Home
Characteristics
Quick Facts
Data Acquisition
Gallery
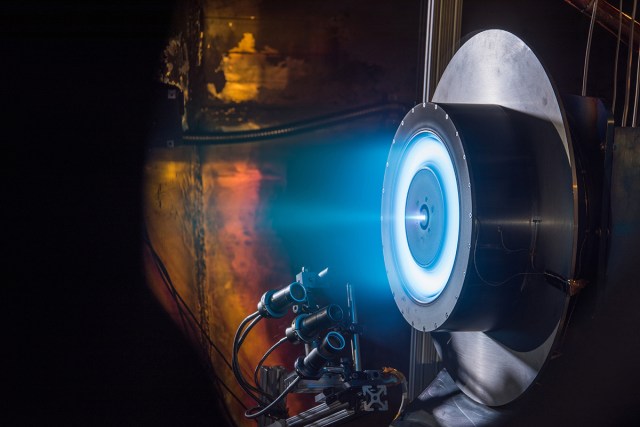
The Propulsion Systems Laboratory is NASA’s only ground-based test facility that can provide true flight simulation for experimental research on air-breathing propulsion systems.
Characteristics and Performance
- Altitude simulation to 90,000 ft
- Two engine test cells: PSL-3 and PSL-4
- Mach Number Range:
- PSL-3: to 3.0
- PSL-4: to 4.0
- PSL-4: Freejet Mach No. with auxiliary heater – to 6.0
- Tied to central compressed air and exhaust systems
- Thrust measurement: 50,000 lbf horizontal axis, 15,000 lbf vertical and lateral axes
Combustion Air System
- Main Supply
- 480 lbs/sec @ ambient temperature and 55 psia
- 380 lbs/sec @ ambient temperature and 165 psia
- 240 lbs/sec @ 1100°F and 165 psia
- 380 lbs/sec @ -40°F and 25 psia (PSL-3)
- 30 lbs/sec @ -90°F and 25 psia (PSL-4)
- Cooling Air Supply
- 100 lbs/sec @ ambient temperature and 55 psia to 165 psia
Altitude Exhaust System
- Altitude Range: sea level standard to 90,000 ft
- Mass Flow: up to 750 lbs/sec
Support Systems
- Jet Fuel System: Two 25,000 gallon tanks supporting various types of fuel (JET-A, JP-4, JP-5, JP-8)
- Natural Gas system: 10 inch header @ 50 psig
- Gaseous Hydrogen System: 1 lb/sec @ 600 psig — 3 lbs/sec @ 1100 psig, maximum pressure is 2400 psig
- Gaseous Oxygen System: 3 lbs/sec @ 1200 psig, 10 lbs/sec @ 400 psig, maximum pressure is 2400 psig
- Gaseous Nitrogen System: 132,000 scf @ 2400 psig
- Hydraulic System: 100 gpm @ 3000 psig
- High Pressure Hydraulic System: 100 gpm @ 6000 psig
Propulsion Systems Laboratory (PSL) Fact Sheet