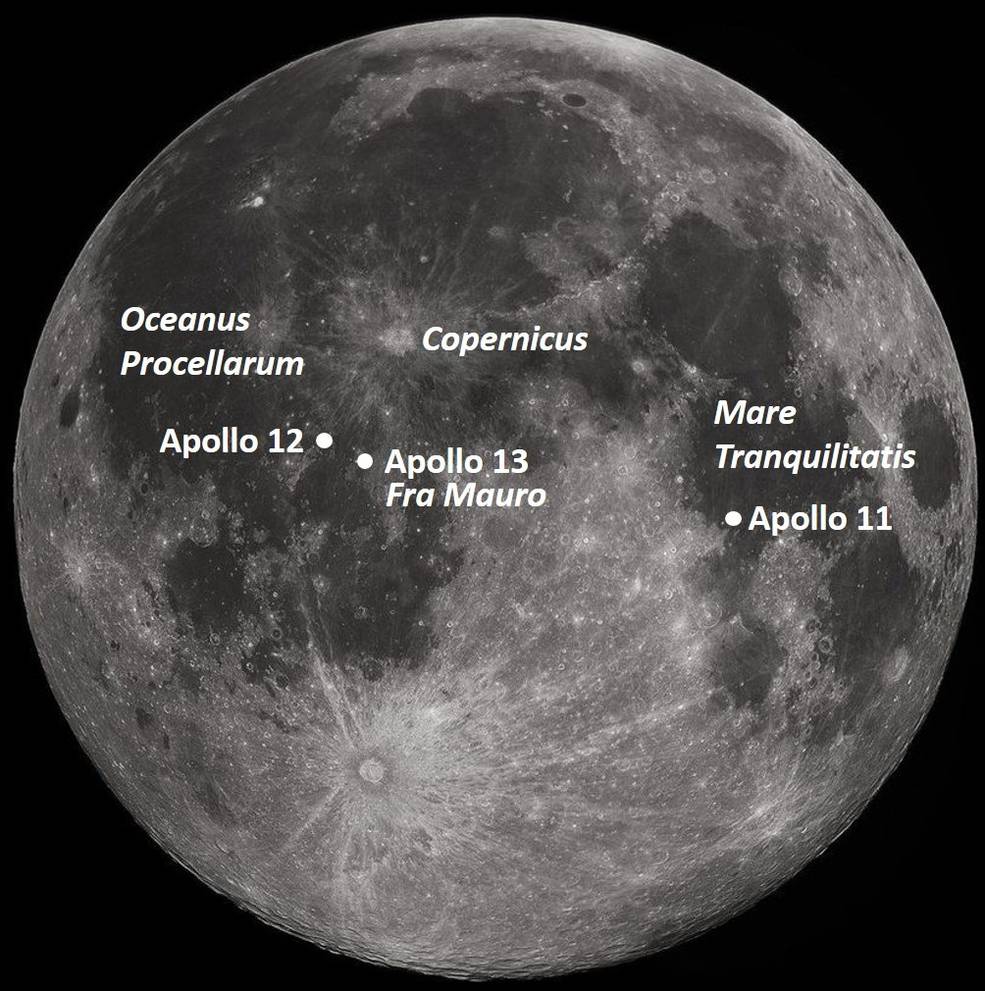
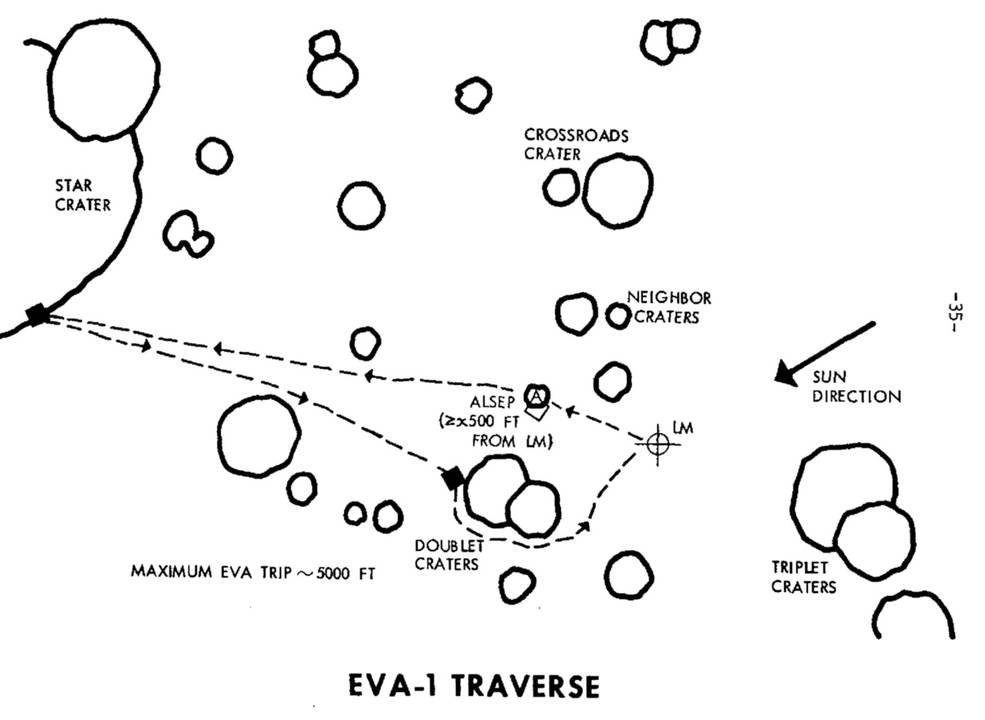
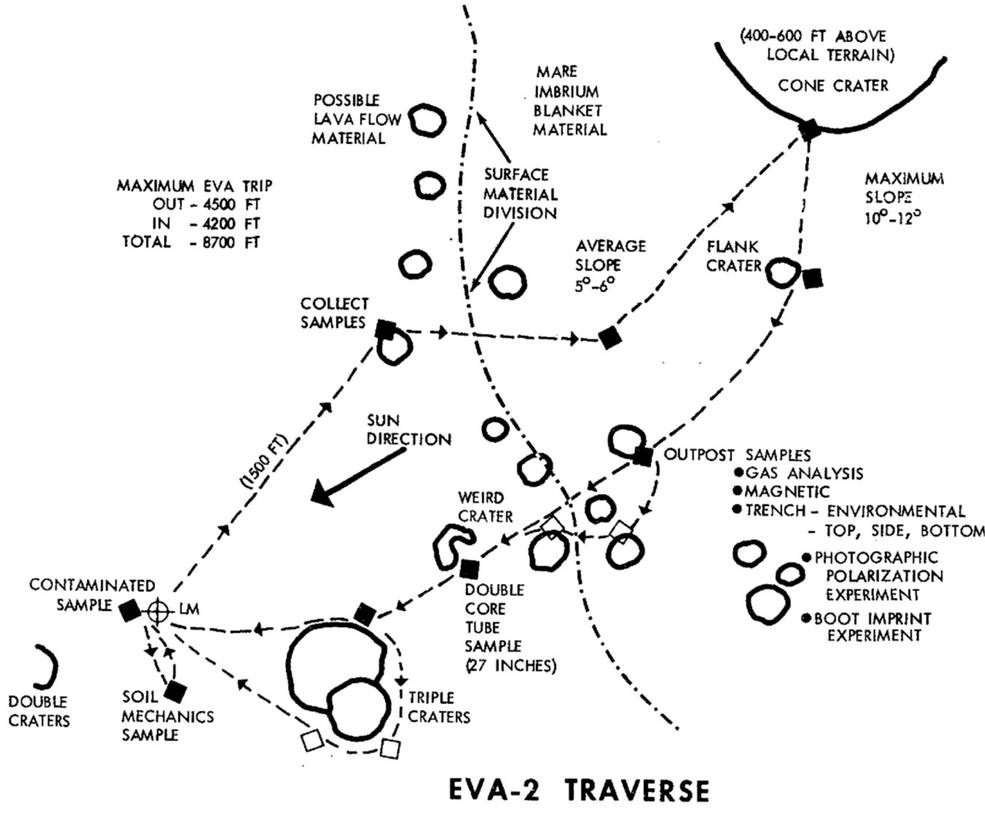
Left: Location of the planned Apollo 13 landing site on the Moon.
Middle and right: Plot of the first and second EVA traverses at Fra Mauro.
One of the greatest challenges astronauts faced during a lunar mission entailed completing a safe landing on the lunar surface. In addition to time spent in simulators, Apollo mission commanders and their backups trained for the final few hundred feet of the descent using the Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV) at Ellington Air Force Base near the Manned Spacecraft Center, now the Johnson Space Center in Houston. Used to simulate the flying characteristics of the Lunar Module (LM) Bell Aerosystems of Buffalo, New York, built three copies of the LLTV for NASA. The first vehicle, LLTV-1, was lost in a crash in December 1968, and Apollo commanders trained using LLTV-2 until managers cleared LLTV-3 for flight in January 1970. Both Lovell and Young completed several flights in February 1970. Due to scheduling constraints with the LLTV, LMPs trained for their role in the landing using the Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) at NASA’s Langley Research Facility in Hampton, Virginia. Haise and Duke completed training sessions with the LLRF in February.
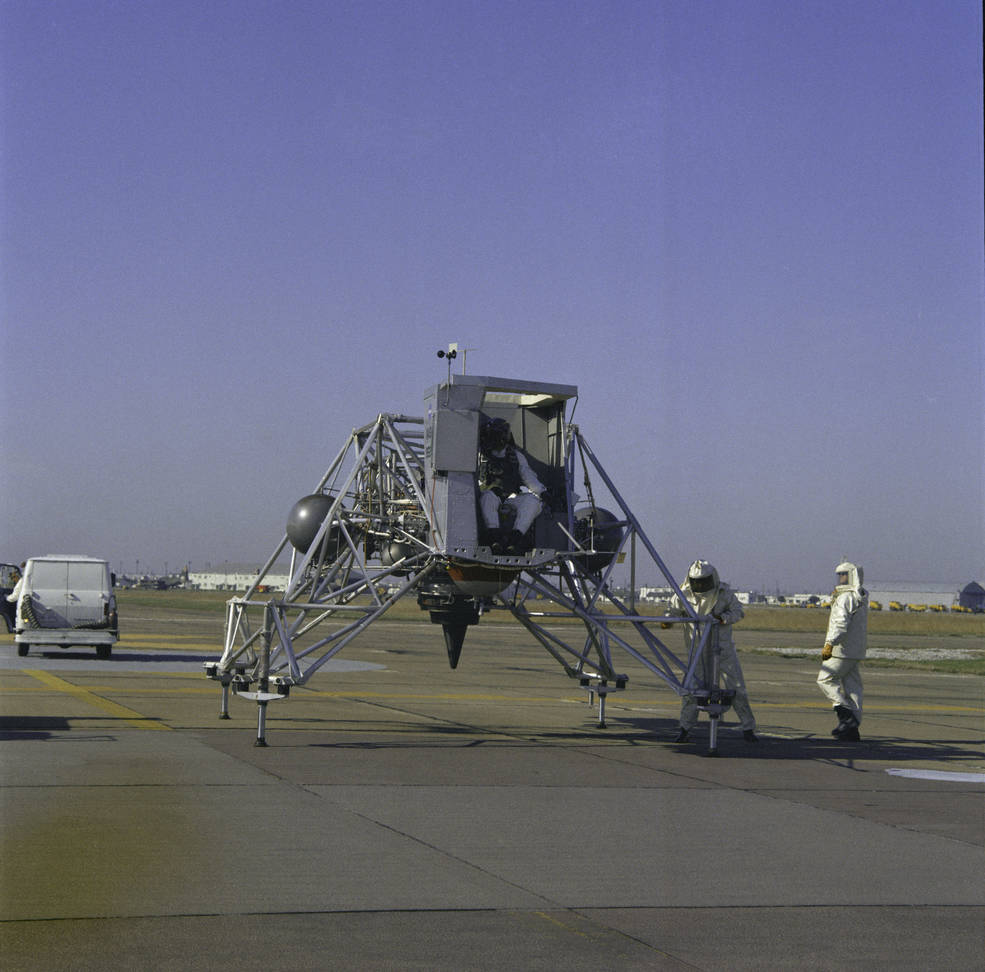
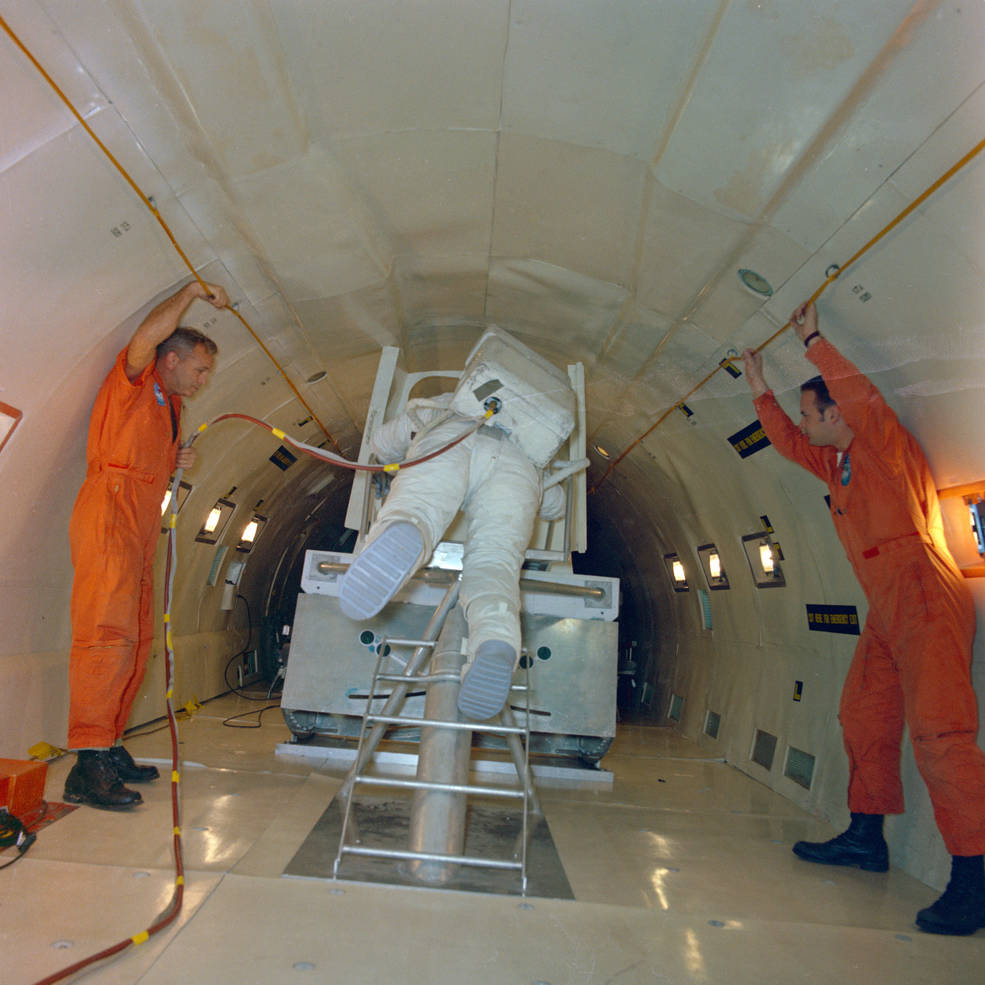
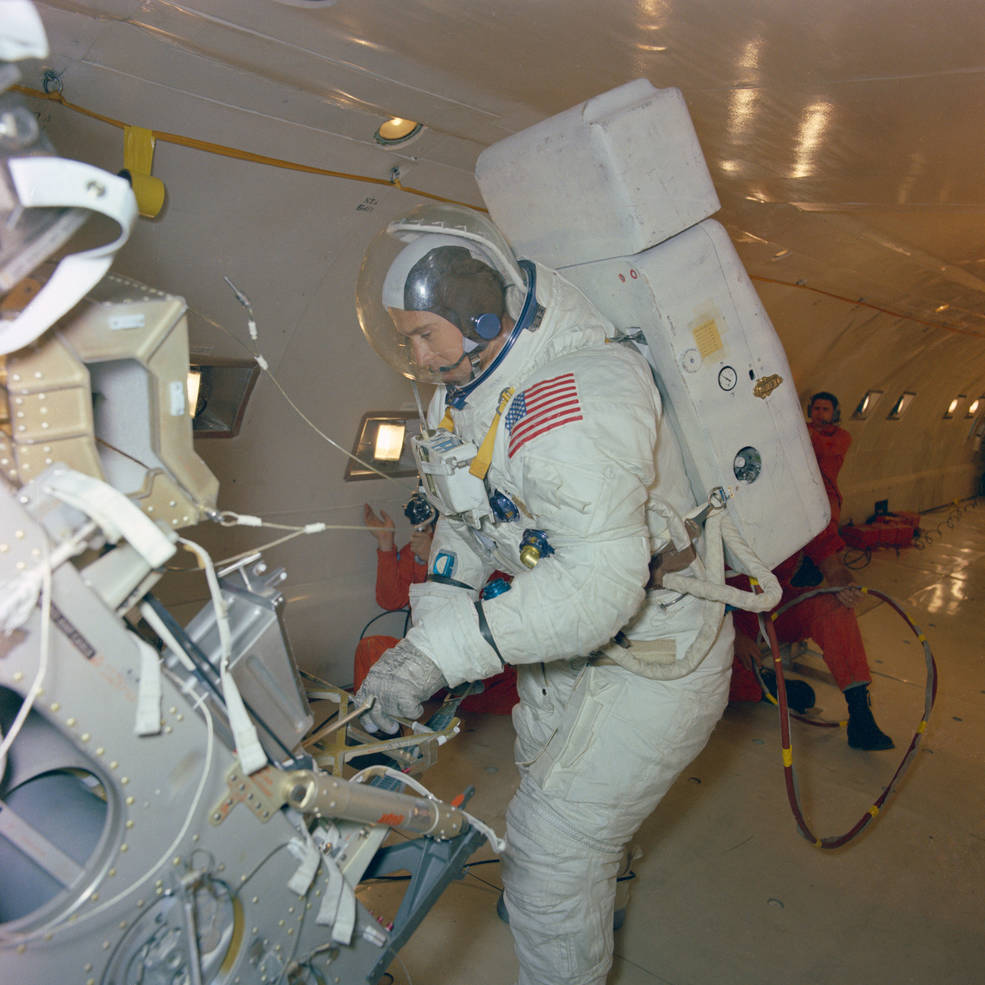



Left: Young after an LLTV training flight. Middle: Duke practicing LM egress during a
KC-135 parabolic flight. Right: Duke rehearsing unstowing equipment from the LM
during a KC-135 parabolic flight.
The Moon walking astronauts also rehearsed the Extravehicular Activities (EVAs) they planned to conduct on the lunar surface. During parabolic flights aboard NASA’s KC-135 aircraft that simulated the low lunar gravity, the astronauts practiced exiting from the LM and descending the ladder to the surface. On the ground, they rehearsed the Moon walks, setting up the American flag and the large S-band communications antenna, and collecting lunar samples. Engineers improved their spacesuits to make the expected longer spacewalks more comfortable for the crewmembers by installing eight-ounce bags of water inside the helmet to provide them with a way to remain hydrated.
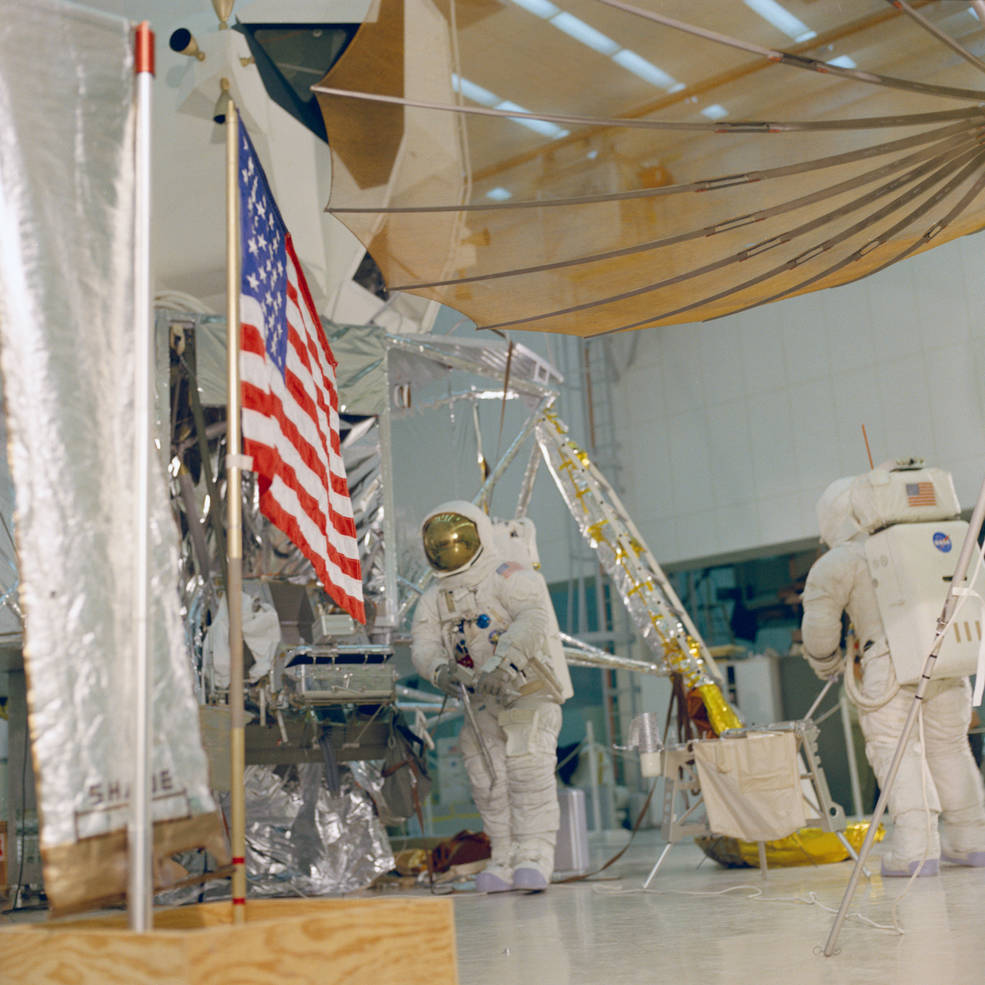
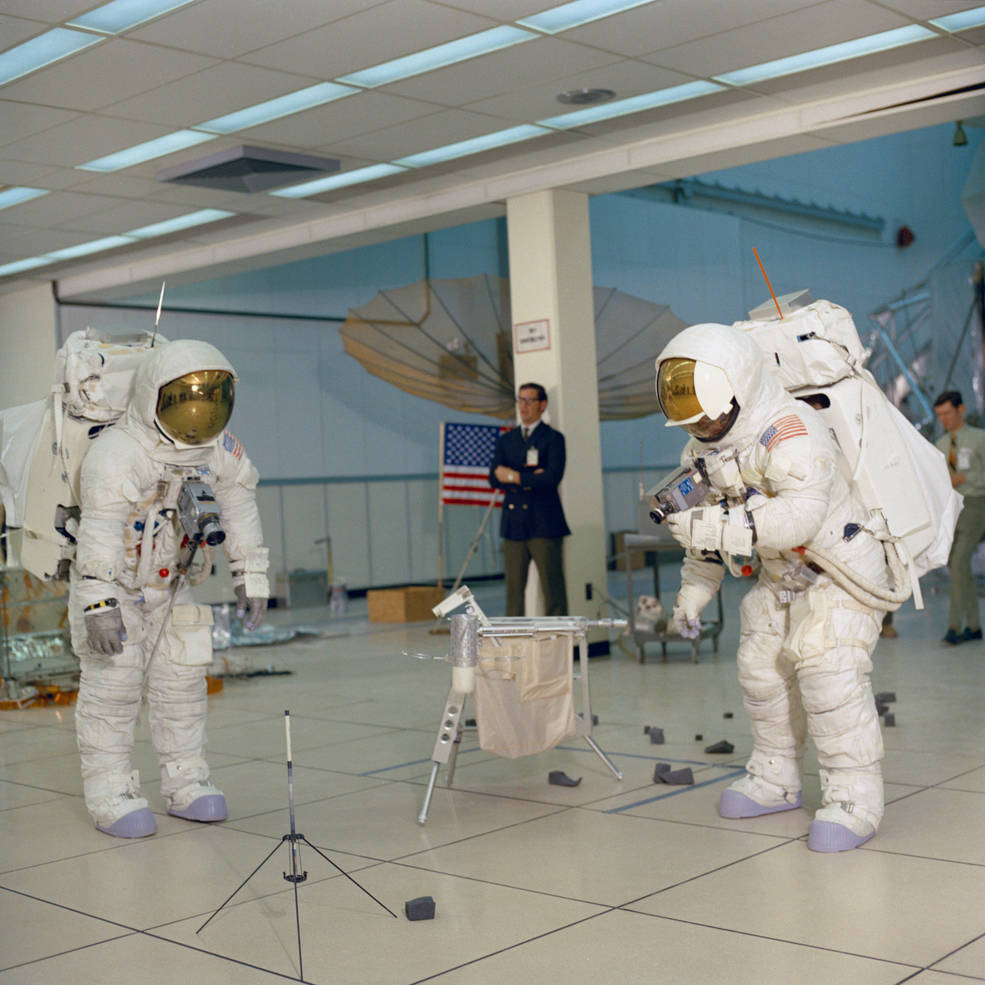
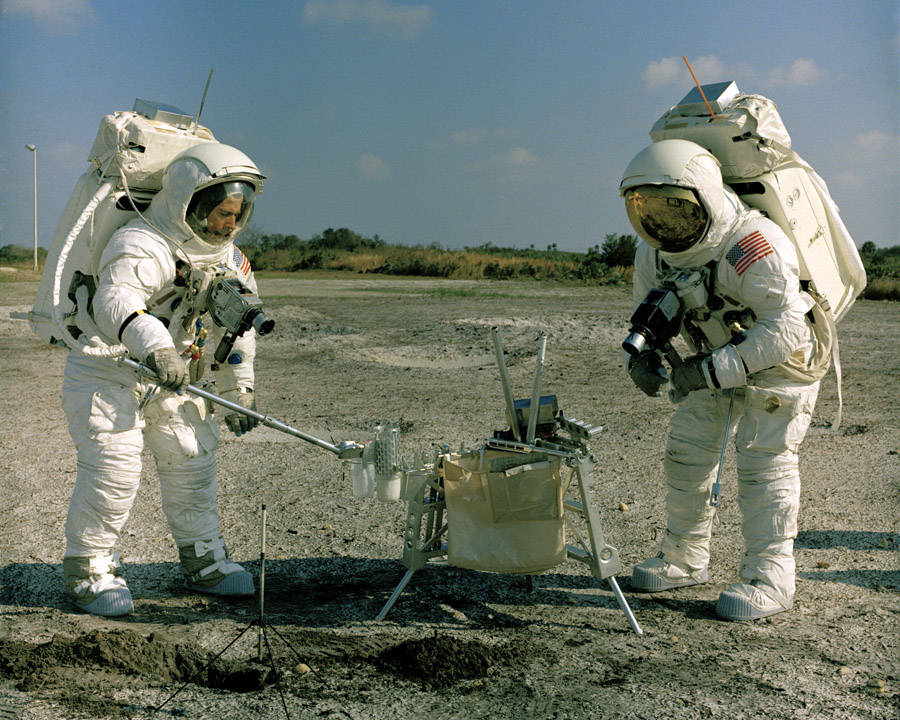



Left: Lovell (at left) and Haise setting up equipment as well as the American flag
and the S-band antenna. Middle: Lovell (at left) and Haise practice collecting rock sanples.
Right: Young (at left) and Duke training to collect rock samples.
During their 33.5 hours on the Moon’s surface, Lovell and Haise planned to conduct two four-hour EVAs to set up the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP), a suite of four investigations designed to collect data about the lunar environment after the astronauts’ departure, and to conduct geologic explorations of the landing site. The four ALSEP experiments included:
- The Charged Particle Lunar Environment Experiment (CPLEE) designed to measure the flexes of charged particles;
- The Cold Cathode Gauge Experiment (CCGE) designed to measure the pressure of the lunar atmosphere;
- The Heat Flow Experiment (HFE) designed to make thermal measurements of the lunar subsurface;
- The Passive Seismic Experiment (PSE) designed to measure any moonquakes, either naturally occurring or caused by artificial means;
The HFE required the astronauts to drill into the Moon’s surface to emplace the sensors up to a depth of three meters. A Central Station provided command and communications between the experiments and scientists on Earth while a Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG) provided power to the experiments using the heat produced by the radioactive decay of the plutonium-238 fuel element. The astronauts planned to deploy and retrieve after about 20 hours of exposure on the lunar surface the Solar Wind Composition (SWC) experiment, a sheet of aluminum foil to collect particles from the solar wind for analysis by scientists back on Earth.
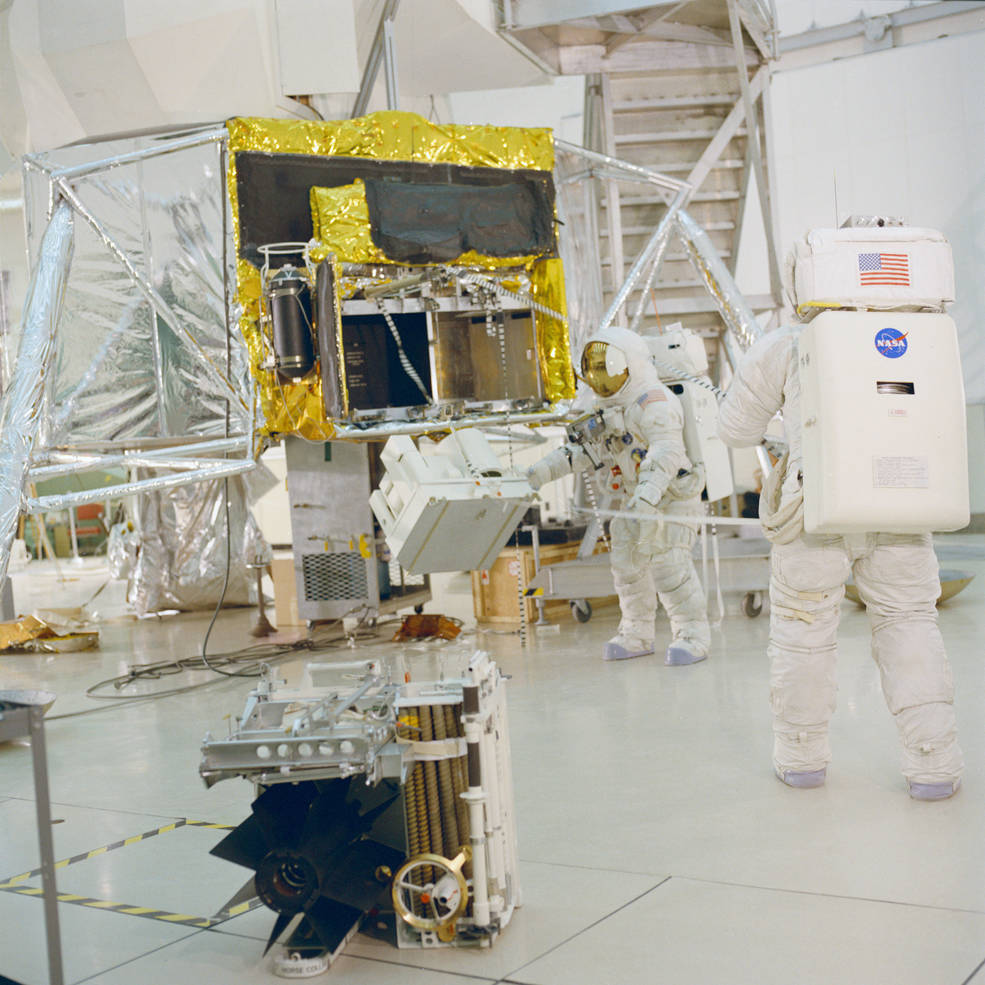
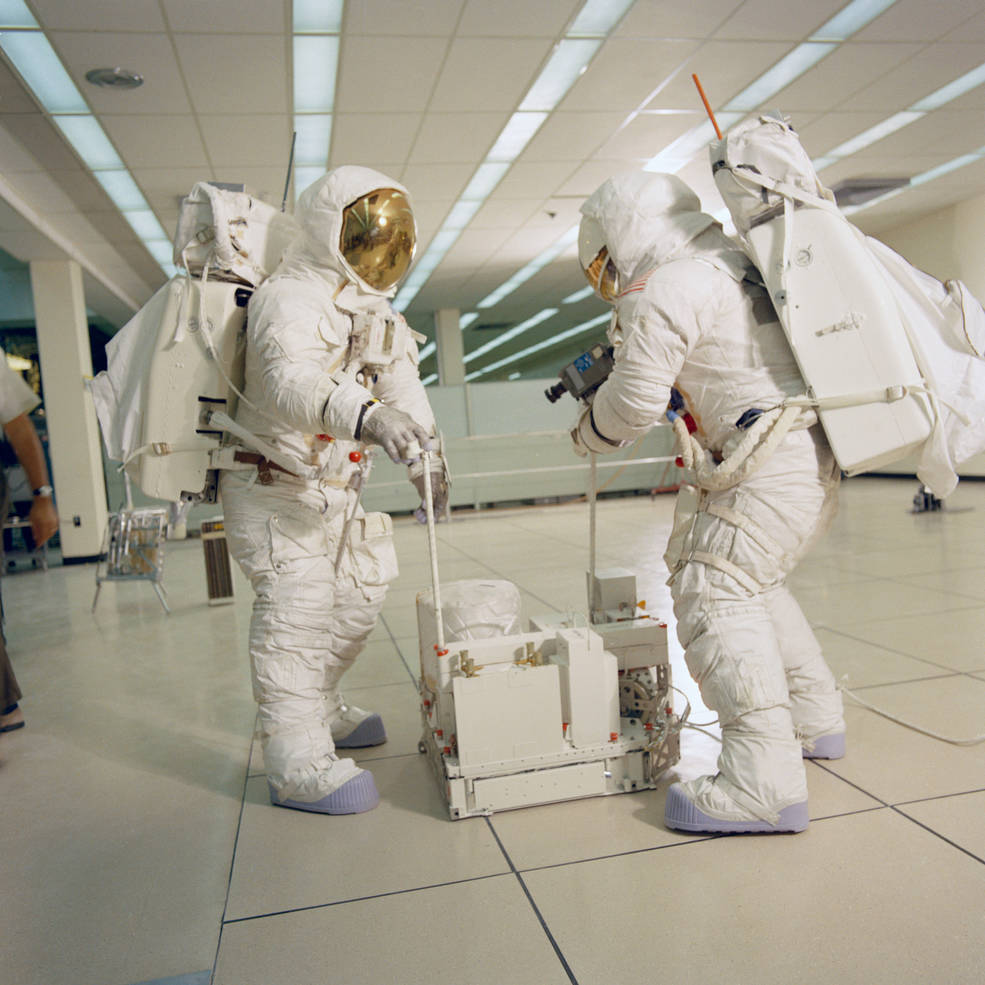
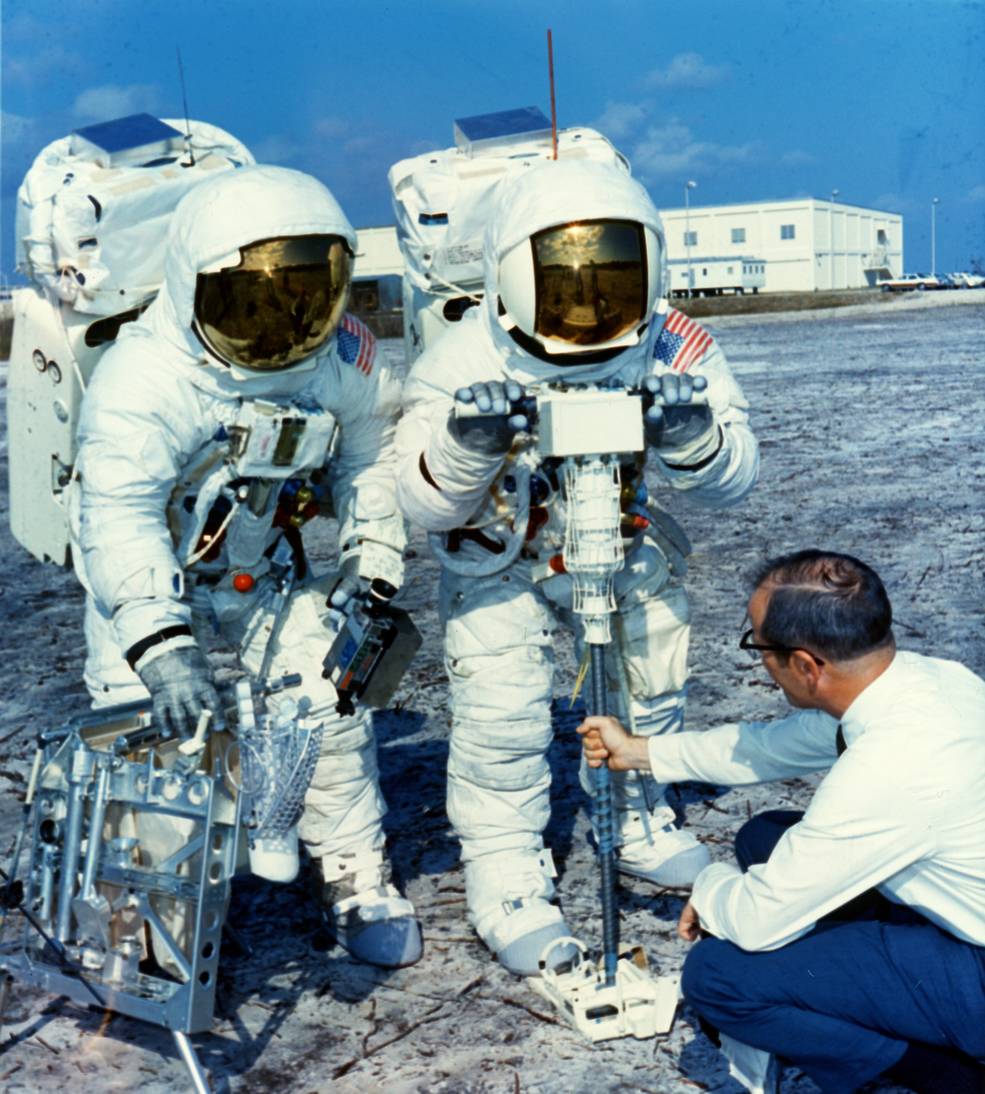



Left: Haise (at left) and Lovell practice lowering the ALSEP experiments from the LM.
Middle: Lovell (at left) and Haise practice setting up the ALSEP experiments.
Right: Lovell (left) and Haise practice drilling for the Heat Flow Experiment.
With one lunar mission just two months away, NASA continued preparations for the following flight, Apollo 14, then scheduled for October 1970 with a landing targeted for the Littrow region of the Moon, an area scientists believed to be of volcanic origin. Apollo 14 astronauts Commander Alan B. Shepard, CMP Stuart A. Roosa, and LMP Edgar D. Mitchell and their backups Eugene A. Cernan, Ronald E. Evans, and Joe H. Engle spent much of their time learning spacecraft systems in the simulators. Accompanied by a team of geologists led by Richard H. “Dick” Jahns, Shepard, Mitchell, Cernan, and Engle participated in a geology expedition to the Pinacate Mountain Range in northern Mexico between Feb. 14 and 18, 1970. In addition to learning the volcanic geology at the site, the astronauts practiced using the Modular Equipment Transporter (MET), a two-wheeled conveyance nicknamed the “Rickshaw” to transport their tools and samples once on the lunar surface.
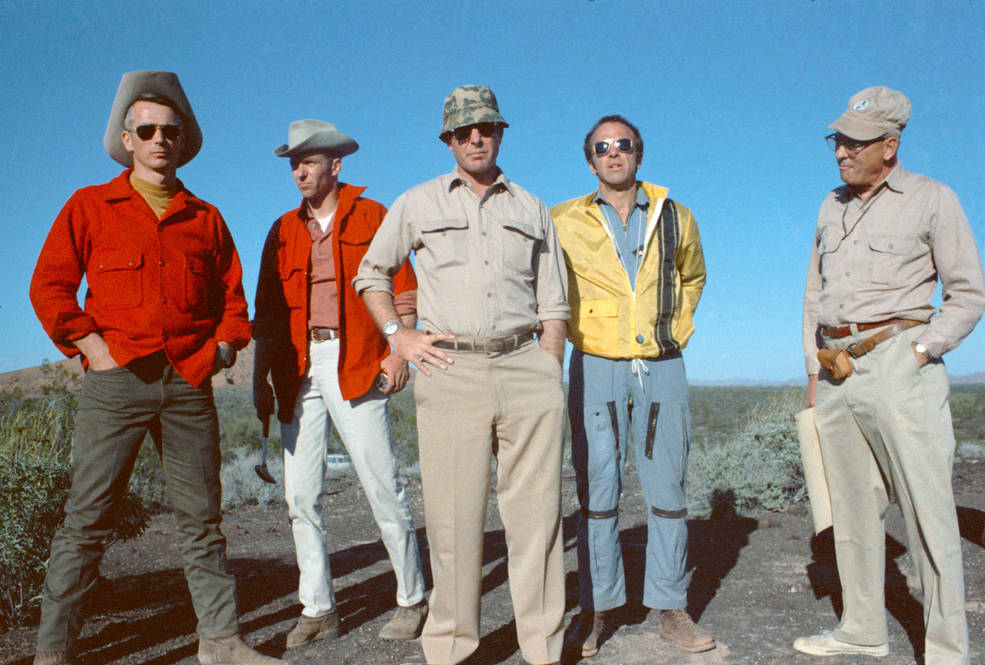
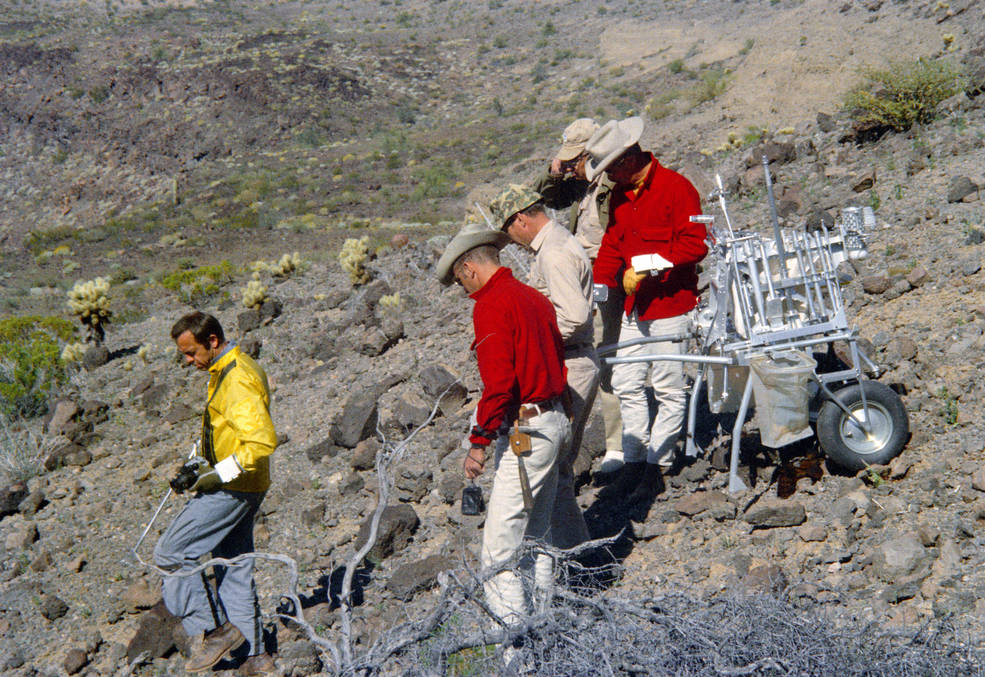


Left: Apollo 14 astronauts (left to right) Cernan, Engle, Mitchell, and Shepard with geologist
Jahns in the Pinacates Mountains. Right: Apollo 14 astronauts (left to right) Shepard,
Engle, Mitchell, and Cernan training with the MET, accompanied by geologist Jahns.
The release to scientists of the lunar material that the Apollo 12 astronauts returned from the Moon’s Ocean of Storms in November 1969 followed a less formal process than the Apollo 11 samples. Although some scientists preferred to receive their samples in person, as occurred with the Apollo 11 samples, NASA began send most of the Apollo 12 material via certified mail on Feb. 13, 1970. In all, 139 US and 54 international investigators in 16 countries received 28.6 pounds of material in the form of rocks, chips, fine material, and thin sections, comprising a total of 1,620 separate samples. The scientists analyzed the samples for mineralogy, chemical composition, physical properties, and biologic and organic studies and reported their results at the second Lunar Science Conference in Houston in January 1971. Apollo 12 astronauts Charles “Pete” Conrad, Richard F. Gordon, and Alan L. Bean, accompanied by their wives and NASA and State Department officials, departed Houston’s Ellington Air Force Base on Feb. 16 for their 38-day Bullseye Presidential Goodwill World Tour. They first traveled to Latin America making stops in Caracas, Venezuela, Lima, Peru, Santiago, Chile, and Panama City, Panama before continuing on to Europe, Africa, and Asia.


Left: Mail out of Apollo 12 lunar samples. Right: Apollo 12 astronauts (left to right) Conrad,
Gordon, and Bean ride in a motorcade in Lima, Peru.
Early 1970 saw several significant management changes at NASA. Administrator Thomas O. Paine announced on Jan. 27 that he appointed Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Wernher von Braun as Deputy Associate for Planning at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC, responsible for planning NASA’s future programs. Von Braun’s deputy Eberhard Rees succeeded him as MSFC Director. On Feb. 13, NASA established a Space Shuttle Program Office at MSC, and named Robert F. “Bob” Thompson as its Chief. The small office initially concerned itself with developing requirements for the reusable space vehicle. President Richard M. Nixon gave the official go ahead for Space Shuttle development in 1972. On Feb. 24, NASA officially renamed the Apollo Application Program (AAP), designed to use leftover Apollo hardware to place an experimental space station into Earth orbit, as the Skylab Program and named Kenneth S. Kleinknecht as its Chief, replacing Thompson. At the time, NASA planned to launch the Skylab orbital workshop in late 1972 followed by three astronaut crews staying aboard for 28, 56, and 56 days.
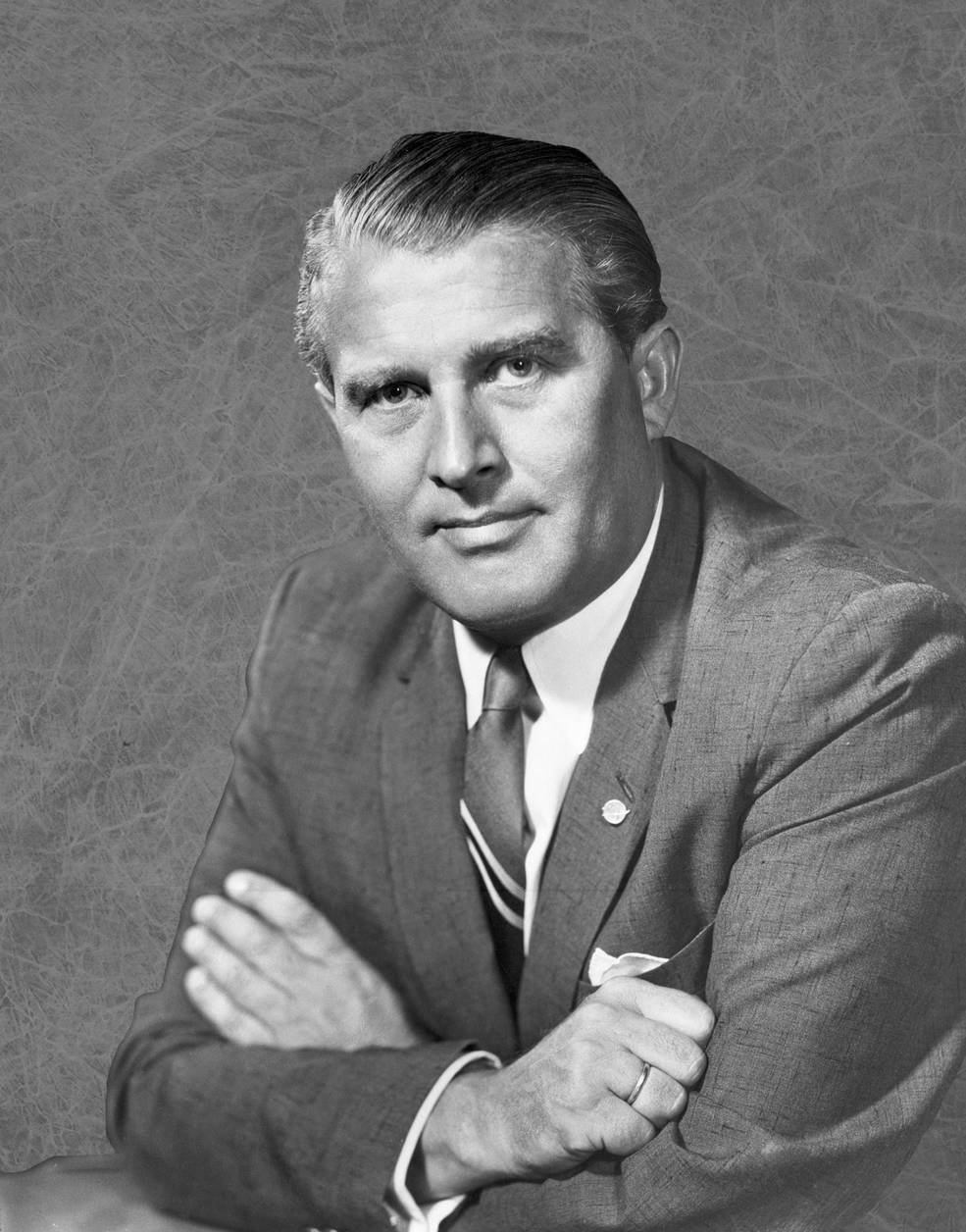
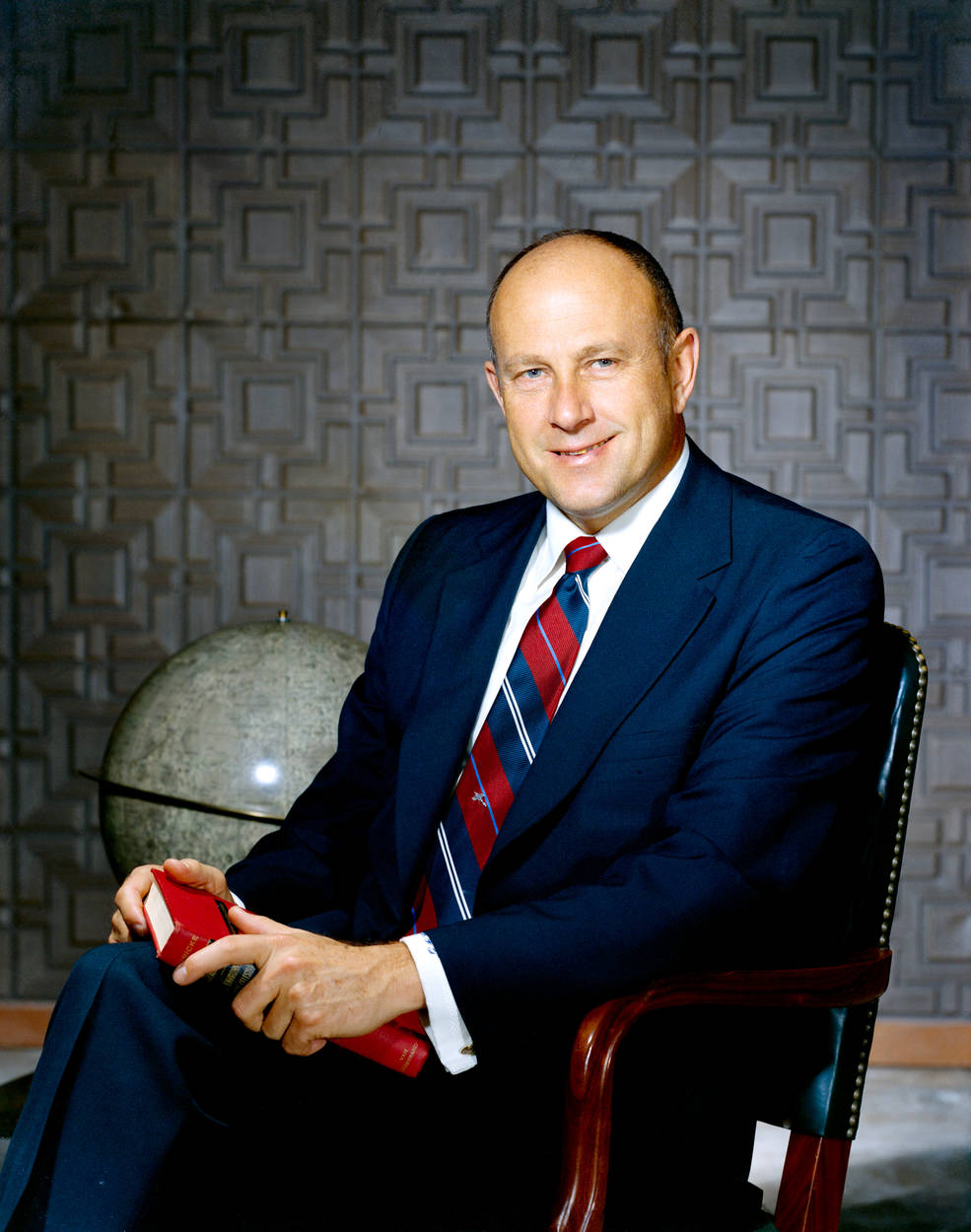
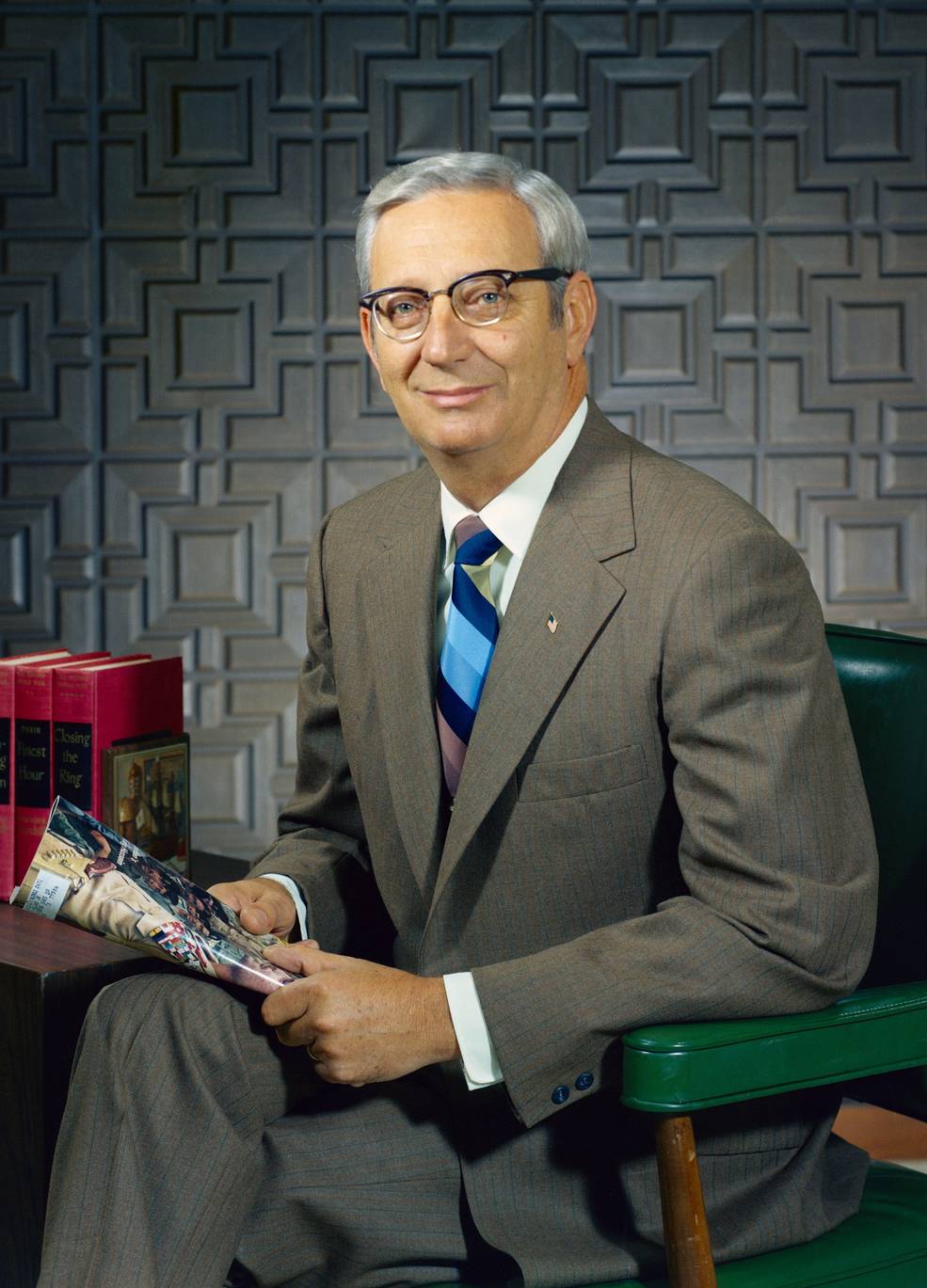



Left: Von Braun. Middle: Thompson. Right: Kleinknecht.
News events from around the world in February 1970:
Feb. 6 – The National Basketball Association (NBA) expands to 18 cities with teams in Buffalo, Cleveland, Houston, and Portland
Feb. 11 – Japan becomes 4th nation to put a satellite (Osumi) into orbit
Feb. 13 – Black Sabbath releases first heavy metal album
Feb. 21 – Jackson 5 make television debut on American Bandstand
Feb. 26 – The Beatles release Beatles Again album, better known as the Hey Jude album