Igor Bargatin
University of Pennsylvania
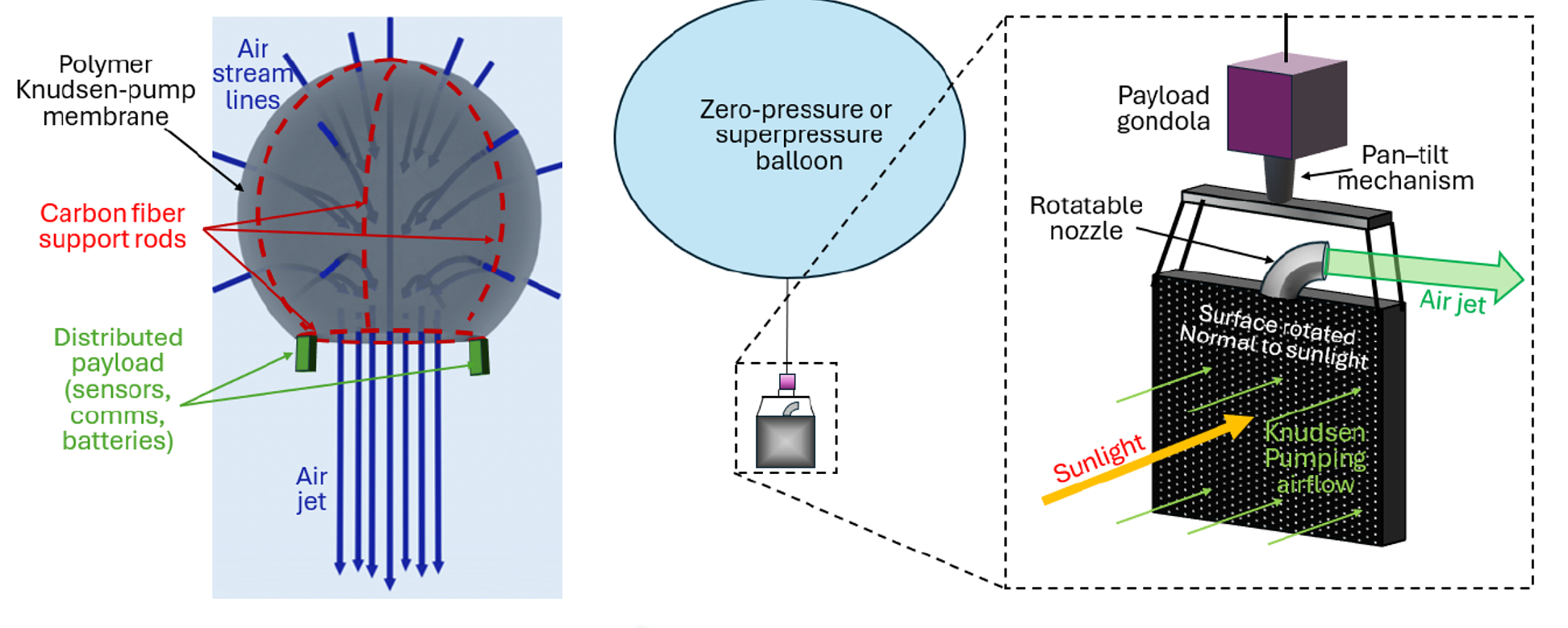
We propose to use the photophoretic levitation and propulsion mechanism to create no-moving-parts flying vehicles that can be used to explore Earth’s upper atmosphere. The photophoretic force arises when a solid is heated relative to the ambient gas through illumination, inducing momentum exchange between the solid and the gas. The force creates lift in structures that absorb light on the bottom yet stay cool on the top, and we engineered our plate mechanical metamaterials to maximize this lift force and payload. The levitation and payload capabilities of our plates typically peak at ambient pressures in the 0.1-1000 Pa range, ideal for applications in Earth’s mesosphere and Mars’s low gravity and thin atmosphere. For example, in the Earth’s mesosphere (i.e., at altitudes from ~50 to ~80 km), the air is too thin for conventional airplanes or balloons but too thick for satellites, such that measurements can be performed for only a few minutes at a time during the short flight of a research rocket. However, the range of ambient pressures in the mesosphere (1-100 Pa) is nearly optimal for our plates’ payload capabilities. Phase 2 of the proposal focuses on the scalable fabrication of Knudsen pump structures that will enable missions with kg-scale payloads in the mesosphere as well as trajectory control with 1 m/s velocity control in existing stratospheric balloon vehicles.