Experiment Unique Equipment for the European Modular Cultivation System
Overview
Experiment-unique hardware developed by the Space Biosciences Division at NASA’s Ames Research Center for spaceflight plant biology research is configured to work with the European Space Agency’s European Modular Cultivation System (EMCS). The EMCS is a unique incubator system aboard the International Space Station that provides dedicated, controllable life support for biological experiments in a multi-gravity environment. Two independent centrifuge rotors inside the EMCS create gravitational forces ranging from 0 g (static rotor) to 2 g.
Detailed Description
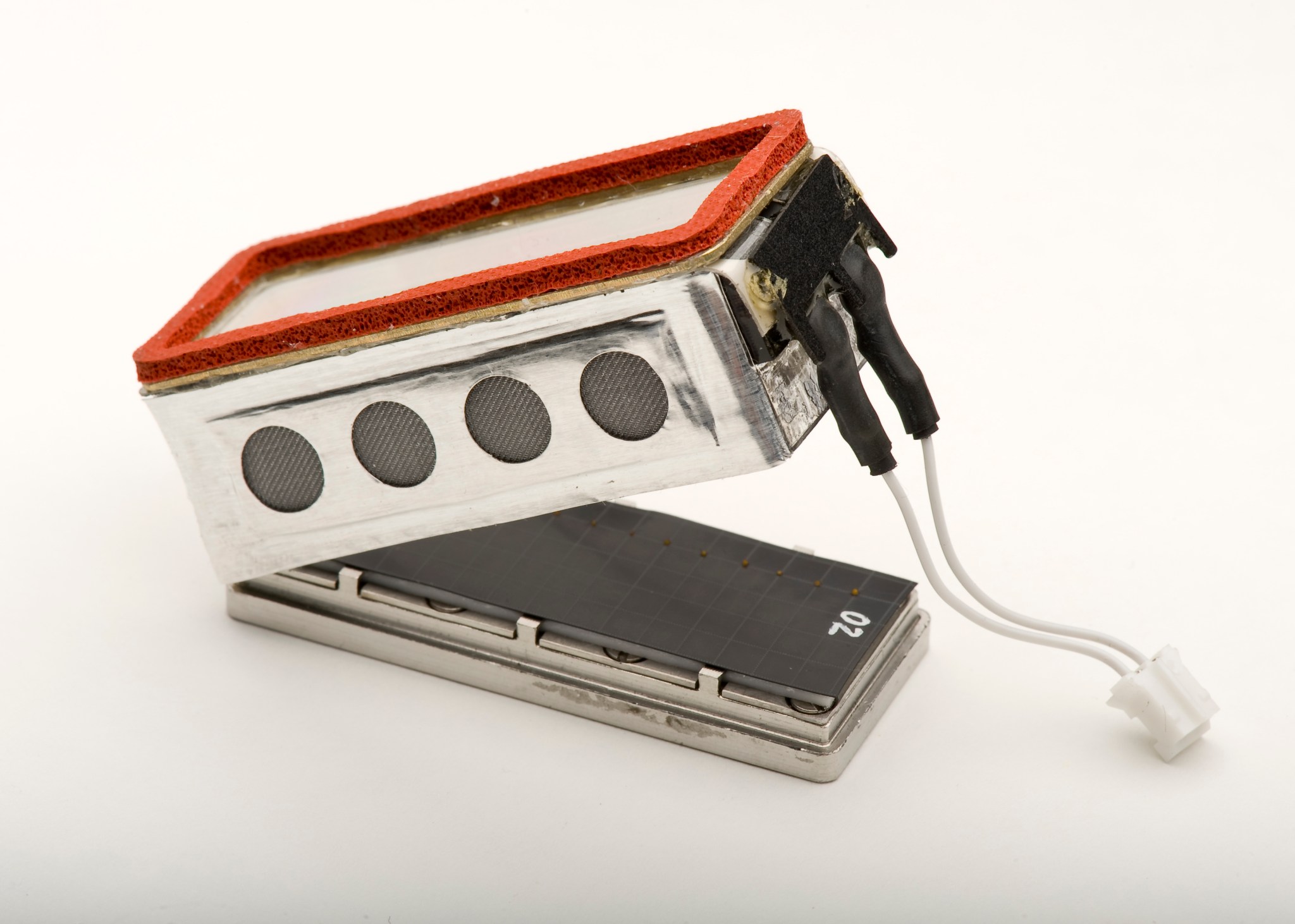
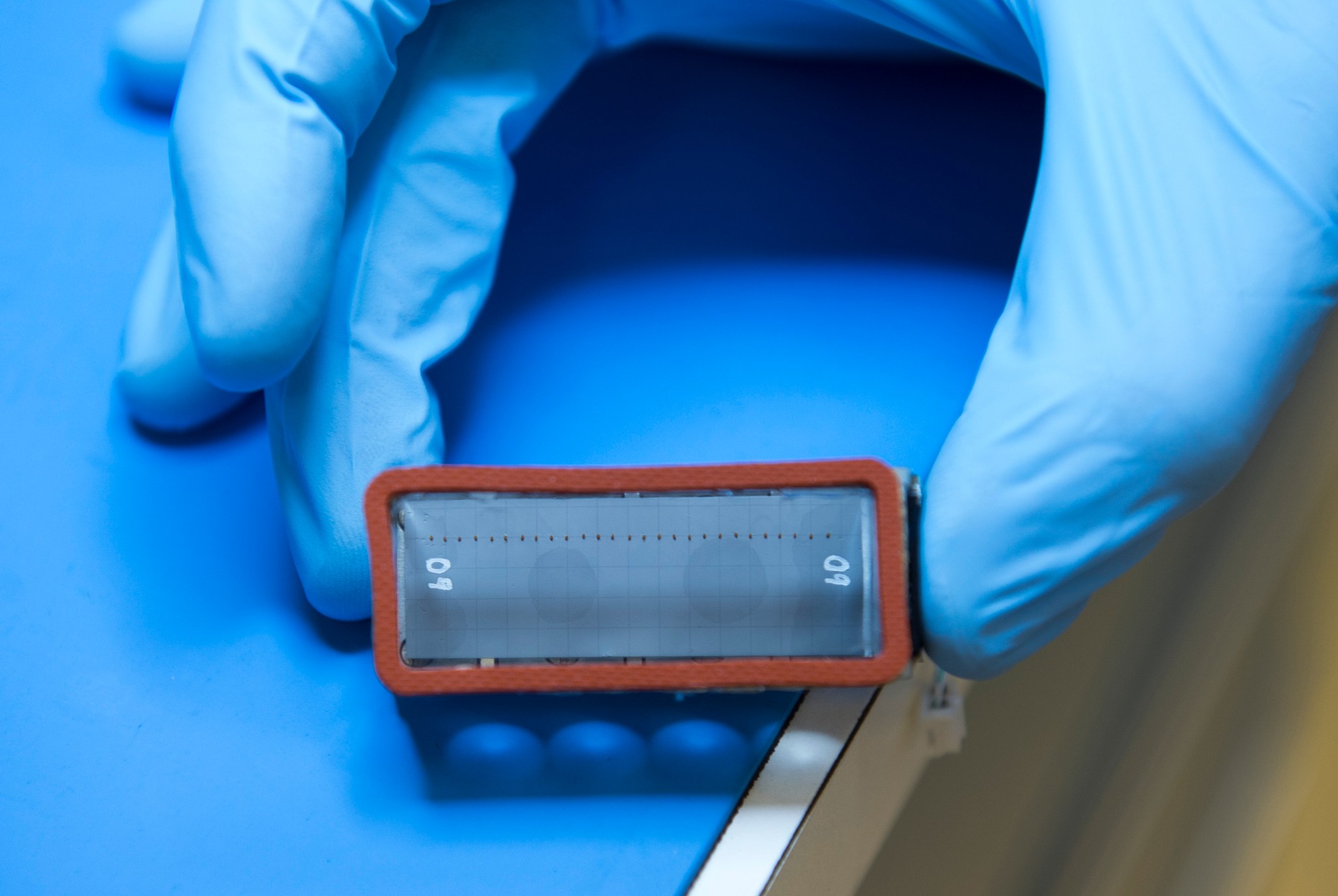
To support spaceflight studies of germination and early growth of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, experiment-unique hardware was designed and developed by the Space Biosciences Division at Ames. This equipment includes seed cassettes and lighting, hydration and air circulation systems. A heating system eliminates condensation on the surface of the seed cassettes, ensuring that clear views of seedlings are available for real-time imaging by the EMCS rotor-mounted camera. The Ames experiment-unique equipment is integrated within ESA-developed experiment containers. First used for the TROPI-1 mission in 2006, this system has supported multiple plant biology investigations in space including Plant RNA Regulation, Plant Signaling, Seedling Growth-1, Seedling Growth-2, and TROPI-2.
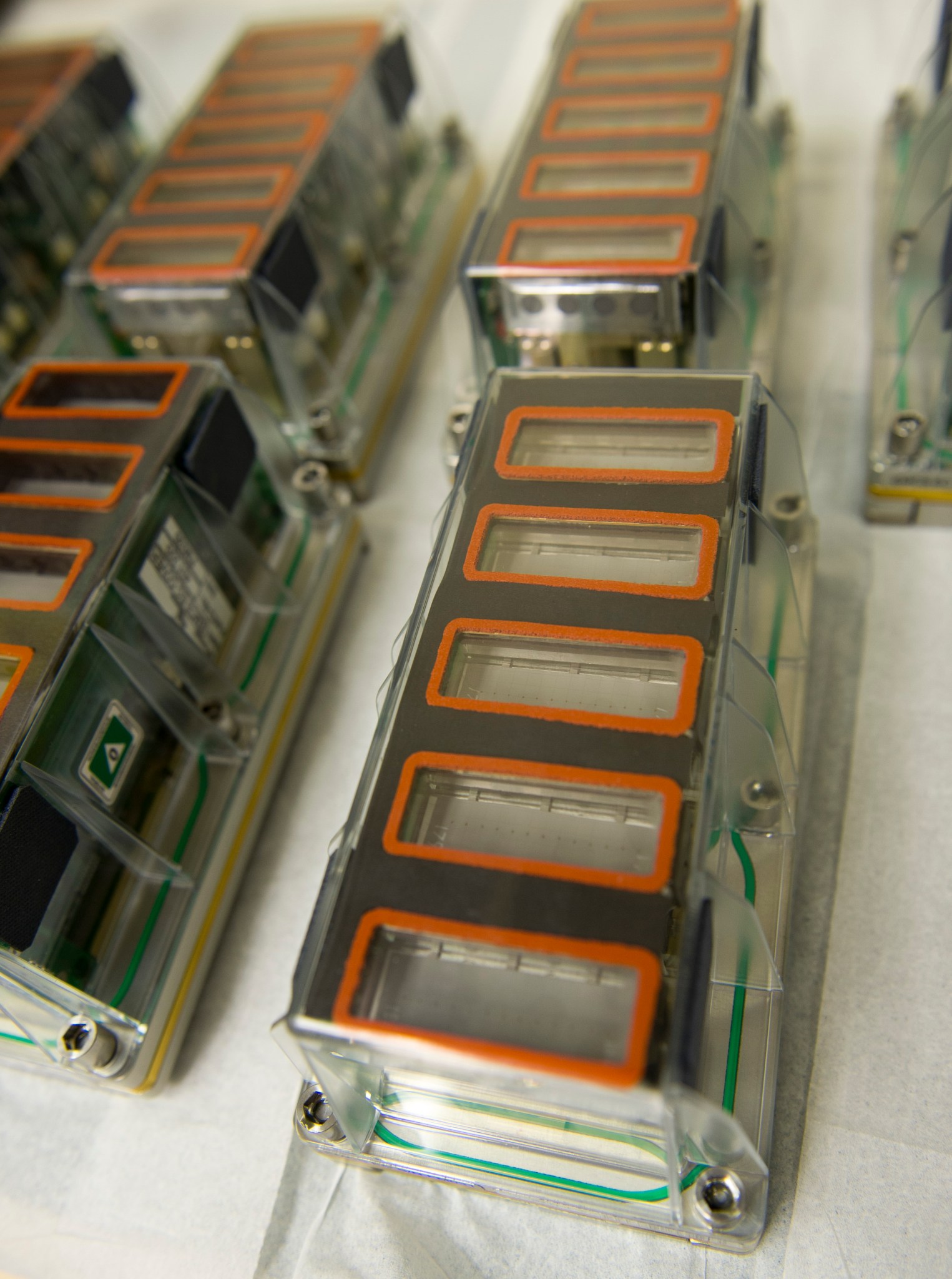
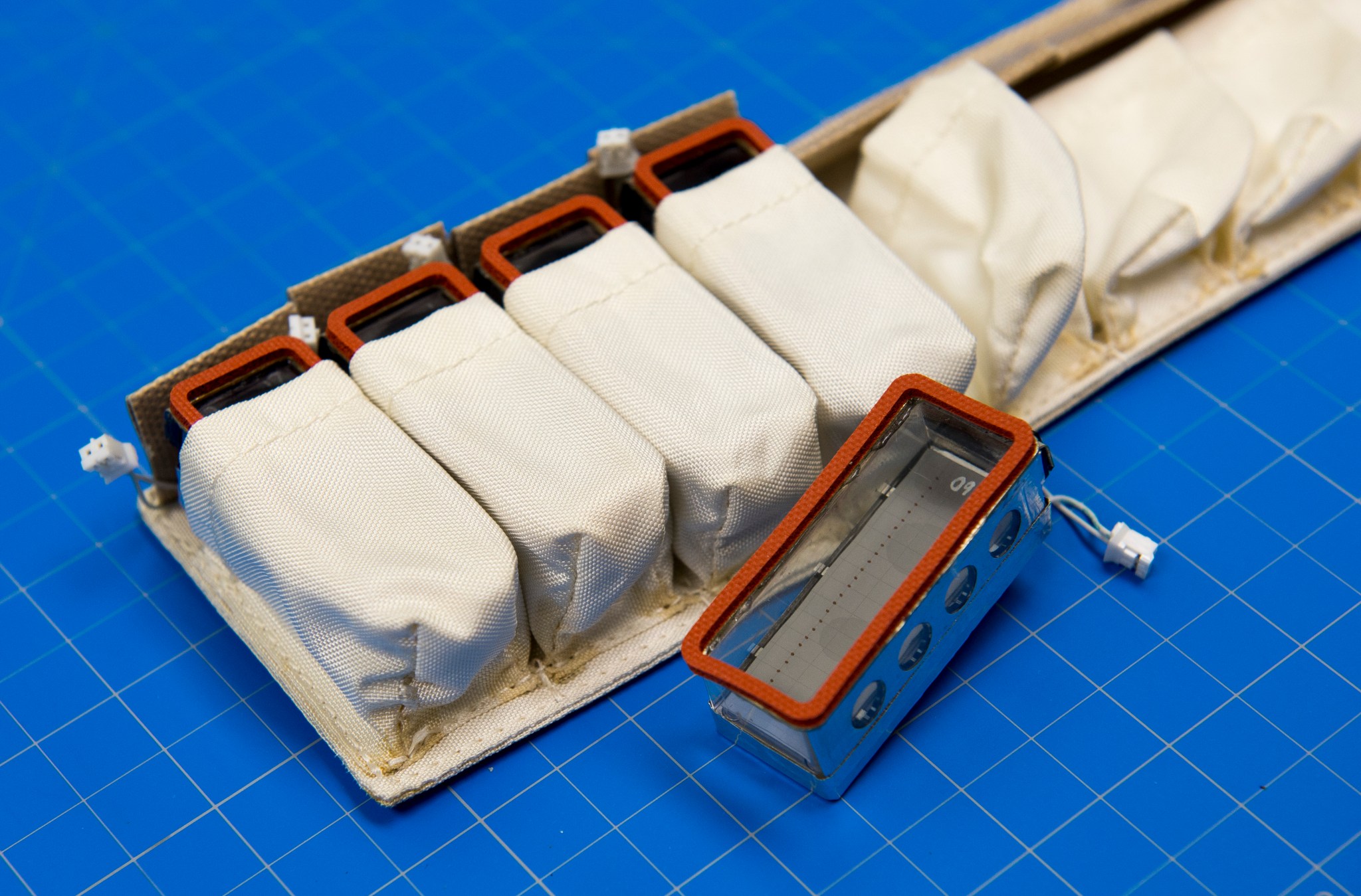
The basic modular component of the EMCS is an ESA-developed experiment container with an internal volume of 6-by-6-by-16 centimeters that mounts onto the centrifuge rotors. These experiment containers hold experiment specific hardware and provide gas, water, electrical and data connections to their contents from the EMCS. The EMCS provides lighting and control of temperature, humidity and gaseous atmosphere composition, including ethylene scrubbing. Rotor-mounted camera systems capture images for near real-time downlink to the ground. Each experiment container has a transparent cover and accommodates five seed cassettes along with associated hardware. Up to eight experiment containers can be integrated into the EMCS during a single experimental run. The experiment containers work with the EMCS to provide lighting, water, environmental control, monitoring, video, and digital still image capture.
Although research conducted in the EMCS has historically focused on plant biology, the EMCS system can accommodate experiments involving various organisms, such as cell and tissue cultures, and small invertebrates or aquatic specimens.
Facility Operations
During a hardware build before for a flight mission, biospecimens (e.g. Arabidopsis seeds) are mounted onto seed cassettes. The seed cassettes and other hardware are loaded into experiment containers. Prior to launch the loaded experiment containers are turned over for stowage at ambient conditions.
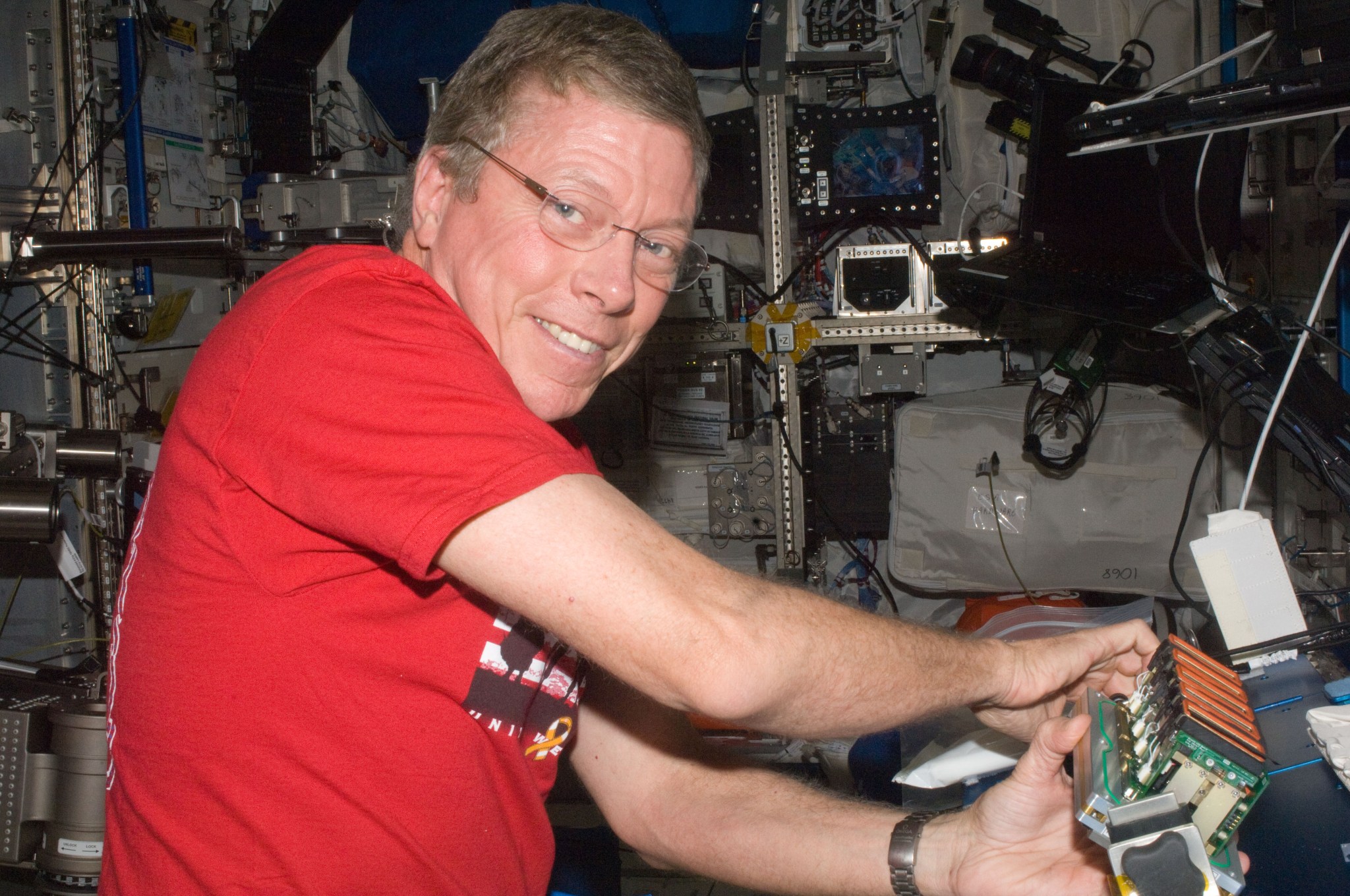
Aboard the space station the experiment containers are placed into ambient stowage until experiment operations begin. The experiment containers are loaded manually by station crew into the EMCS. Once the loading by the crew is completed, the experiments are performed automatically inside the EMCS. Video and still image data are downlinked during the experiments.
Upon completion of each experiment the cassettes can be removed from the experiment containers by station crew and placed into cold stowage bags. Frozen or preserved samples are returned to Earth aboard a SpaceX Dragon capsule for post-flight analysis.