This article is for students grades 5-8.
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an important part of NASA’s Artemis missions that plan to send a new generation of astronauts to explore the Moon. Missions at the Moon will help NASA prepare to send astronauts to Mars.
What does SLS do?
SLS is a super heavy-lift rocket. That means it has the power to carry heavy loads into space. It can send more than 27 metric tons or 59,500 pounds to the Moon. These loads can include the crew and their supplies, or the large and heavy equipment needed to explore the Moon and, eventually, Mars.
The SLS rocket itself does not fly all the way to the Moon. About eight and a half minutes after launch, after giving the Orion spacecraft the push it needs to send astronauts and cargo to lunar orbit, it separates from the spacecraft.
On the launch pad, SLS stands taller than the Statue of Liberty and weighs almost 6 million pounds (almost 3 million kilograms). That’s the weight of eight fully loaded 747 jumbo jets. The SLS rocket will travel at a top speed of over 6 miles (9.7 kilometers) per second. This is so fast that SLS could:
- Go from New York City to San Francisco in eight minutes.
- Travel from Nashville, Tennessee, to Paris, France, in 11.5 minutes.
- Circle the world in 66 minutes.
——————————————————————————————————————————————
Words to Know
cargo: goods carried on a large vehicle
thrust: the force that propels an object forward
payload: anything carried by a rocket. This can include cargo, people, hardware, scientific instruments, or satellites
——————————————————————————————————————————————
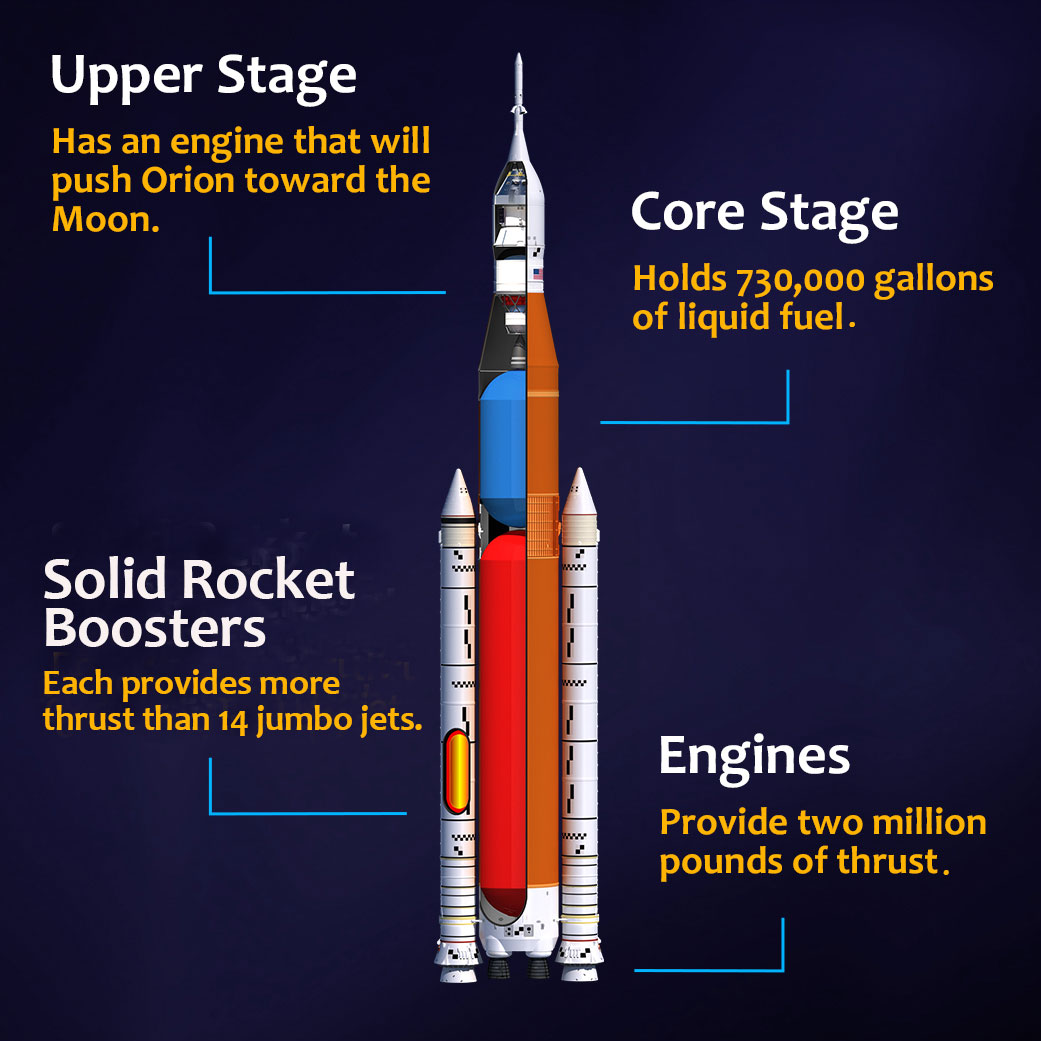
What are the parts of the SLS?
The SLS has four main sections:
- The upper stage: This section is below Orion. After the SLS launches into space, the upper stage will provide the propulsion needed to set Orion on a course to the Moon.
- The core stage: This is the large orange tank that makes up most of the rocket. It contains liquid propellants that power the engines.
- Core stage engines: The four engines at the bottom of the core stage provide thrust for the eight-minute climb to orbit.
- Solid rocket boosters: Along with the engines on the core stage, the two white solid rocket boosters provide the initial thrust to push SLS away from Earth’s gravity.
How does the SLS launch?
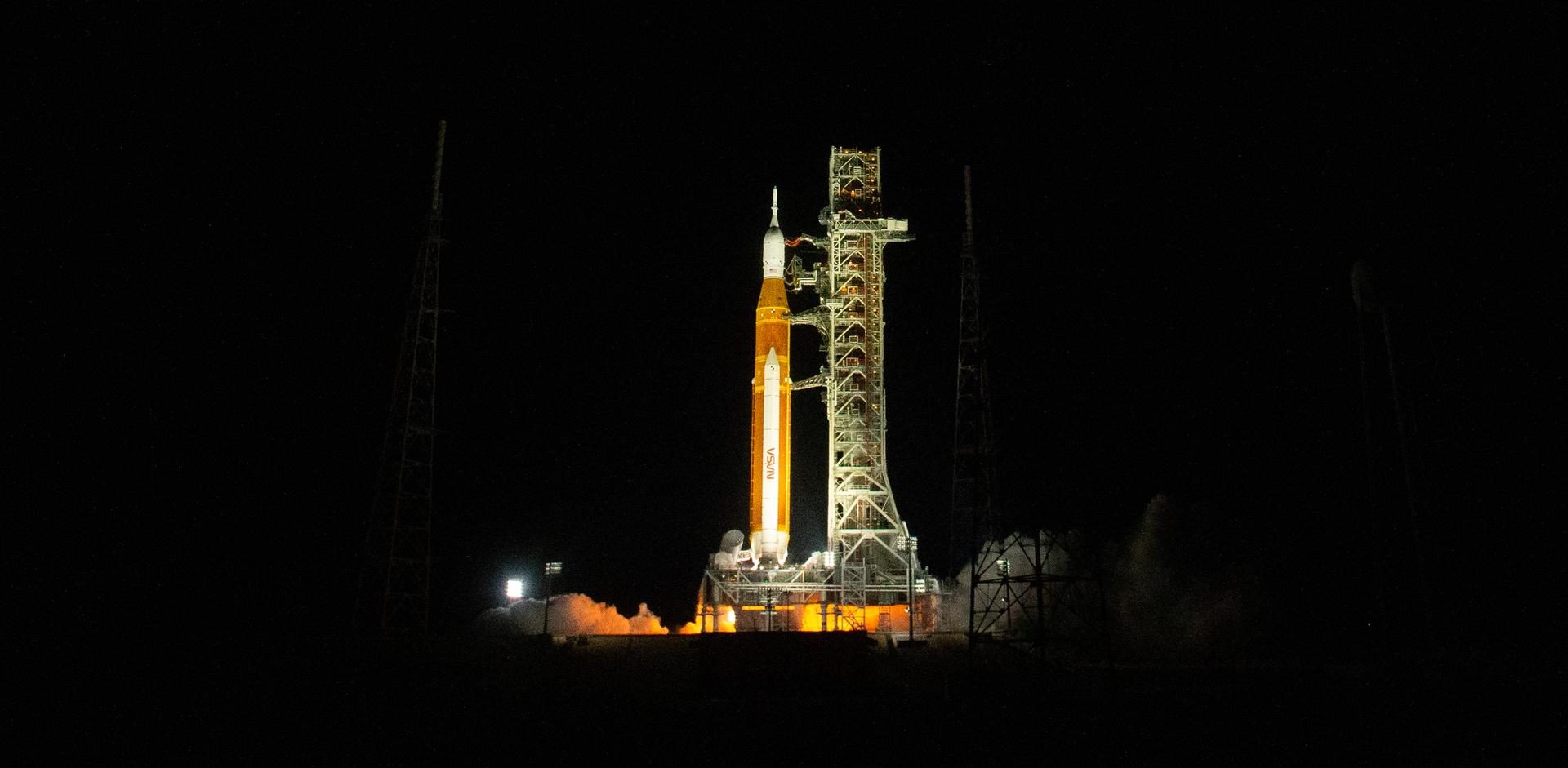
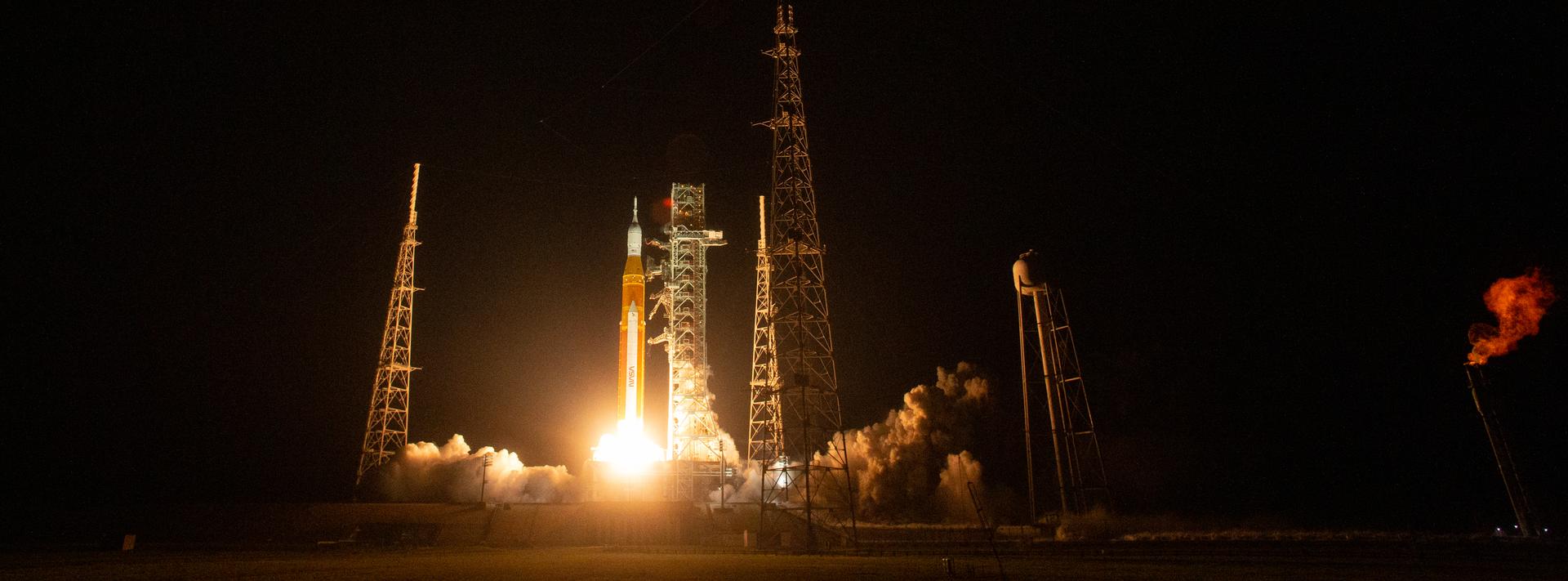
SLS launches from Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. On launch day, countdown clocks tick down toward zero. Then the rocket’s boosters ignite, carrying Orion and its payload into space.
Click the times below to see the pictures.
00:00:02—SLS uses 8.8 million pounds of thrust to launch.
00:02:00—The rocket is high above Earth. The solid rocket boosters fall off when the fuel inside them is used.
00:03:40—SLS is 57 miles (91 km) above Earth. Orion is safely in orbit and no longer needs the launch abort system.
00:08:14—The orange core stage is no longer needed and drops off. Only the upper stage of SLS remains to push Orion higher.
01:25:00—Orion is 373 miles (601 km) above Earth. The upper stage engine speeds the rocket from 17,500 mph (28,164 kph) to its top speed of 24,500 mph (39,429 kph).
01:53:00—In less than two hours, Orion is 2,392 miles (3,850 km) above Earth. The work of the SLS rocket is finished. The upper stage separates and burns up. Orion completes the trip to the Moon without SLS.
Has SLS flown yet?
Yes! The first SLS mission was called Artemis I. It launched Nov. 16, 2022. Artemis I was a lunar flight test that did not carry astronauts. It was also the first time Orion and the SLS flew together. On this mission, Orion flew around the Moon and back to Earth. The 25-day flight ended with Orion splashing down in the Pacific Ocean on Dec. 11, 2022. Artemis I set the stage for future crewed missions. Watch the below video to learn more about the historic Artemis I mission.
What's next for SLS?
SLS is scheduled to fly astronauts for the first time in 2026. On the next mission, Artemis II, SLS will launch Orion carrying a crew of four astronauts. Orion will fly past the Moon and back. Artemis II will be the farthest humans have ever traveled into space.
Career Corner
What are some jobs people have that get to work on the SLS?
Machinist: Operates machines to cut, shape, and form metal and other materials into precise parts and components needed for the SLS. This career generally requires trade school training or a college degree.
Crane Operator: Controls the heavy-duty cranes that raise the core stage to vertical, lift and stack the solid rocket booster segments, and place the Orion spacecraft on the top of the SLS rocket. Crane operators typically have a college degree or certification as a mechanical technician.
Electrical Engineer: Handles electrical needs, such as the wiring, power, avionics, and sensors that help different SLS systems work correctly. This career generally requires a college degree.
More to Explore
Build an SLS Model With School Supplies
Heavy Lifting Activity From NASA STEM: Forward to the Moon
What Is the Artemis Program?
What Is Orion?
Puzzle Book
Poster: SLS: Meet the Rocket
Video: Artemis I – Pushing Farther Into Deep Space
Video: 3, 2, 1… Lift-Off of the Artemis 1 Mission to the Moon
Video: How We Are Going to the Moon
Video: Rocket Science in 60 Seconds: What Is the Space Launch System?
Video: To the Moon and Back: The Journey of Artemis I