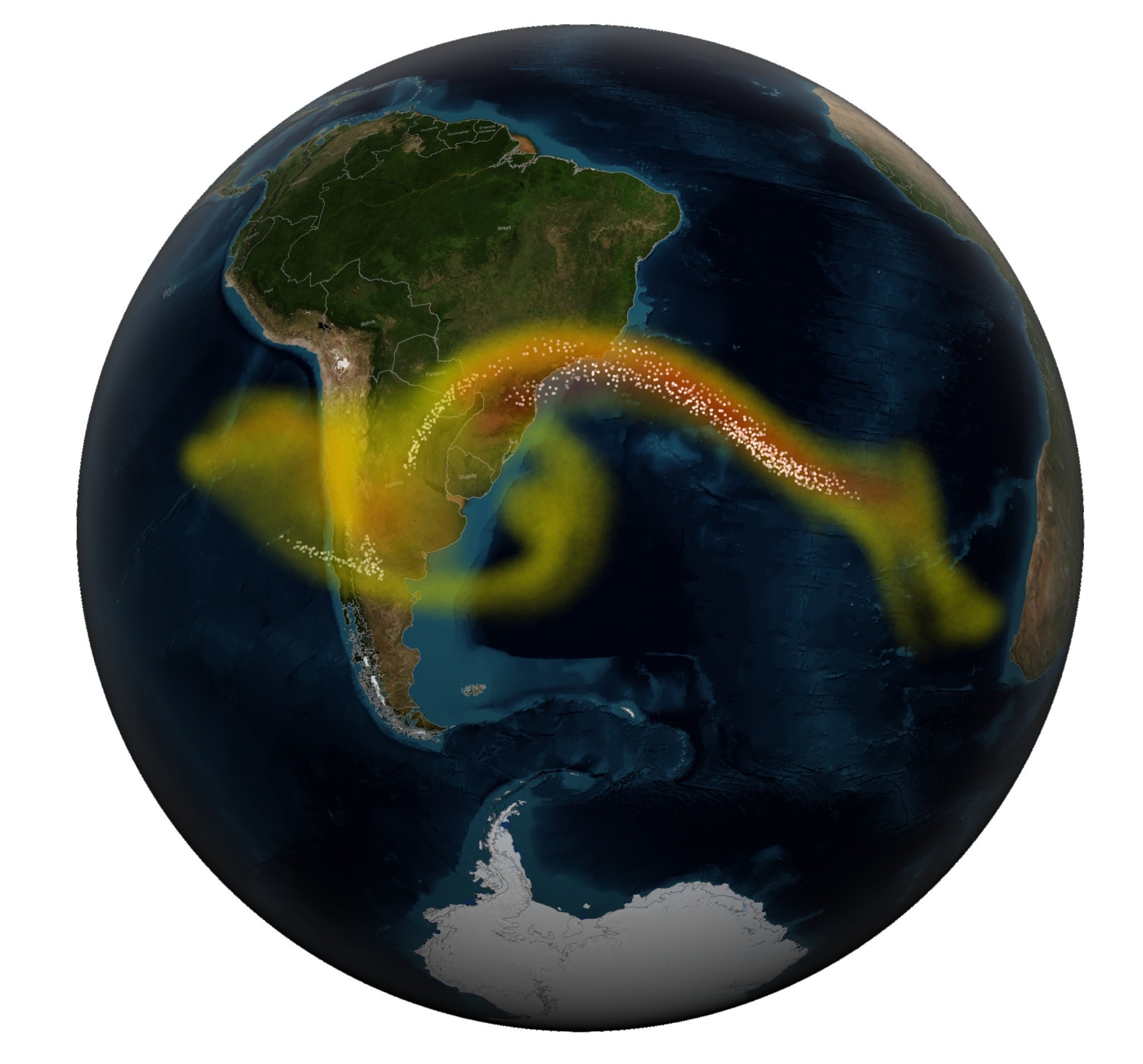
Scientists know that changing tree leaves can indicate when a nearby volcano is becoming more active and might erupt. In a new collaboration between NASA and the Smithsonian Institution, scientists now believe they can detect these changes from space.
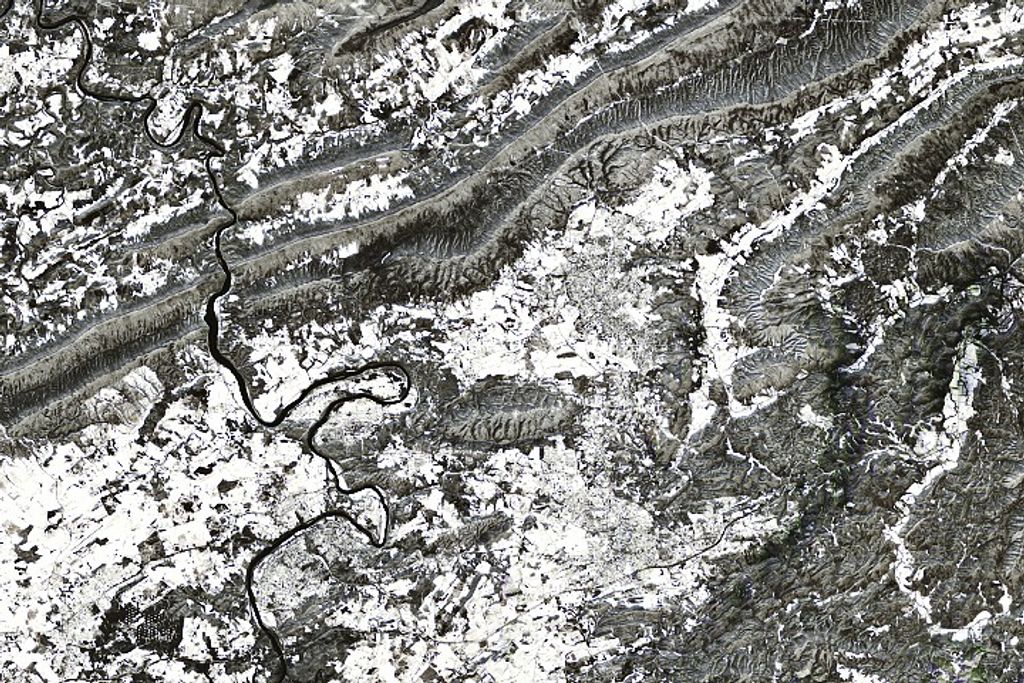
As volcanic magma ascends through the Earth’s crust, it releases carbon dioxide and other gases which rise to the surface. Trees that take up the carbon dioxide become greener and more lush. These changes are visible in images from NASA satellites such as Landsat 8, along with airborne instruments flown as part of the Airborne Validation Unified Experiment: Land to Ocean (AVUELO).
Ten percent of the world’s population lives in areas susceptible to volcanic hazards. People who live or work within a few miles of an eruption face dangers that include ejected rock, dust, and surges of hot, toxic gases. Further away, people and property are susceptible to mudslides, ashfalls, and tsunamis that can follow volcanic blasts. There’s no way to prevent volcanic eruptions, which makes the early signs of volcanic activity crucial for public safety. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, NASA’s Landsat mission partner, the United States is one of the world’s most volcanically active countries.
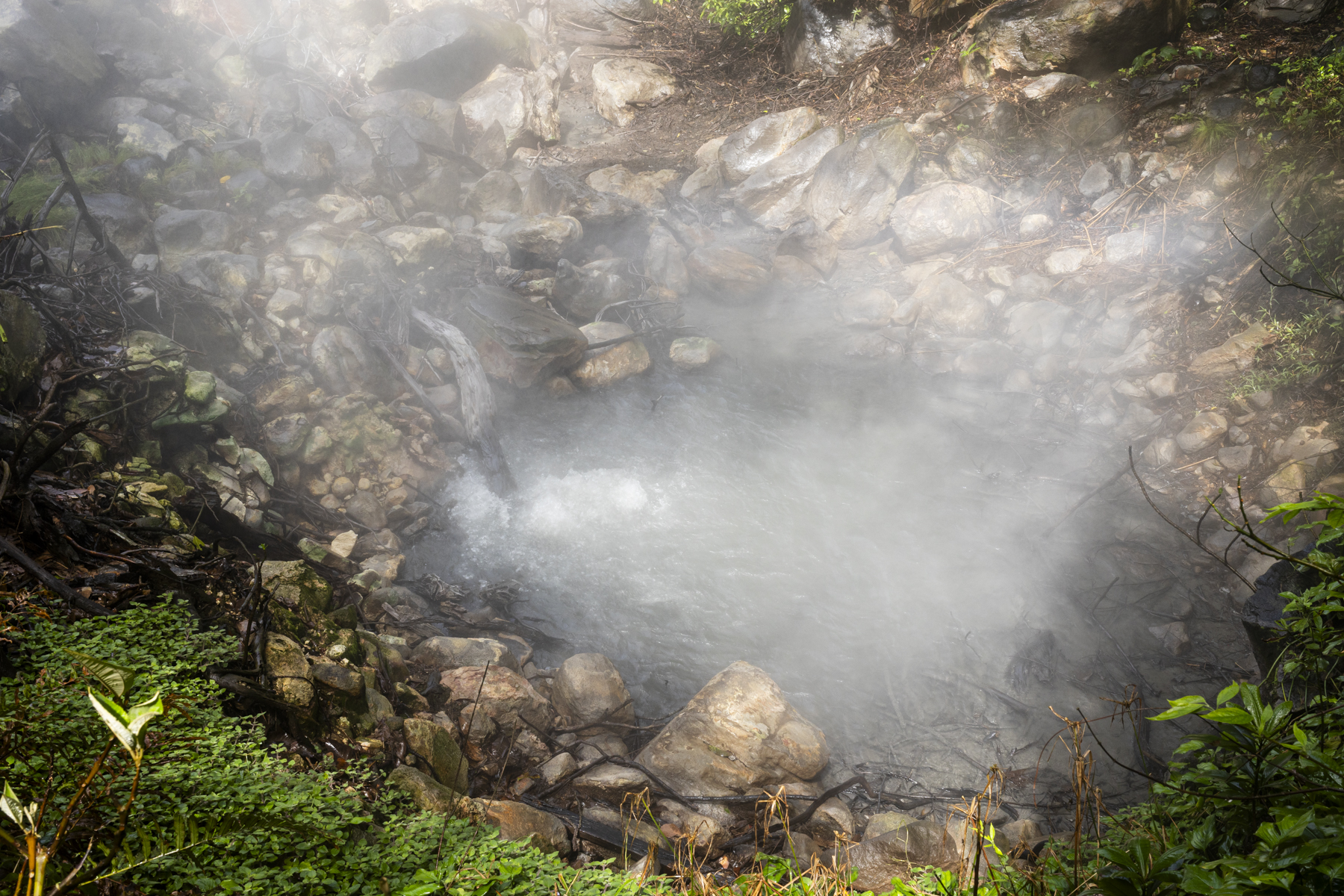
When magma rises underground before an eruption, it releases gases, including carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide. The sulfur compounds are readily detectable from orbit. But the volcanic carbon dioxide emissions that precede sulfur dioxide emissions – and provide one of the earliest indications that a volcano is no longer dormant – are difficult to distinguish from space.
The remote detection of carbon dioxide greening of vegetation potentially gives scientists another tool — along with seismic waves and changes in ground height—to get a clear idea of what’s going on underneath the volcano. “Volcano early warning systems exist,” said volcanologist Florian Schwandner, chief of the Earth Science Division at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley, who had teamed up with climate scientist Josh Fisher of Chapman University in Orange, California and volcanologist Robert Bogue of McGill University in Montreal a decade ago. “The aim here is to make them better and make them earlier.”
“Volcanoes emit a lot of carbon dioxide,” said Bogue, but there’s so much existing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that it’s often hard to measure the volcanic carbon dioxide specifically. While major eruptions can expel enough carbon dioxide to be measurable from space with sensors like NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2, detecting these much fainter advanced warning signals has remained elusive. “A volcano emitting the modest amounts of carbon dioxide that might presage an eruption isn’t going to show up in satellite imagery,” he added.
Because of this, scientists must trek to volcanoes to measure carbon dioxide directly. However, many of the roughly 1,350 potentially active volcanoes worldwide are in remote locations or challenging mountainous terrain. That makes monitoring carbon dioxide at these sites labor-intensive, expensive, and sometimes dangerous.
Volcanologists like Bogue have joined forces with botanists and climate scientists to look at trees to monitor volcanic activity. “The whole idea is to find something that we could measure instead of carbon dioxide directly,” Bogue said, “to give us a proxy to detect changes in volcano emissions.”
“There are plenty of satellites we can use to do this kind of analysis,” said volcanologist Nicole Guinn of the University of Houston. She has compared images collected with Landsat 8, NASA’s Terra satellite, ESA’s (European Space Agency) Sentinel-2, and other Earth-observing satellites to monitor trees around the Mount Etna volcano on the coast of Sicily. Guinn’s study is the first to show a strong correlation between tree leaf color and magma-generated carbon dioxide.
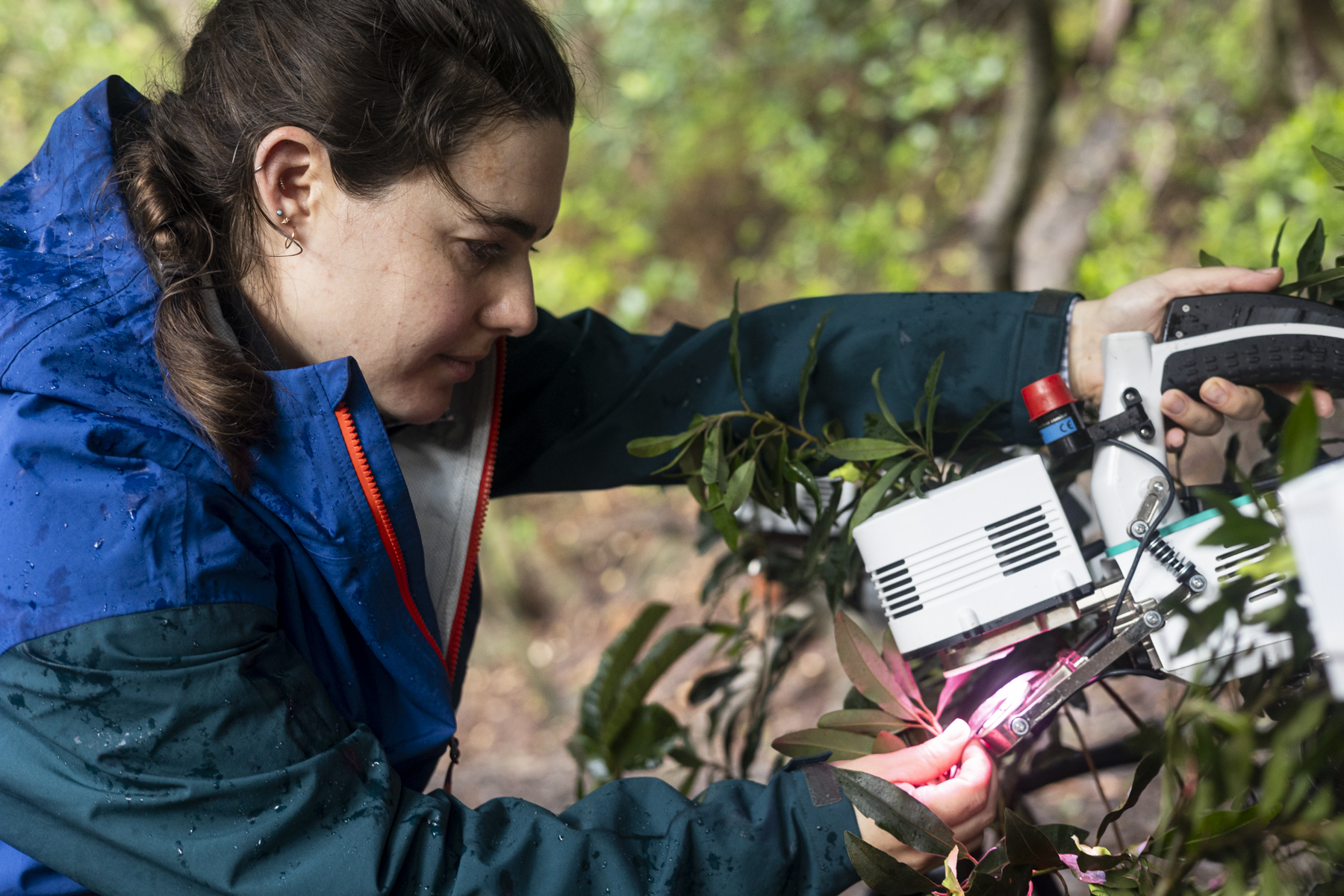
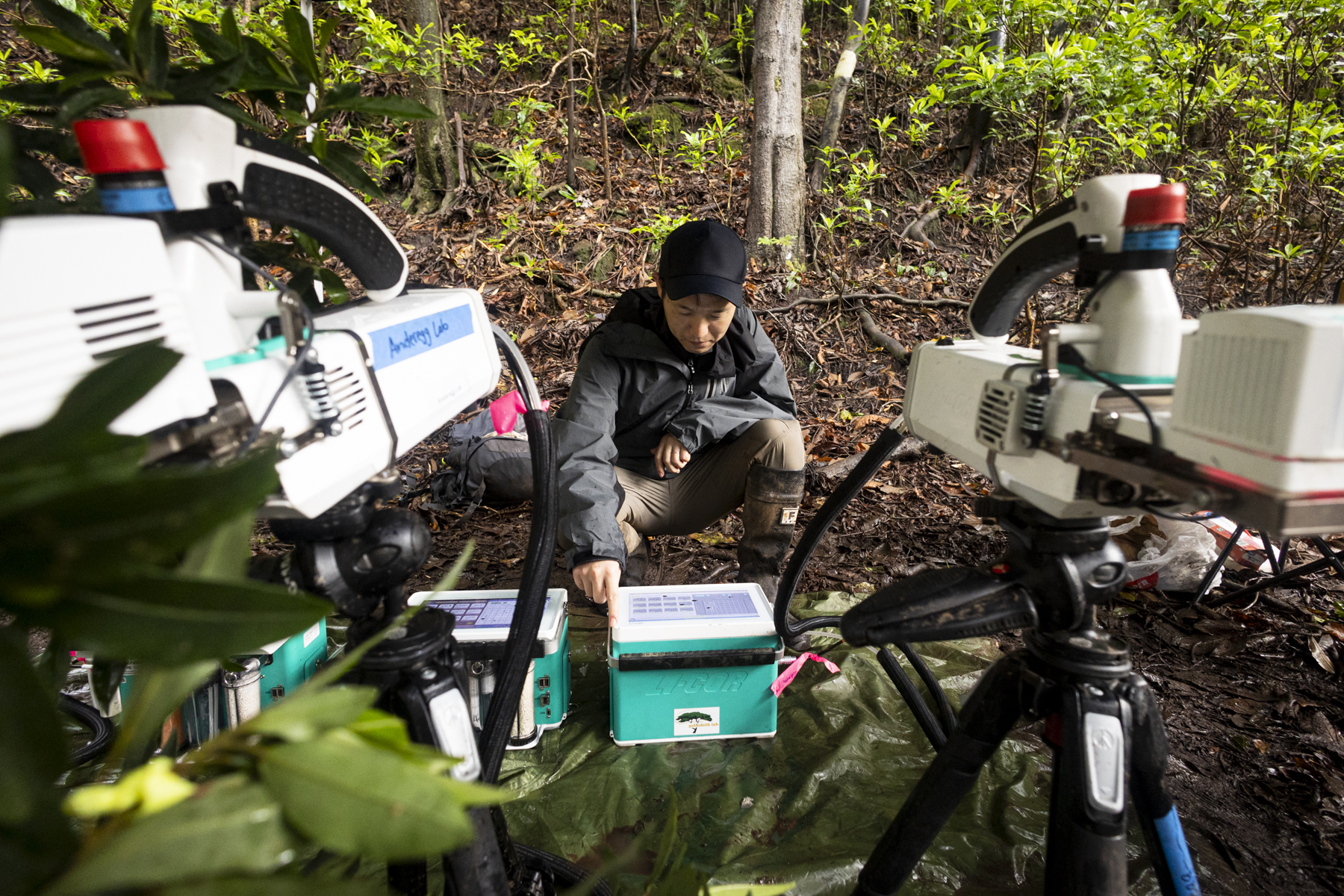
Confirming accuracy on the ground that validates the satellite imagery is a challenge that Fisher is tackling with surveys of trees around volcanoes. During the March 2025 Airborne Validation Unified Experiment: Land to Ocean mission with NASA and the Smithsonian Institution scientists deployed a spectrometer on a research plane to analyze the colors of plant life in Panama and Costa Rica.
Fisher directed a group of investigators who collected leaf samples from trees near the active Rincon de la Vieja volcano in Costa Rica while also measuring carbon dioxide levels. “Our research is a two-way interdisciplinary intersection between ecology and volcanology,” Fisher said. “We’re interested not only in tree responses to volcanic carbon dioxide as an early warning of eruption, but also in how much the trees are able to take up, as a window into the future of the Earth when all of Earth’s trees are exposed to high levels of carbon dioxide.”
Relying on trees as proxies for volcanic carbon dioxide has its limitations. Many volcanoes feature climates that don’t support enough trees for satellites to image. In some forested environments, trees respond differently to changing carbon dioxide levels. And fires, changing weather conditions, and plant diseases can complicate the interpretation of satellite data on volcanic gases.
Still, Schwandner has witnessed the potential benefits of volcanic carbon dioxide observations first-hand. He led a team that upgraded the monitoring network at Mayon volcano in the Philippines to include carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide sensors. In December 2017, government researchers in the Philippines used this system to detect signs of an impending eruption and advocated for mass evacuations of the area around the volcano. Over 56,000 people were safely evacuated before a massive eruption began on January 23, 2018. As a result of the early warnings, there were no casualties.
Using satellites to monitor trees around volcanoes would give scientists earlier insights into more volcanoes and offer earlier warnings of future eruptions. “There’s not one signal from volcanoes that’s a silver bullet,” Schwandner said. “And tracking the effects of volcanic carbon dioxide on trees will not be a silver bullet. But it will be something that could change the game.”
By James Riordon
NASA’s Earth Science News Team
Media contact: Elizabeth Vlock
NASA Headquarters