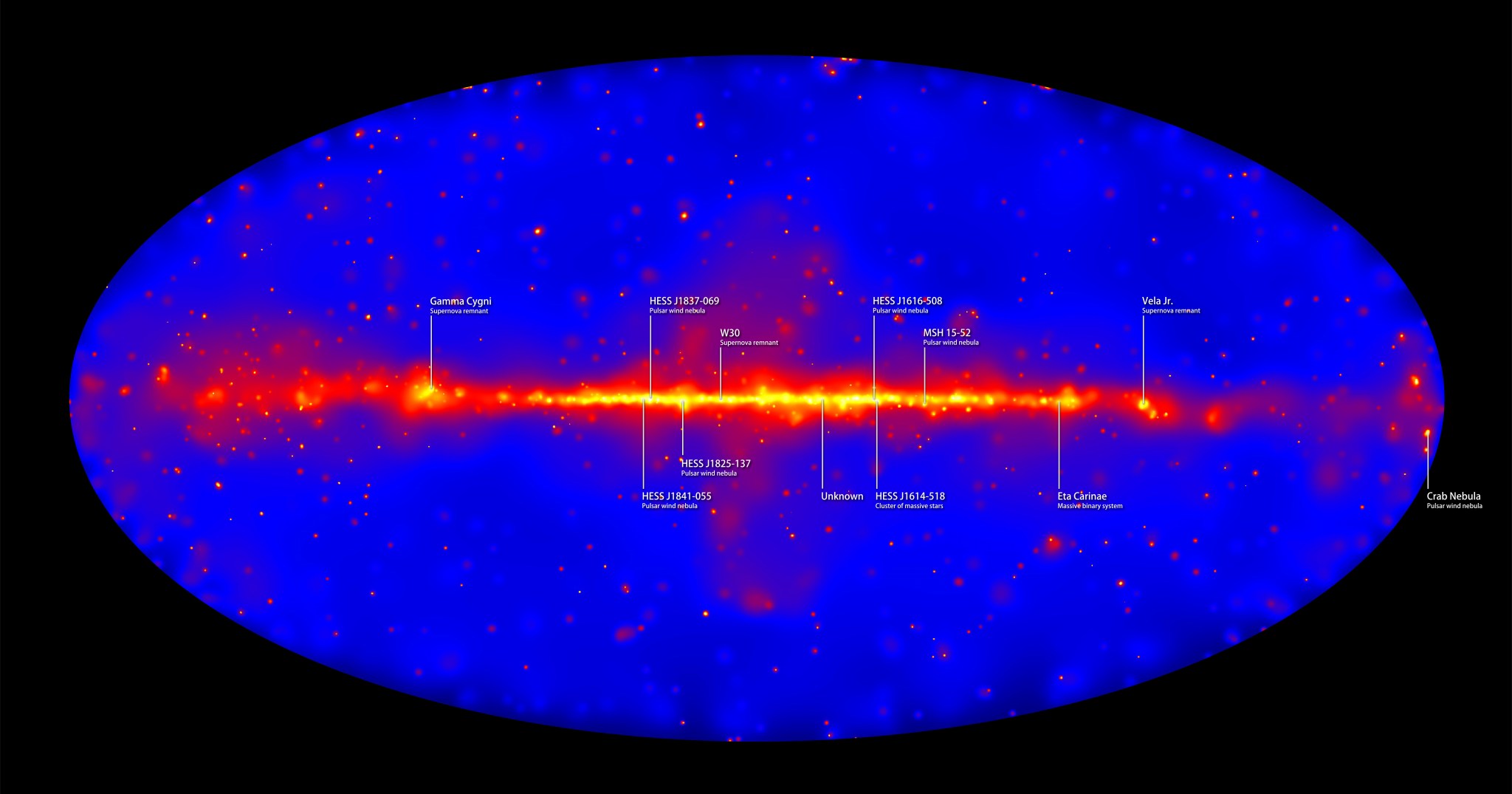
Major improvements to methods used to process observations from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have yielded an expanded, higher-quality set of data that allows astronomers to produce the most detailed census of the sky yet made at extreme energies. A new sky map reveals hundreds of these sources, including 12 that produce gamma rays with energies exceeding a trillion times the energy of visible light. The survey also discovered four dozen new sources that remain undetected at any other wavelength.
“What made this advance possible was a complete reanalysis, which we call Pass 8, of all data acquired by Fermi’s Large Area Telescope (LAT),” said Marco Ajello, a Fermi team member at Clemson University in South Carolina. “The end result is effectively a complete instrument upgrade without our ever having to leave the ground.”
By carefully reexamining every gamma-ray and particle detection by the LAT since Fermi’s 2008 launch, scientists improved their knowledge of the detector’s response to each event and to the background environment in which it was measured. This enabled the Fermi team to find many gamma rays that previously had been missed while simultaneously improving the LAT’s ability to determine the directions of incoming gamma rays. These improvements effectively sharpen the LAT’s view while also significantly widening its useful energy range.
Using 61,000 Pass 8 gamma rays collected over 80 months, Ajello and his colleagues constructed a map of the entire sky at energies ranging from 50 billion (GeV) to 2 trillion electron volts (TeV). For comparison, the energy of visible light ranges from about 2 to 3 electron volts.
“Of the 360 sources we cataloged, about 75 percent are blazars, which are distant galaxies sporting jets powered by supermassive black holes,” said co-investigator Alberto Domínguez at the Complutense University in Madrid. “The highest-energy sources, all located in our galaxy, are mostly remnants of supernova explosions and pulsar wind nebulae, places where rapidly rotating neutron stars accelerate particles to near the speed of light.” One famous example, the Crab Nebula, tops the list of the highest-energy Fermi sources, producing a steady drizzle of gamma rays exceeding 1 TeV.
Astronomers think these very high-energy gamma rays are produced when lower-energy light collides with accelerated particles. This results in a small energy loss for the particle and a big gain for the light, transforming it into a gamma ray.
For the first time, Fermi data now extend to energies previously seen only by ground-based detectors. Because ground-based telescopes have much smaller fields of view than the LAT, which scans the whole sky every three hours, they have detected only about a quarter of the objects in the catalog. This study provides ground facilities with more than 280 new targets for follow-up observations.
“An exciting aspect of this catalog is that we find many new sources that emit gamma rays over a comparatively large patch of the sky,” explained Jamie Cohen, a University of Maryland graduate student working with the Fermi team at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt. “Finding more of these objects enables us to probe their structures as well as better understand mechanisms that accelerate the subatomic particles that ultimately produce gamma-ray emission.” The new catalog identifies 25 of these extended objects, including three new pulsar wind nebulae and two new supernova remnants.
Ajello presented the findings Thursday at the 227th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Kissimmee, Florida. A paper describing the catalog has been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement.
NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is an astrophysics and particle physics partnership, developed in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Energy and with important contributions from academic institutions and partners in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Sweden and the United States.
For more information about NASA’s Fermi, visit:
By Francis Reddy
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland