UPDATE June 1, 2016 EVE Successfully Launches: The EUV Variability Experiment or EVE, from the University of Colorado, was successfully flown on a NASA Black Brant IX suborbital sounding rocket at 3 p.m. EDT, June 1, from the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The science team reports that good data was obtained and comprehensive success may have been obtained. The 1,169 pound payload flew to an altitude of 180.67 miles. The payload will be recovered.
UPDATE May 25, 2016 EVE Launch Postponed: The Black Brant IX sounding rocket carrying the EVE scientific payload schedule for launch May 25 at the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico has been postponed because of inclement weather. The launch is now scheduled for 3 p.m. EDT, Wednesday, June 1.
Satellites provide data daily on our own planet, our sun and the universe around us. The instruments on these spacecraft are constantly bombarded with solar particles and intense light, not to mention the normal wear and tear from operating in space.
If it were a car that’s a few years old, you would take it to the mechanic for a tune-up to make sure it continues running smoothly. However, with a spacecraft it’s not that easy. Thus, scientists may turn to calibration flights to make sure the instruments are kept up to snuff and providing validated data.
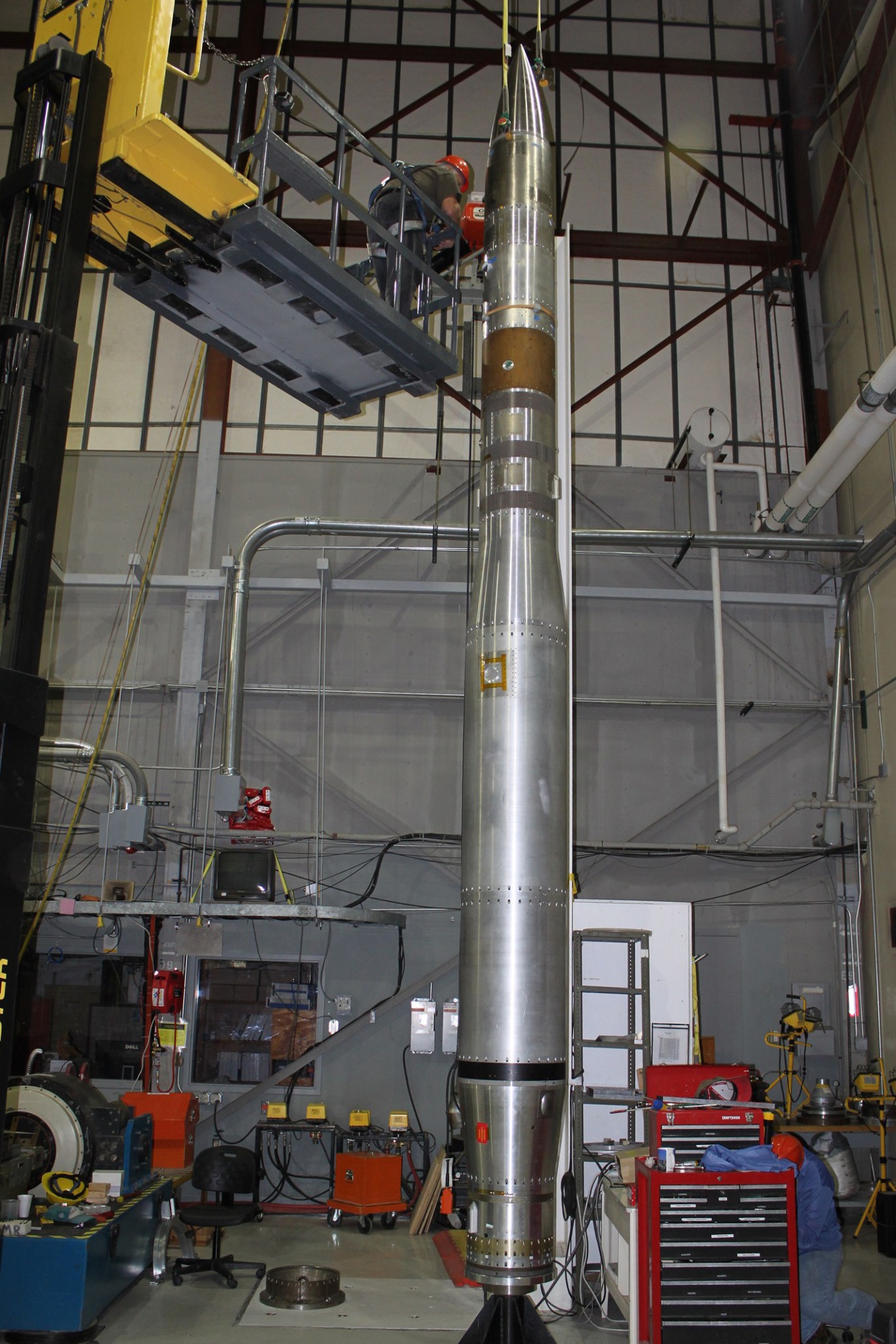
One such flight will be the Extreme UltraViolet (EUV) Variability Experiment, or EVE, from the University of Colorado, Boulder, to observe the sun from a NASA Black Brant IX sounding rocket at 3:02 p.m. EDT May 25 at the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico.
“The experiment’s primary goal is to provide the under-flight calibration for the SDO EVE spectrometers and the solar EUV imager aboard SDO,” said Tom Woods, the principal investigator for this mission as well as the EVE instrument on NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. “The calibration rocket measurements also support the calibration and validation for several other solar soft X-ray and extreme ultraviolet spectrometers and imagers on NASA solar observatories.”
The sounding rocket flight will be the eighth calibration flight of the EVE rocket instrument. After suffering a launch vehicle failure on a flight in May 2015, the instruments were recovered, refurbished and are ready for this mission, according to Woods.
The flights of the sounding rocket EVE instrument have been conducted since 2006 with the first launches to calibrate the solar EUV instrument aboard NASA’s TIMED satellite. With the launch of SDO in February 2010, unprecedented information has been received on our closest star that includes over 10 million EUV spectra and over 100 million solar images.
Woods said, “There is a lot of science and many exciting — some unexpected — results from the SDO satellite measurements. For example, while most EUV emissions increase during a solar flare, some emissions decrease, or dim, during a flare, and this dimming is providing new information about the mass loss during eruptive flare events. This calibration rocket flight contributes to those satellite measurements by providing the most accurate and updated calibration for the satellite instruments. It is invaluable for helping to understand how the satellite instruments are degrading.”
He continued, “One of the unexpected results in analysis of the instrument degradation trends, especially the spectral signature of the degradation trend for SDO EVE, is that most of the degradation in some of the EUV instruments is from oxidation of the metal foil filters and not from hydrocarbon contamination as has been the case for past satellite missions. In other words, despite the fact that SDO is a very clean spacecraft (with no significant hydrocarbon contamination), the satellite instruments still are degrading in space.”
The EVE on the 56.5-foot Black Brant IX sounding rocket is expected to fly to approximately 180 miles altitude during a 16-minute flight and provide about five minutes of solar viewing time. For Woods and his team this is all the time needed to gather data for a tune-up of the various satellite instruments.
The calibration rocket measurements also support the calibration and validation for several other solar soft X-ray and extreme ultraviolet spectrometers and imagers on NASA’s Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics, Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment, Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, ESA/NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/NASA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite Program, and the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency/NASA’s Hinode.
The EVE calibration mission is supported through NASA’s Sounding Rocket Program at the Goddard Space Flight Center’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. NASA’s Heliophysics Division manages the sounding rocket program.
Keith Koehler
NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia